Power of Cooperative Supervision: Multiple Teachers Framework for Enhanced 3D Semi-Supervised Object Detection

0
Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Power of Cooperative Supervision: Multiple Teachers Framework for Enhanced 3D Semi-Supervised Object Detection
Jin-Hee Lee, Jae-Keun Lee, Je-Seok Kim, Soon Kwon
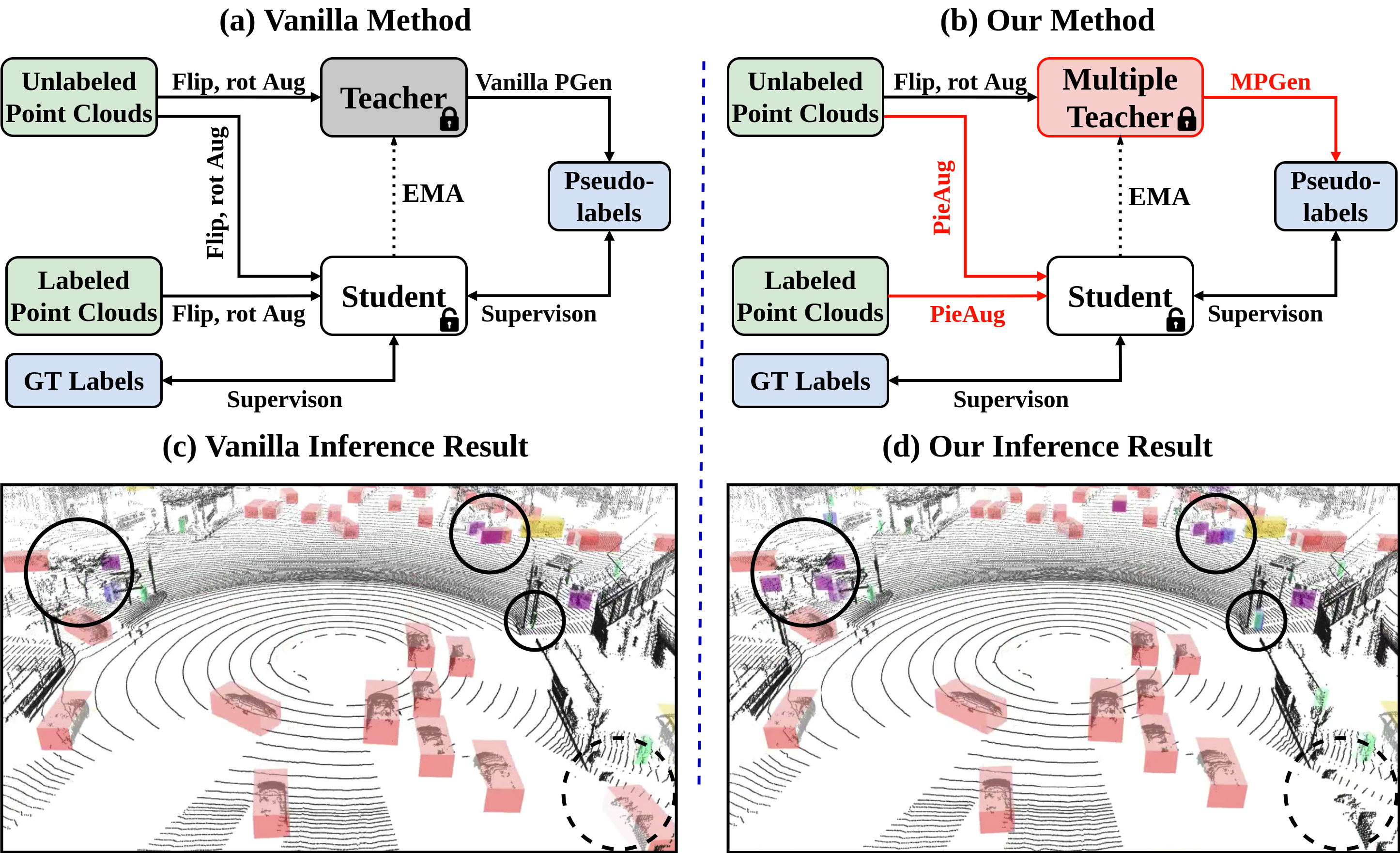
To ensure safe urban driving for autonomous platforms, it is crucial not only to develop high-performance object detection techniques but also to establish a diverse and representative dataset that captures various urban environments and object characteristics. To address these two issues, we have constructed a multi-class 3D LiDAR dataset reflecting diverse urban environments and object characteristics, and developed a robust 3D semi-supervised object detection (SSOD) based on a multiple teachers framework. This SSOD framework categorizes similar classes and assigns specialized teachers to each category. Through collaborative supervision among these category-specialized teachers, the student network becomes increasingly proficient, leading to a highly effective object detector. We propose a simple yet effective augmentation technique, Pie-based Point Compensating Augmentation (PieAug), to enable the teacher network to generate high-quality pseudo-labels. Extensive experiments on the WOD, KITTI, and our datasets validate the effectiveness of our proposed method and the quality of our dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art 3D semi-supervised object detection methods across all datasets. We plan to release our multi-class LiDAR dataset and the source code available on our Github repository in the near future.
Read more6/3/2024
🔎

0
Collaboration of Teachers for Semi-supervised Object Detection
Liyu Chen, Huaao Tang, Yi Wen, Hanting Chen, Wei Li, Junchao Liu, Jie Hu
Recent semi-supervised object detection (SSOD) has achieved remarkable progress by leveraging unlabeled data for training. Mainstream SSOD methods rely on Consistency Regularization methods and Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which form a cyclic data flow. However, the EMA updating training approach leads to weight coupling between the teacher and student models. This coupling in a cyclic data flow results in a decrease in the utilization of unlabeled data information and the confirmation bias on low-quality or erroneous pseudo-labels. To address these issues, we propose the Collaboration of Teachers Framework (CTF), which consists of multiple pairs of teacher and student models for training. In the learning process of CTF, the Data Performance Consistency Optimization module (DPCO) informs the best pair of teacher models possessing the optimal pseudo-labels during the past training process, and these most reliable pseudo-labels generated by the best performing teacher would guide the other student models. As a consequence, this framework greatly improves the utilization of unlabeled data and prevents the positive feedback cycle of unreliable pseudo-labels. The CTF achieves outstanding results on numerous SSOD datasets, including a 0.71% mAP improvement on the 10% annotated COCO dataset and a 0.89% mAP improvement on the VOC dataset compared to LabelMatch and converges significantly faster. Moreover, the CTF is plug-and-play and can be integrated with other mainstream SSOD methods.
Read more5/24/2024


0
SOOD++: Leveraging Unlabeled Data to Boost Oriented Object Detection
Dingkang Liang, Wei Hua, Chunsheng Shi, Zhikang Zou, Xiaoqing Ye, Xiang Bai
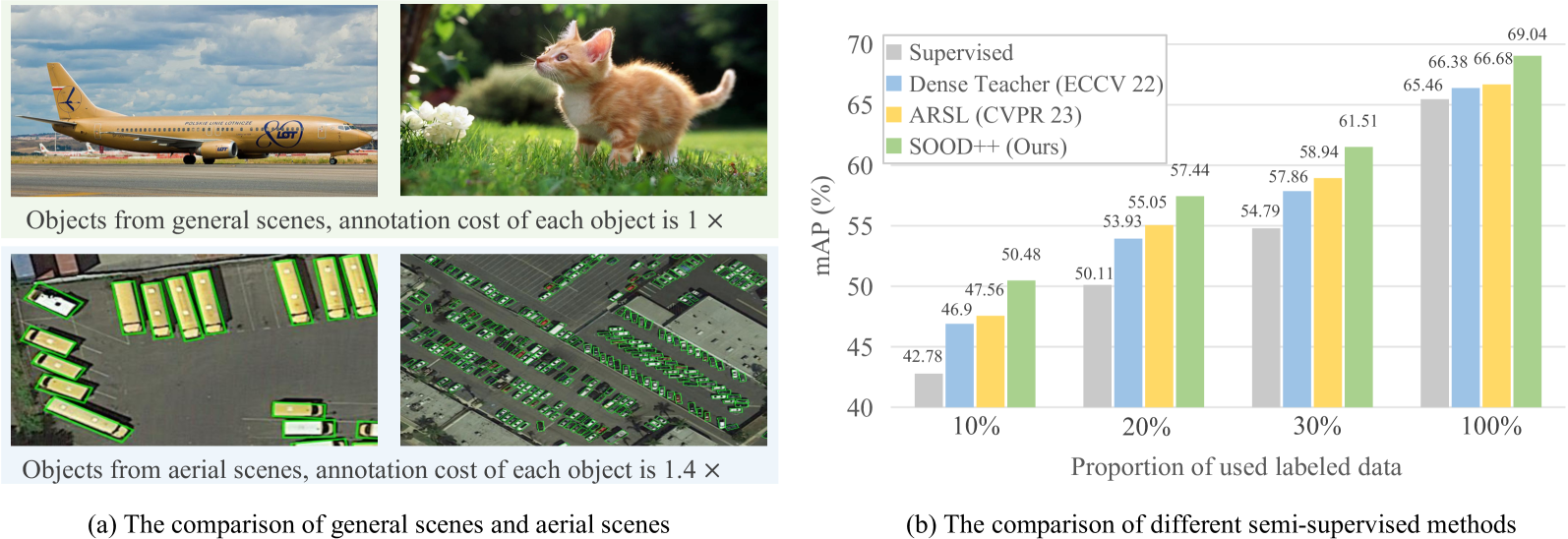
Semi-supervised object detection (SSOD), leveraging unlabeled data to boost object detectors, has become a hot topic recently. However, existing SSOD approaches mainly focus on horizontal objects, leaving multi-oriented objects common in aerial images unexplored. At the same time, the annotation cost of multi-oriented objects is significantly higher than that of their horizontal counterparts. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a simple yet effective Semi-supervised Oriented Object Detection method termed SOOD++. Specifically, we observe that objects from aerial images are usually arbitrary orientations, small scales, and aggregation, which inspires the following core designs: a Simple Instance-aware Dense Sampling (SIDS) strategy is used to generate comprehensive dense pseudo-labels; the Geometry-aware Adaptive Weighting (GAW) loss dynamically modulates the importance of each pair between pseudo-label and corresponding prediction by leveraging the intricate geometric information of aerial objects; we treat aerial images as global layouts and explicitly build the many-to-many relationship between the sets of pseudo-labels and predictions via the proposed Noise-driven Global Consistency (NGC). Extensive experiments conducted on various multi-oriented object datasets under various labeled settings demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. For example, on the DOTA-V1.5 benchmark, the proposed method outperforms previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) by a large margin (+2.92, +2.39, and +2.57 mAP under 10%, 20%, and 30% labeled data settings, respectively) with single-scale training and testing. More importantly, it still improves upon a strong supervised baseline with 70.66 mAP, trained using the full DOTA-V1.5 train-val set, by +1.82 mAP, resulting in a 72.48 mAP, pushing the new state-of-the-art. The code will be made available.
Read more7/2/2024


0
Semi-supervised 3D Object Detection with PatchTeacher and PillarMix
Xiaopei Wu, Liang Peng, Liang Xie, Yuenan Hou, Binbin Lin, Xiaoshui Huang, Haifeng Liu, Deng Cai, Wanli Ouyang
Semi-supervised learning aims to leverage numerous unlabeled data to improve the model performance. Current semi-supervised 3D object detection methods typically use a teacher to generate pseudo labels for a student, and the quality of the pseudo labels is essential for the final performance. In this paper, we propose PatchTeacher, which focuses on partial scene 3D object detection to provide high-quality pseudo labels for the student. Specifically, we divide a complete scene into a series of patches and feed them to our PatchTeacher sequentially. PatchTeacher leverages the low memory consumption advantage of partial scene detection to process point clouds with a high-resolution voxelization, which can minimize the information loss of quantization and extract more fine-grained features. However, it is non-trivial to train a detector on fractions of the scene. Therefore, we introduce three key techniques, i.e., Patch Normalizer, Quadrant Align, and Fovea Selection, to improve the performance of PatchTeacher. Moreover, we devise PillarMix, a strong data augmentation strategy that mixes truncated pillars from different LiDAR scans to generate diverse training samples and thus help the model learn more general representation. Extensive experiments conducted on Waymo and ONCE datasets verify the effectiveness and superiority of our method and we achieve new state-of-the-art results, surpassing existing methods by a large margin. Codes are available at https://github.com/LittlePey/PTPM.
Read more7/16/2024