Kalman filter based localization in hybrid BLE-UWB positioning system
2404.02349

0
0
Abstract
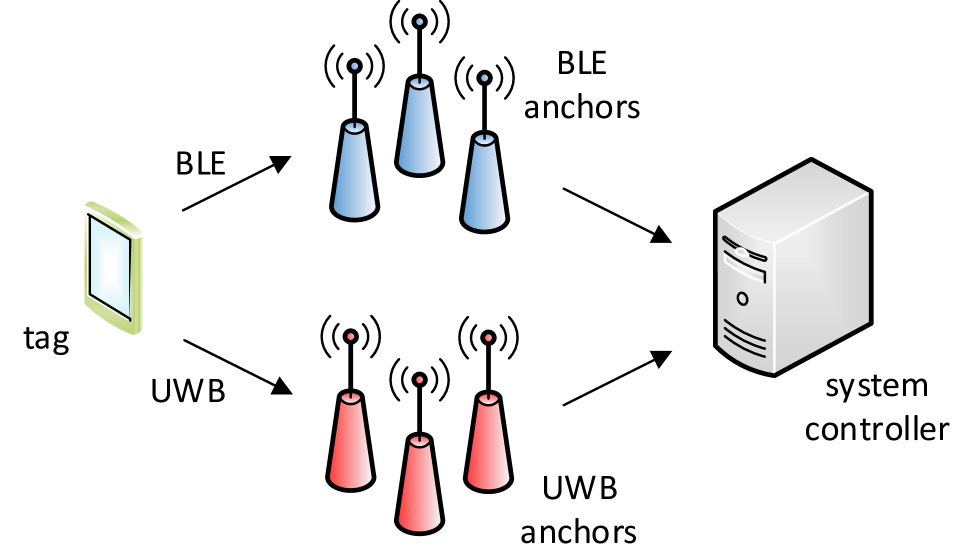
In this paper a concept of hybrid Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Ultra-wideband (UWB) positioning system is presented. The system is intended to be energy efficient. Low energy BLE unit is used as a primary source of measurement data and for most of the time localization is calculated based on received signal strength (RSS). UWB technology is used less often. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) values measured with UWB radios are periodically used to improve RSS based localization. The paper contains a description of proposed hybrid positioning algorithm. Results of simulations and experiments confirming algorithm's efficiency are also included.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Explores a hybrid Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Ultra-Wideband (UWB) positioning system
- Utilizes a Kalman Filter to improve localization accuracy
- Focuses on indoor environments where GPS signals may be weak or unavailable
Plain English Explanation
This paper describes a positioning system that combines Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technologies to improve indoor localization. BLE is a widely-used wireless standard that can provide approximate location information, while UWB offers more precise distance measurements. By fusing data from both BLE and UWB sensors, the researchers developed a Kalman Filter-based algorithm to estimate the position of a target more accurately than using either technology alone.
The Kalman Filter is a mathematical technique that can optimally combine multiple noisy measurements to produce a best estimate of the true state. In this case, the state represents the 3D position of the target, and the Kalman Filter is used to smooth out the fluctuations in the BLE and UWB readings to provide a more stable and reliable location estimate.
The hybrid BLE-UWB positioning system can be particularly useful in indoor environments where GPS signals may be weak or unavailable, such as in buildings, warehouses, or underground facilities. By leveraging the complementary strengths of BLE and UWB, this approach can achieve better localization accuracy compared to using either technology alone.
Technical Explanation
The proposed system architecture consists of a set of BLE beacons and UWB anchors installed in the environment, along with a mobile device or tag carried by the target. The BLE beacons provide approximate location information based on received signal strength, while the UWB anchors measure the time-of-flight of UWB signals to determine the distance between the tag and each anchor.
The researchers then apply a Kalman Filter to fuse the BLE and UWB measurements and estimate the 3D position of the target. The Kalman Filter is designed to handle the different error characteristics of the two technologies, with BLE providing less accurate but more stable readings and UWB offering higher precision but more noise.
To mitigate the effects of non-line-of-sight (NLOS) conditions, which can degrade the UWB distance measurements, the researchers also incorporated a NLOS detection and compensation algorithm into the Kalman Filter. This helps to improve the overall robustness of the localization system.
The performance of the proposed approach was evaluated through experiments in a real-world indoor environment, where the hybrid BLE-UWB system demonstrated superior localization accuracy compared to using BLE or UWB alone. The results also showed the system's ability to monitor the wandering behavior of persons suffering from dementia, which could have important applications in healthcare and assisted living.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive investigation of the hybrid BLE-UWB positioning system and its ability to leverage the strengths of both technologies. The Kalman Filter-based approach seems well-designed to handle the different error characteristics of the BLE and UWB measurements, and the inclusion of NLOS mitigation is a valuable addition.
However, the paper does not fully address the potential limitations of the system, such as the dependence on the availability and placement of the BLE beacons and UWB anchors, which could be a practical challenge in real-world deployments. Additionally, the experiments were conducted in a single indoor environment, so further testing in diverse settings would be beneficial to assess the system's robustness and generalizability.
Conclusion
The proposed hybrid BLE-UWB positioning system with Kalman Filter-based localization represents a promising approach to improving indoor positioning accuracy compared to using either technology alone. By combining the complementary strengths of BLE and UWB, this system can provide more reliable and stable location estimates, which could have important applications in areas like healthcare, smart buildings, and asset tracking. Further research to address the practical deployment challenges and test the system in a wider range of environments would help to strengthen the findings and expand the potential use cases of this technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
❗
Utilizing acceleration measurements to improve TDOA based localization
Marcin Kolakowski

0
0
In this paper localization using UWB positioning system and an inertial unit containing a single accelerometer is considered. The main part of the paper describes a novel algorithm for person localization. The algorithm is based on modified Extended Kalman Filter and utilizes TDOA (Time Difference of Arrival) results obtained from UWB system and results of acceleration measurement performed by the localized tag device. The proposed algorithm has been experimentally investigated through simulation and experiments. The results are included in the paper.
4/1/2024
🎯
Improving BLE Based Localization Accuracy Using Proximity Sensors
Marcin Kolakowski

0
0
Bluetooth Low Energy systems are one of the most popular solutions used for indoor localization. Unfortunately their accuracy might not be sufficient for some of the applications. One way to reduce localization errors is hybrid positioning, which combines measurement results obtained with different techniques. The paper describes a concept of a hybrid localization system in which Bluetooth Low Energy technology is supported with the use of laser proximity sensors. Results from both system parts are fused using a novel, simple positioning algorithm. The proposed system concept was tested using BLE and proximity sensors evaluation boards.
4/1/2024
Adaptive Anchor Pairs Selection in a TDOA-based System Through Robot Localization Error Minimization
Marcin Kolakowski

0
0
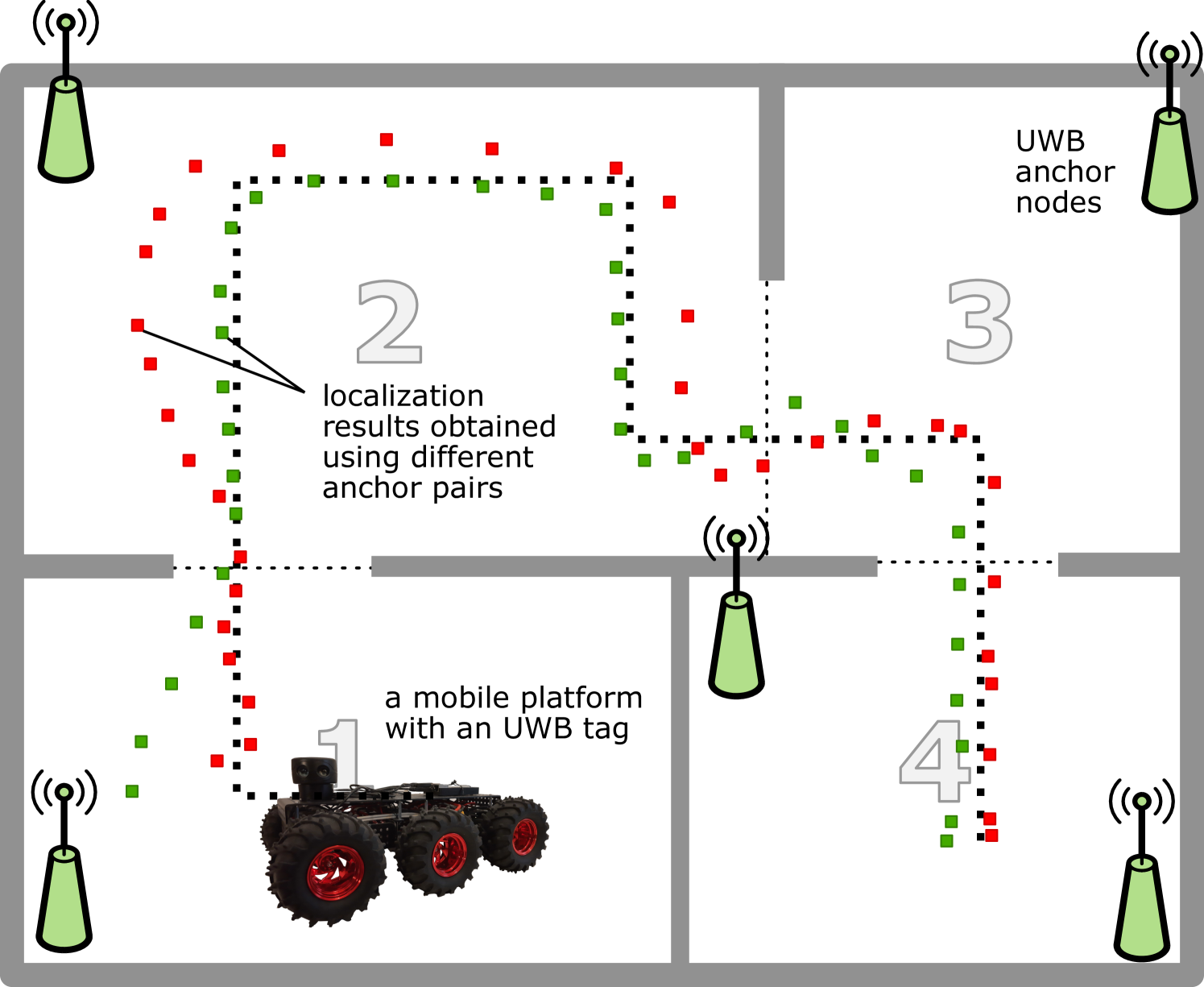
The following paper presents an adaptive anchor pairs selection method for ultra-wideband (UWB) Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) based positioning systems. The method divides the area covered by the system into several zones and assigns them anchor pair sets. The pair sets are determined during calibration based on localization root mean square error (RMSE). The calibration assumes driving a mobile platform equipped with a LiDAR sensor and a UWB tag through the specified zones. The robot is localized separately based on a large set of different TDOA pairs and using a LiDAR, which acts as the reference. For each zone, the TDOA pairs set for which the registered RMSE is lowest is selected and used for localization in the routine system work. The proposed method has been tested with simulations and experiments. The results for both simulated static and experimental dynamic scenarios have proven that the adaptive selection of the anchor nodes leads to an increase in localization accuracy. In the experiment, the median trajectory error for a moving person localization was at a level of 25 cm.
4/9/2024

Multi-Robot Collaborative Localization and Planning with Inter-Ranging
Derek Knowles, Adam Dai, Grace Gao

0
0
Robots often use feature-based image tracking to identify their position in their surrounding environment; however, feature-based image tracking is prone to errors in low-textured and poorly lit environments. Specifically, we investigate a scenario where robots are tasked with exploring the surface of the Moon and are required to have an accurate estimate of their position to be able to correctly geotag scientific measurements. To reduce localization error, we complement traditional feature-based image tracking with ultra-wideband (UWB) distance measurements between the robots. The robots use an advanced mesh-ranging protocol that allows them to continuously share distance measurements amongst each other rather than relying on the common anchor and tag UWB architecture. We develop a decentralized multi-robot coordination algorithm that actively plans paths based on measurement line-of-sight vectors amongst all robots to minimize collective localization error. We then demonstrate the emergent behavior of the proposed multi-robot coordination algorithm both in simulation and hardware to lower a geometry-based uncertainty metric and reduce localization error.
6/26/2024