Put Your Money Where Your Mouth Is: Evaluating Strategic Planning and Execution of LLM Agents in an Auction Arena
2310.05746

0
0
📶
Abstract
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) showcase advanced reasoning, yet NLP evaluations often depend on static benchmarks. Evaluating this necessitates environments that test strategic reasoning in dynamic, competitive scenarios requiring long-term planning. We introduce AucArena, a novel evaluation suite that simulates auctions, a setting chosen for being highly unpredictable and involving many skills related to resource and risk management, while also being easy to evaluate. We conduct controlled experiments using state-of-the-art LLMs to power bidding agents to benchmark their planning and execution skills. Our research demonstrates that LLMs, such as GPT-4, possess key skills for auction participation, such as budget management and goal adherence, which improve with adaptive strategies. This highlights LLMs' potential in modeling complex social interactions in competitive contexts. However, variability in LLM performance and occasional outperformance by simpler methods indicate opportunities for further advancements in LLM design and the value of our simulation environment for ongoing testing and refinement.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- Researchers introduce AucArena, a novel evaluation suite that simulates auctions to test the strategic reasoning and planning skills of large language models (LLMs).
- Auctions are chosen as a testing environment because they involve unpredictable, dynamic, and competitive scenarios that require long-term planning and resource/risk management.
- The researchers conduct experiments using state-of-the-art LLMs, such as GPT-4, to power bidding agents and benchmark their performance in the auction environment.
- The results demonstrate that LLMs possess key skills for auction participation, like budget management and goal adherence, which can be improved through adaptive strategies.
- However, the variability in LLM performance and occasional outperformance by simpler methods indicate opportunities for further advancements in LLM design and the value of the AucArena simulation environment for ongoing testing and refinement.
Plain English Explanation
Imagine you're at an auction, where buyers and sellers compete to get the best deals on valuable items. This kind of auction environment is unpredictable, fast-paced, and requires careful planning and decision-making. Researchers wanted to see how well advanced language models, like GPT-4, could handle the challenges of this auction scenario.
They created a new simulation environment called AucArena that mimics the dynamics of real auctions. In this virtual auction house, the researchers had their language model-powered bidding agents compete against each other, testing their ability to manage their budgets, set strategic goals, and adapt their tactics over time.
The results showed that these powerful language models can indeed handle many of the key skills needed for successful auction participation, like keeping track of their spending and sticking to their objectives. But the models' performance was also quite variable, and sometimes simpler methods outperformed them. This suggests there's still room for improvement in how these language models are designed and trained to handle complex, real-world competitive scenarios.
The AucArena simulation environment provides a useful testing ground for continuing to push the boundaries of what these advanced language models can do. By challenging them in dynamic, unpredictable settings like auctions, researchers can better understand the models' strengths and weaknesses, and work on making them even smarter and more capable.
Technical Explanation
The researchers introduce AucArena, a novel evaluation suite that simulates auctions to test the strategic reasoning and planning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Auctions were chosen as the testing environment because they involve highly unpredictable, dynamic, and competitive scenarios that require long-term planning and skills related to resource and risk management.
The researchers conducted controlled experiments using state-of-the-art LLMs, such as GPT-4, to power bidding agents in the AucArena environment. This allowed them to benchmark the models' performance in tasks like budget management, goal adherence, and adaptive strategy implementation.
The results demonstrate that LLMs possess key skills relevant to auction participation. For example, the models were able to effectively manage their budgets and adhere to their strategic objectives, with their performance improving through the use of adaptive bidding strategies. This highlights the potential of LLMs to model complex social interactions in competitive contexts.
However, the researchers also observed variability in LLM performance and occasional outperformance by simpler methods. This indicates that there are still opportunities for further advancements in LLM design to improve their capabilities in dynamic, strategic environments like auctions. The AucArena simulation environment is proposed as a valuable tool for ongoing testing and refinement of LLM technologies.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling approach to evaluating the strategic reasoning and planning capabilities of LLMs using a simulated auction environment. The choice of auctions as the testing ground is well-justified, as they involve the kind of unpredictability, competition, and long-term planning that can challenge the current abilities of language models.
One potential limitation of the research is the scope of the experiments. While the results demonstrate that LLMs like GPT-4 possess relevant skills for auction participation, the paper does not provide a comprehensive assessment of the models' performance across the full range of auction dynamics and scenarios. It would be valuable to see how the models fare in more diverse auction settings, such as those with different bidding rules, item types, or numbers of participants.
Additionally, the paper acknowledges the variability in LLM performance and the occasional outperformance of simpler methods. This suggests that the current state-of-the-art LLMs may still have room for improvement in their strategic reasoning and planning abilities, particularly when faced with complex, dynamic, and competitive environments. Further research could explore the specific factors that contribute to this variability and identify opportunities for enhancing the models' capabilities.
Overall, the AucArena evaluation suite and the insights gained from the experiments represent an important step forward in assessing the real-world problem-solving skills of LLMs. The findings highlight the potential of these models to engage in complex social interactions and decision-making, while also underscoring the need for continued refinement and adaptation to meet the demands of challenging, unpredictable scenarios.
Conclusion
The introduction of the AucArena evaluation suite and the experiments conducted with state-of-the-art LLMs provide valuable insights into the strategic reasoning and planning capabilities of these advanced language models. The simulation of auction environments, known for their unpredictability and competitive dynamics, serves as a robust testing ground for evaluating the models' ability to manage resources, set goals, and adapt their strategies over time.
The research demonstrates that LLMs, such as GPT-4, possess key skills relevant to auction participation, including effective budget management and goal adherence. The models' performance can be further improved through the adoption of adaptive bidding strategies, highlighting their potential to model complex social interactions in competitive contexts.
However, the variability in LLM performance and occasional outperformance by simpler methods suggest that there are still opportunities for further advancements in LLM design and architecture. The AucArena evaluation suite provides a valuable platform for ongoing testing and refinement, allowing researchers to identify the strengths and weaknesses of these models and drive continued progress in the field of strategic reasoning and planning.
As language models become increasingly capable and integrated into various real-world applications, the ability to assess their problem-solving skills in dynamic, competitive environments is crucial. The insights gained from this research contribute to a deeper understanding of the current state of LLM capabilities and pave the way for the development of even more sophisticated and adaptable language-based systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
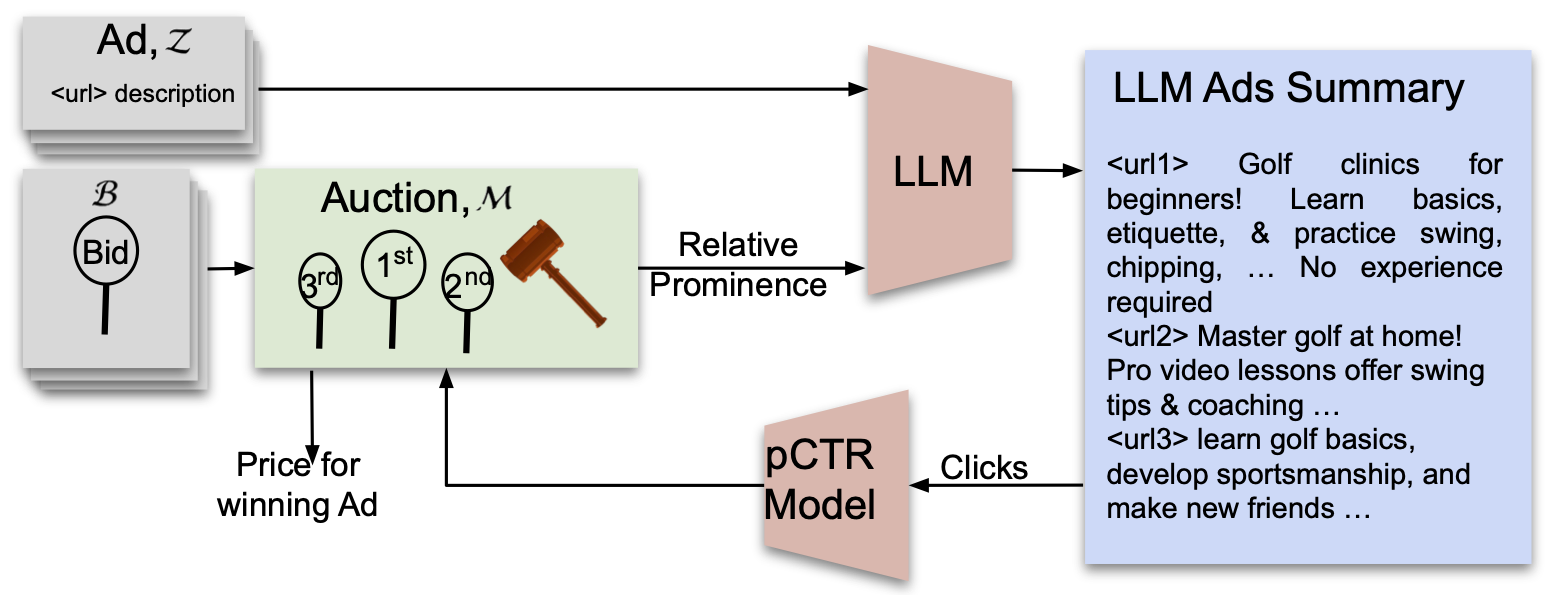
Auctions with LLM Summaries
Kumar Avinava Dubey, Zhe Feng, Rahul Kidambi, Aranyak Mehta, Di Wang

0
0
We study an auction setting in which bidders bid for placement of their content within a summary generated by a large language model (LLM), e.g., an ad auction in which the display is a summary paragraph of multiple ads. This generalizes the classic ad settings such as position auctions to an LLM generated setting, which allows us to handle general display formats. We propose a novel factorized framework in which an auction module and an LLM module work together via a prediction model to provide welfare maximizing summary outputs in an incentive compatible manner. We provide a theoretical analysis of this framework and synthetic experiments to demonstrate the feasibility and validity of the system together with welfare comparisons.
4/15/2024
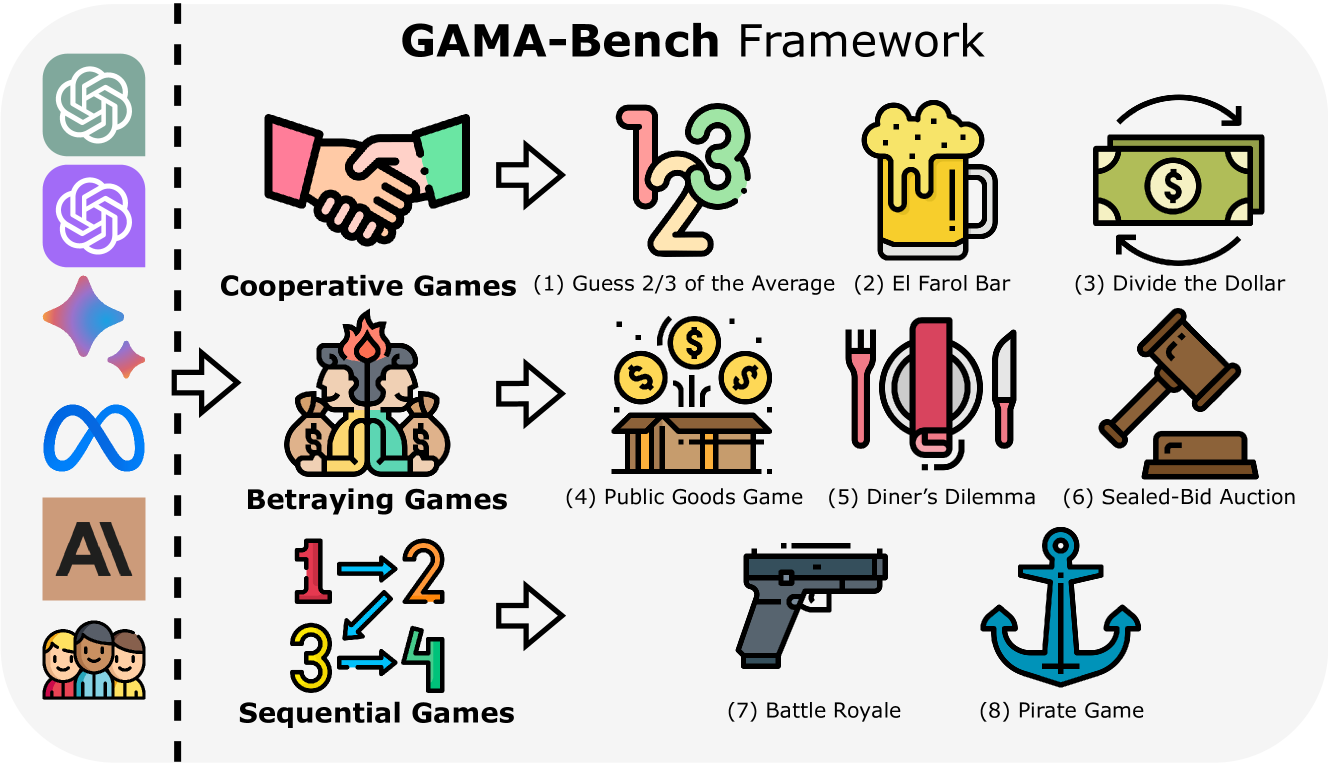
How Far Are We on the Decision-Making of LLMs? Evaluating LLMs' Gaming Ability in Multi-Agent Environments
Jen-tse Huang, Eric John Li, Man Ho Lam, Tian Liang, Wenxuan Wang, Youliang Yuan, Wenxiang Jiao, Xing Wang, Zhaopeng Tu, Michael R. Lyu

0
0
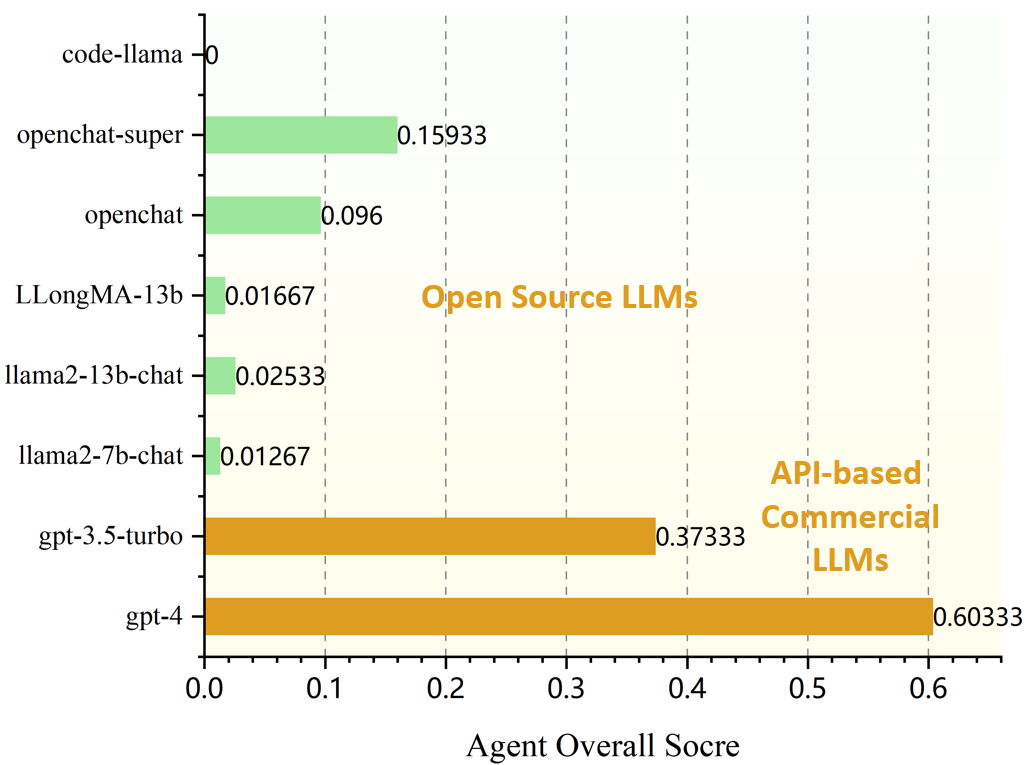
Decision-making, a complicated task requiring various types of abilities, presents an excellent framework for assessing Large Language Models (LLMs). Our research investigates LLMs' decision-making capabilities through the lens of a well-established field, Game Theory. We focus specifically on games that support the participation of more than two agents simultaneously. Subsequently, we introduce our framework, GAMA-Bench, including eight classical multi-agent games. We design a scoring scheme to assess a model's performance in these games quantitatively. Through GAMA-Bench, we investigate LLMs' robustness, generalizability, and enhancement strategies. Results reveal that while GPT-3.5 shows satisfying robustness, its generalizability is relatively limited. However, its performance can be improved through approaches such as Chain-of-Thought. Additionally, we conduct evaluations across various LLMs and find that GPT-4 outperforms other models on GAMA-Bench, achieving a score of 60.5. Moreover, Gemini-1.0-Pro and GPT-3.5 (0613, 1106, 0125) demonstrate similar intelligence on GAMA-Bench. The code and experimental results are made publicly available via https://github.com/CUHK-ARISE/GAMABench.
4/26/2024
Enhancing the General Agent Capabilities of Low-Parameter LLMs through Tuning and Multi-Branch Reasoning
Qinhao Zhou, Zihan Zhang, Xiang Xiang, Ke Wang, Yuchuan Wu, Yongbin Li

0
0
Open-source pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit strong language understanding and generation capabilities, making them highly successful in a variety of tasks. However, when used as agents for dealing with complex problems in the real world, their performance is far inferior to large commercial models such as ChatGPT and GPT-4. As intelligent agents, LLMs need to have the capabilities of task planning, long-term memory, and the ability to leverage external tools to achieve satisfactory performance. Various methods have been proposed to enhance the agent capabilities of LLMs. On the one hand, methods involve constructing agent-specific data and fine-tuning the models. On the other hand, some methods focus on designing prompts that effectively activate the reasoning abilities of the LLMs. We explore both strategies on the 7B and 13B models. We propose a comprehensive method for constructing agent-specific data using GPT-4. Through supervised fine-tuning with constructed data, we find that for these models with a relatively small number of parameters, supervised fine-tuning can significantly reduce hallucination outputs and formatting errors in agent tasks. Furthermore, techniques such as multi-path reasoning and task decomposition can effectively decrease problem complexity and enhance the performance of LLMs as agents. We evaluate our method on five agent tasks of AgentBench and achieve satisfactory results.
4/1/2024
↗️
Unveiling the Competitive Dynamics: A Comparative Evaluation of American and Chinese LLMs
Zhenhui Jiang, Jiaxin Li, Yang Liu

0
0
The strategic significance of Large Language Models (LLMs) in economic expansion, innovation, societal development, and national security has been increasingly recognized since the advent of ChatGPT. This study provides a comprehensive comparative evaluation of American and Chinese LLMs in both English and Chinese contexts. We proposed a comprehensive evaluation framework that encompasses natural language proficiency, disciplinary expertise, and safety and responsibility, and systematically assessed 16 prominent models from the US and China under various operational tasks and scenarios. Our key findings show that GPT 4-Turbo is at the forefront in English contexts, whereas Ernie-Bot 4 stands out in Chinese contexts. The study also highlights disparities in LLM performance across languages and tasks, stressing the necessity for linguistically and culturally nuanced model development. The complementary strengths of American and Chinese LLMs point to the value of Sino-US collaboration in advancing LLM technology. The research presents the current LLM competition landscape and offers valuable insights for policymakers and businesses regarding strategic LLM investments and development. Future work will expand on this framework to include emerging LLM multimodal capabilities and business application assessments.
5/14/2024