Rate-Splitting for Joint Unicast and Multicast Transmission in LEO Satellite Networks with Non-Uniform Traffic Demand

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The provided paper explores rate-splitting techniques for transmitting both unicast and multicast data in low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite networks with non-uniform traffic demands.
- It proposes a hybrid transmission scheme that combines unicast and multicast approaches to efficiently serve users with varying data requirements.
- The key focus is on optimizing the rate allocation between unicast and multicast components to maximize overall throughput.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how to efficiently send two different types of data - unicast (meant for individual users) and multicast (meant for groups of users) - through satellites orbiting close to Earth, known as LEO satellite networks.
These networks often have non-uniform traffic demands, meaning some areas need more data than others. The researchers develop a hybrid approach that combines unicast and multicast transmission to better match the varying needs of users across the network.
The core idea is to carefully split the transmission rates between the unicast and multicast components to maximize the overall amount of data that can be delivered. This rate-splitting technique aims to optimize the usage of the satellite network's limited resources to serve all users as effectively as possible.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) scheme to enable joint unicast and multicast transmission in LEO satellite networks with non-uniform traffic demands.
The authors develop a hybrid transmission framework that combines unicast delivery for individual users and multicast delivery for groups of users. This allows the system to flexibly adjust the allocation of transmission resources based on the varying data requirements across different regions.
Key aspects of the technical approach include:
- Optimization of rate allocation: The researchers formulate an optimization problem to determine the optimal split between unicast and multicast transmission rates to maximize the overall system throughput.
- Heterogeneous traffic modeling: The model accounts for the non-uniform spatial distribution of traffic demands, representing the uneven data needs across the satellite coverage area.
- Resource management: The system dynamically assigns transmission resources (e.g., bandwidth, power) to the unicast and multicast components based on the optimized rate allocation.
The paper provides detailed mathematical analysis and simulations to evaluate the performance of the proposed RSMA-based approach compared to conventional unicast-only or multicast-only transmission schemes.
Critical Analysis
The research presented in the paper introduces an innovative hybrid transmission technique to address the challenges of non-uniform traffic demands in LEO satellite networks. By intelligently combining unicast and multicast approaches, the proposed RSMA scheme demonstrates potential advantages in terms of improved overall system throughput.
However, the paper also acknowledges several limitations and areas for further investigation:
- The analysis assumes perfect channel state information is available, which may not be realistic in practical deployments.
- The optimization problem formulation relies on centralized decision-making, which could pose scalability issues in large-scale satellite networks.
- The impact of user mobility on the performance of the rate-splitting approach is not addressed.
- The security and privacy implications of the unicast-multicast hybrid transmission scheme are not examined.
Further research could explore decentralized or distributed rate allocation strategies, as well as investigate the performance of the RSMA approach under more realistic channel and mobility conditions. Addressing these aspects could enhance the practical applicability of the proposed techniques.
Conclusion
The paper presents a novel rate-splitting approach for joint unicast and multicast transmission in LEO satellite networks with non-uniform traffic demands. By optimizing the allocation of transmission resources between the unicast and multicast components, the proposed RSMA scheme aims to improve the overall system throughput and better serve the varying data requirements of users across the satellite coverage area.
The research highlights the potential benefits of hybrid transmission techniques in addressing the challenges of heterogeneous traffic patterns in next-generation satellite communication systems. While the paper identifies several areas for further investigation, the proposed RSMA framework offers a promising direction for enhancing the efficiency and flexibility of future LEO satellite networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Rate-Splitting for Joint Unicast and Multicast Transmission in LEO Satellite Networks with Non-Uniform Traffic Demand
Jaehyup Seong, Juha Park, Dong-Hyun Jung, Jeonghun Park, Wonjae Shin
Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite communications (SATCOM) with ubiquitous global connectivity is deemed a pivotal catalyst in advancing wireless communication systems for 5G and beyond. LEO SATCOM excels in delivering versatile information services across expansive areas, facilitating both unicast and multicast transmissions via high-speed broadband capability. Nonetheless, given the broadband coverage of LEO SATCOM, traffic demand distribution within the service area is non-uniform, and the time/frequency/power resources available at LEO satellites remain significantly limited. Motivated by these challenges, we propose a rate-matching framework for non-orthogonal unicast and multicast (NOUM) transmission. Our approach aims to minimize the difference between offered rates and traffic demands for both unicast and multicast messages. By multiplexing unicast and multicast transmissions over the same radio resource, rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) is employed to manage interference between unicast and multicast streams, as well as inter-user interference under imperfect channel state information at the LEO satellite. To address the formulated problems non-smoothness and non-convexity, the common rate is approximated using the LogSumExp technique. Thereafter, we represent the common rate portion as the ratio of the approximated function, converting the problem into an unconstrained form. A generalized power iteration (GPI)-based algorithm, coined GPI-RS-NOUM, is proposed upon this reformulation. Through comprehensive numerical analysis across diverse simulation setups, we demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms various benchmarks for LEO SATCOM with uneven traffic demands.
Read more8/7/2024


0
A Bistatic ISAC Framework for LEO Satellite Systems: A Rate-Splitting Approach
Juha Park, Jaehyup Seong, Jaehak Ryu, Yijie Mao, Wonjae Shin
Aiming to achieve ubiquitous global connectivity and target detection on the same platform with improved spectral/energy efficiency and reduced onboard hardware cost, low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems capable of simultaneously performing communications and radar have attracted significant attention. Designing such a joint system should address not only the challenges of integrating two functions but also the unique propagation characteristics of the satellites. To overcome severe echo signal path loss due to the high altitude of the satellite, we put forth a bistatic integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) framework with a radar receiver separated from the satellite. For robust and effective interference management, we employ rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA), which splits and encodes users messages into private and common streams. We optimize the dual-functional precoders to maximize the minimum rate among all users while satisfying the Cramer-Rao bound (CRB) constraints. Given the challenge of acquiring instantaneous channel state information (iCSI) for LEO satellites, we exploit the geometrical and statistical characteristics of the satellite channel. To develop an efficient optimization algorithm, semidefinite relaxation (SDR), sequential rank-1 constraint relaxation (SROCR), and successive convex approximation (SCA) are utilized. Numerical results show that the proposed framework efficiently performs both communication and radar, demonstrating superior interference control capabilities. Furthermore, it is validated that the common stream plays three vital roles: i) beamforming towards the radar target, ii) interference management between communications and radar, and iii) interference management among communication users.
Read more7/15/2024
🏅

0
QoE-Aware and Secure UAV-Aided Rate-Splitting Multiple Access Based Communications
Abuzar B. M. Adam, Xiaoyu Wan, Mohammed Saleh Ali Muthanna
In this work, we address the issue of quality of experience (QoE) in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) aided multiuser rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) networks under secrecy constraints. The problem is formulated as maximization of sum mean opinion scores (MOSs) of the users. The problem is decomposed into two subproblems, beamforming and rate allocation and UAV trajectory subproblem. For, beamforming and rate allocation subproblem, we use the epigraph method, property of polynomials, and the norm-bounded error of channels, we linearize the objective function. Then, applying second-order conic (SOC) and first Taylor expansion, we convexify the remaining nonconvex constraints. For the highly nonconvex UAV trajectory, we unroll the constraints and we apply first Taylor expansion on the unrolled constraints. The simulation results demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed framework.
Read more5/24/2024

0
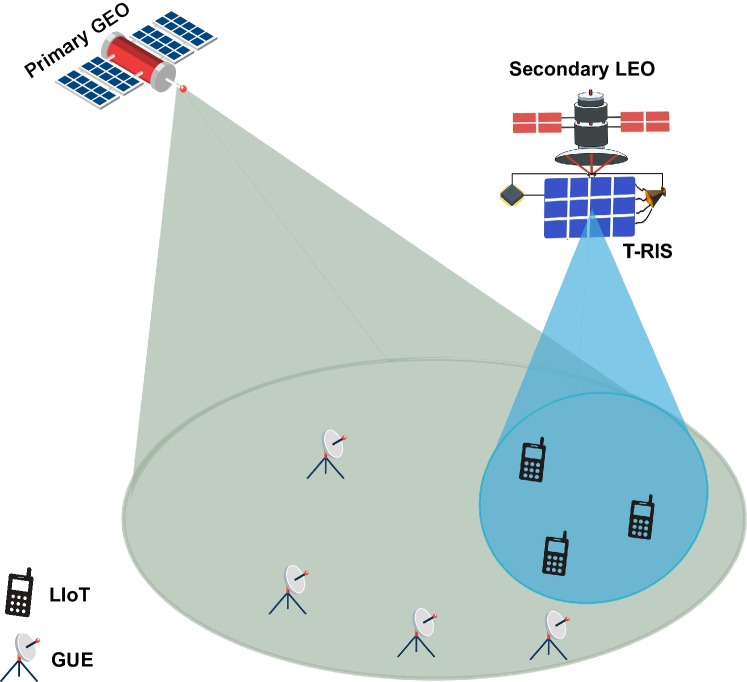
CR-Enabled NOMA Integrated Non-Terrestrial IoT Networks with Transmissive RIS
Wali Ullah Khan, Zain Ali, Asad Mahmood, Eva Lagunas, Syed Tariq Shah, Symeon Chatzinotas
This work proposes a T-RIS-equipped LEO satellite communication in cognitive radio-enabled integrated NTNs. In the proposed system, a GEO satellite operates as a primary network, and a T-RIS-equipped LEO satellite operates as a secondary IoT network. The objective is to maximize the sum rate of T-RIS-equipped LEO satellite communication using downlink NOMA while ensuring the service quality of GEO cellular users. Our framework simultaneously optimizes the total transmit power of LEO, NOMA power allocation for LEO IoT (LIoT) and T-RIS phase shift design subject to the service quality of LIoT and interference temperature to the primary GEO network. To solve the non-convex sum rate maximization problem, we first adopt successive convex approximations to reduce the complexity of the formulated optimization. Then, we divide the problem into two parts, i.e., power allocation of LEO and phase shift design of T-RIS. The power allocation problem is solved using KKT conditions, while the phase shift problem is handled by Taylor approximation and semidefinite programming. Numerical results are provided to validate the proposed optimization framework.
Read more8/28/2024