Privacy-Preserving and Trustworthy Localization in an IoT Environment

0
📊
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the challenge of ensuring privacy and trustworthiness in localization systems for the Internet of Things (IoT) environment.
- It proposes a novel blockchain-based approach to address these concerns while maintaining the accuracy and reliability of IoT localization.
- The paper covers the key goals, technical details, and critical analysis of the proposed solution.
Plain English Explanation
In the rapidly growing world of the Internet of Things (IoT), devices and sensors are becoming increasingly interconnected, enabling a wide range of innovative applications. However, as these IoT systems become more pervasive, the need to accurately locate and track these devices has become crucial.
The paper addresses the challenge of ensuring privacy and trustworthiness in these localization systems. Often, the location data of IoT devices can contain sensitive information that users may not want to share. Additionally, the reliability and accuracy of the localization process are critical to the success of many IoT applications.
To tackle these issues, the researchers propose a blockchain-based approach that aims to preserve the privacy of users while maintaining the trustworthiness and reliability of the localization system. By leveraging the decentralized nature and secure ledger of blockchain technology, the proposed solution aims to provide a more secure and transparent way of managing location data and the localization process.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a novel framework that combines edge computing, federated learning, and blockchain technology to address the privacy and trustworthiness concerns in IoT localization.
The system architecture involves IoT devices, edge nodes, and a blockchain network. IoT devices collect location data, which is then processed and aggregated at the edge nodes. The edge nodes then submit the processed data to the blockchain network, where it is stored in a secure and tamper-resistant manner.
The Kalman filter-based localization is used to ensure accurate and reliable positioning of the IoT devices, while the blockchain network provides a decentralized and transparent platform for verifying the integrity of the location data.
Critical Analysis
The proposed approach offers several advantages over traditional centralized localization systems. By leveraging blockchain technology, the system enhances the privacy and trustworthiness of the localization process, as the location data is stored in a secure and decentralized manner, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or manipulation.
However, the paper acknowledges that the implementation of the blockchain-based system may introduce additional computational and storage overhead, which could be a concern for resource-constrained IoT devices. Additionally, the scalability of the system as the number of IoT devices and edge nodes increases may require further investigation.
It would also be valuable for the researchers to explore the potential impact of federated learning on the overall performance and privacy-preservation capabilities of the system, as well as to consider potential vulnerabilities or attack vectors that may arise from the integration of these different technologies.
Conclusion
The paper presents a promising approach to addressing the privacy and trustworthiness challenges in IoT localization systems. By combining edge computing, federated learning, and blockchain technology, the proposed framework aims to provide a more secure and reliable way of managing location data and the localization process.
While the technical details and experimental results demonstrate the potential of this approach, further research and real-world deployment may be necessary to fully evaluate its scalability, efficiency, and practical implications for the broader IoT ecosystem.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📊

0
Privacy-Preserving and Trustworthy Localization in an IoT Environment
Guglielmo Zocca, Omar Hasan
The Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly prevalent in various applications, such as healthcare and logistics. One significant service of IoT technologies that is essential for these applications is localization. The goal of this service is to determine the precise position of a specific target. The localization data often needs to be private, accessible only to specific entities, and must maintain authenticity and integrity to ensure trustworthiness. IoT technology has evolved significantly, with Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) technology enhancing localization speed and precision. However, IoT device security remains a concern, as devices can be compromised or act maliciously. Furthermore, localization data is typically stored centrally, which can also be a point of vulnerability. Our approach leverages the features of a permissioned blockchain, specifically Hyperledger Fabric, to address these challenges. Hyperledger Fabric's collection feature ensures data privacy, and its smart contracts (chaincode) enhance trustworthiness. We tested our solution using a network of devices known as CLOVES, demonstrating robust performance characteristics with UWB technology. Additionally, we evaluated our approach through an indoor localization use case.
Read more6/26/2024

0
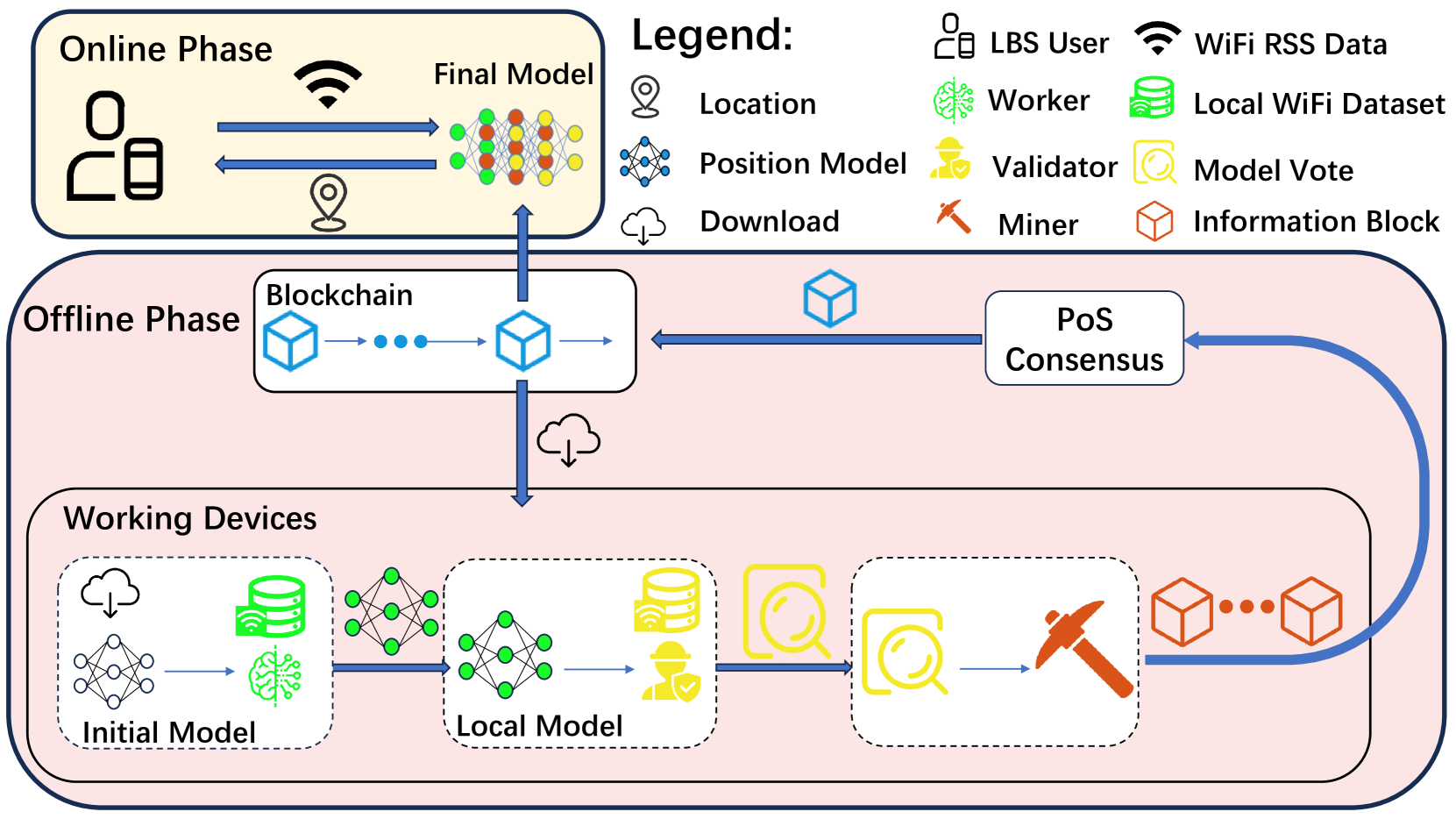
A Trustworthy AIoT-enabled Localization System via Federated Learning and Blockchain
Junfei Wang, He Huang, Jingze Feng, Steven Wong, Lihua Xie, Jianfei Yang
There is a significant demand for indoor localization technology in smart buildings, and the most promising solution in this field is using RF sensors and fingerprinting-based methods that employ machine learning models trained on crowd-sourced user data gathered from IoT devices. However, this raises security and privacy issues in practice. Some researchers propose to use federated learning to partially overcome privacy problems, but there still remain security concerns, e.g., single-point failure and malicious attacks. In this paper, we propose a framework named DFLoc to achieve precise 3D localization tasks while considering the following two security concerns. Particularly, we design a specialized blockchain to decentralize the framework by distributing the tasks such as model distribution and aggregation which are handled by a central server to all clients in most previous works, to address the issue of the single-point failure for a reliable and accurate indoor localization system. Moreover, we introduce an updated model verification mechanism within the blockchain to alleviate the concern of malicious node attacks. Experimental results substantiate the framework's capacity to deliver accurate 3D location predictions and its superior resistance to the impacts of single-point failure and malicious attacks when compared to conventional centralized federated learning systems.
Read more7/12/2024

0
A Unified Deep Transfer Learning Model for Accurate IoT Localization in Diverse Environments
Abdullahi Isa Ahmed, Yaya Etiabi, Ali Waqar Azim, El Mehdi Amhoud
Internet of Things (IoT) is an ever-evolving technological paradigm that is reshaping industries and societies globally. Real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making facilitated by localization solutions form the foundation for location-based services, enabling them to support critical functions within diverse IoT ecosystems. However, most existing works on localization focus on single environment, resulting in the development of multiple models to support multiple environments. In the context of smart cities, these raise costs and complexity due to the dynamicity of such environments. To address these challenges, this paper presents a unified indoor-outdoor localization solution that leverages transfer learning (TL) schemes to build a single deep learning model. The model accurately predicts the localization of IoT devices in diverse environments. The performance evaluation shows that by adopting an encoder-based TL scheme, we can improve the baseline model by about 17.18% in indoor environments and 9.79% in outdoor environments.
Read more5/17/2024


0
Secure Ownership Management and Transfer of Consumer Internet of Things Devices with Self-sovereign Identity
Nazmus Sakib, Md Yeasin Ali, Nuran Mubashshira Momo, Marzia Islam Mumu, Masum Al Nahid, Fairuz Rahaman Chowdhury, Md Sadek Ferdous
The popularity of the Internet of Things (IoT) has driven its usage in our homes and industries over the past 10-12 years. However, there have been some major issues related to identity management and ownership transfer involving IoT devices, particularly for consumer IoT devices, e. g. smart appliances such as smart TVs, smart refrigerators, and so on. There have been a few attempts to address this issue; however, user-centric and effective ownership and identity management of IoT devices have not been very successful so far. Recently, blockchain technology has been used to address these issues with limited success. This article presents a Self-sovereign Identity (SSI) based system that facilitates a secure and user-centric ownership management and transfer of consumer IoT devices. The system leverages a number of emerging technologies, such as blockchain and decentralized identifiers (DID), verifiable credentials (VC), under the umbrella of SSI. We present the architecture of the system based on a threat model and requirement analysis, discuss the implementation of a Proof-of-Concept based on the proposed system and illustrate a number of use-cases with their detailed protocol flows. Furthermore, we analyse its security using ProVerif, a state-of-the art protocol verification tool and examine its performance.
Read more9/2/2024