Recent Advances in Data-Driven Business Process Management
2406.01786

0
0

Abstract
The rapid development of cutting-edge technologies, the increasing volume of data and also the availability and processability of new types of data sources has led to a paradigm shift in data-based management and decision-making. Since business processes are at the core of organizational work, these developments heavily impact BPM as a crucial success factor for organizations. In view of this emerging potential, data-driven business process management has become a relevant and vibrant research area. Given the complexity and interdisciplinarity of the research field, this position paper therefore presents research insights regarding data-driven BPM.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper examines recent advances in data-driven approaches to Business Process Management (BPM)
- It discusses key research challenges in applying machine learning and data analytics to BPM
- The paper covers topics like process discovery, process optimization, and the integration of IoT data into BPM systems
Plain English Explanation
Businesses often rely on well-defined processes to ensure consistent operations and efficient workflows. Recent Advances in Data-Driven Business Process Management explores how new data-driven techniques can improve the way these business processes are managed.
The paper highlights several research areas where data analytics and machine learning are being applied to BPM. For example, process discovery techniques can automatically identify the steps involved in a business process by analyzing event logs. IoT data can also be integrated into BPM systems to provide real-time insights and enable more dynamic process optimization.
By leveraging data more effectively, businesses can gain a better understanding of their operations, identify opportunities for improvement, and make more informed decisions about their processes. This can lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experiences.
Technical Explanation
The paper first provides an overview of the key research challenges in data-driven BPM. These include:
- Process Discovery: Developing methods to automatically discover the structure and dependencies within business processes by analyzing event logs and other data sources.
- Process Monitoring and Optimization: Using real-time data and predictive analytics to monitor process performance and identify opportunities for optimization.
- IoT Integration: Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) data into BPM systems to provide more comprehensive visibility into operations and enable dynamic process adaptation.
- Machine Learning for BPM: Applying machine learning techniques, such as process prediction and process mining, to improve various aspects of BPM.
The paper then discusses several research efforts that address these challenges. For example, it highlights studies that use advanced process discovery algorithms to uncover hidden dependencies and causal relationships within business processes. It also examines how IoT data can be leveraged to enhance process monitoring and optimization.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current research landscape in data-driven BPM. However, it also acknowledges the significant challenges involved in successfully integrating these data-driven approaches into real-world business environments.
One key limitation is the availability and quality of the data required for these techniques to be effective. Businesses may face difficulties in collecting, cleaning, and integrating the necessary data from various sources. Additionally, the paper notes that the interpretability and trustworthiness of the insights generated by machine learning models can be a concern for business stakeholders.
Further research is needed to address these practical challenges and ensure that data-driven BPM solutions are reliable, scalable, and easily adoptable by organizations. Ongoing work in areas like responsible AI and data governance may help to overcome some of these hurdles.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the exciting potential of data-driven approaches to transform Business Process Management. By leveraging the wealth of data available, businesses can gain deeper insights into their operations, optimize their processes, and ultimately deliver better products and services to their customers.
However, the successful implementation of these data-driven BPM techniques will require overcoming significant technical and organizational challenges. Continued research and innovation in areas like process discovery, IoT integration, and responsible AI will be crucial to realizing the full benefits of this data-centric approach to BPM.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Machine learning in business process management: A systematic literature review
Sven Weinzierl, Sandra Zilker, Sebastian Dunzer, Martin Matzner

0
0
Machine learning (ML) provides algorithms to create computer programs based on data without explicitly programming them. In business process management (BPM), ML applications are used to analyse and improve processes efficiently. Three frequent examples of using ML are providing decision support through predictions, discovering accurate process models, and improving resource allocation. This paper organises the body of knowledge on ML in BPM. We extract BPM tasks from different literature streams, summarise them under the phases of a process`s lifecycle, explain how ML helps perform these tasks and identify technical commonalities in ML implementations across tasks. This study is the first exhaustive review of how ML has been used in BPM. We hope that it can open the door for a new era of cumulative research by helping researchers to identify relevant preliminary work and then combine and further develop existing approaches in a focused fashion. Our paper helps managers and consultants to find ML applications that are relevant in the current project phase of a BPM initiative, like redesigning a business process. We also offer - as a synthesis of our review - a research agenda that spreads ten avenues for future research, including applying novel ML concepts like federated learning, addressing less regarded BPM lifecycle phases like process identification, and delivering ML applications with a focus on end-users.
5/28/2024
📊
From Internet of Things Data to Business Processes: Challenges and a Framework
Juergen Mangler, Ronny Seiger, Janik-Vasily Benzin, Joscha Gruger, Yusuf Kirikkayis, Florian Gallik, Lukas Malburg, Matthias Ehrendorfer, Yannis Bertrand, Marco Franceschetti, Barbara Weber, Stefanie Rinderle-Ma, Ralph Bergmann, Estefan'ia Serral Asensio, Manfred Reichert

0
0
The IoT and Business Process Management (BPM) communities co-exist in many shared application domains, such as manufacturing and healthcare. The IoT community has a strong focus on hardware, connectivity and data; the BPM community focuses mainly on finding, controlling, and enhancing the structured interactions among the IoT devices in processes. While the field of Process Mining deals with the extraction of process models and process analytics from process event logs, the data produced by IoT sensors often is at a lower granularity than these process-level events. The fundamental questions about extracting and abstracting process-related data from streams of IoT sensor values are: (1) Which sensor values can be clustered together as part of process events?, (2) Which sensor values signify the start and end of such events?, (3) Which sensor values are related but not essential? This work proposes a framework to semi-automatically perform a set of structured steps to convert low-level IoT sensor data into higher-level process events that are suitable for process mining. The framework is meant to provide a generic sequence of abstract steps to guide the event extraction, abstraction, and correlation, with variation points for plugging in specific analysis techniques and algorithms for each step. To assess the completeness of the framework, we present a set of challenges, how they can be tackled through the framework, and an example on how to instantiate the framework in a real-world demonstration from the field of smart manufacturing. Based on this framework, future research can be conducted in a structured manner through refining and improving individual steps.
5/24/2024
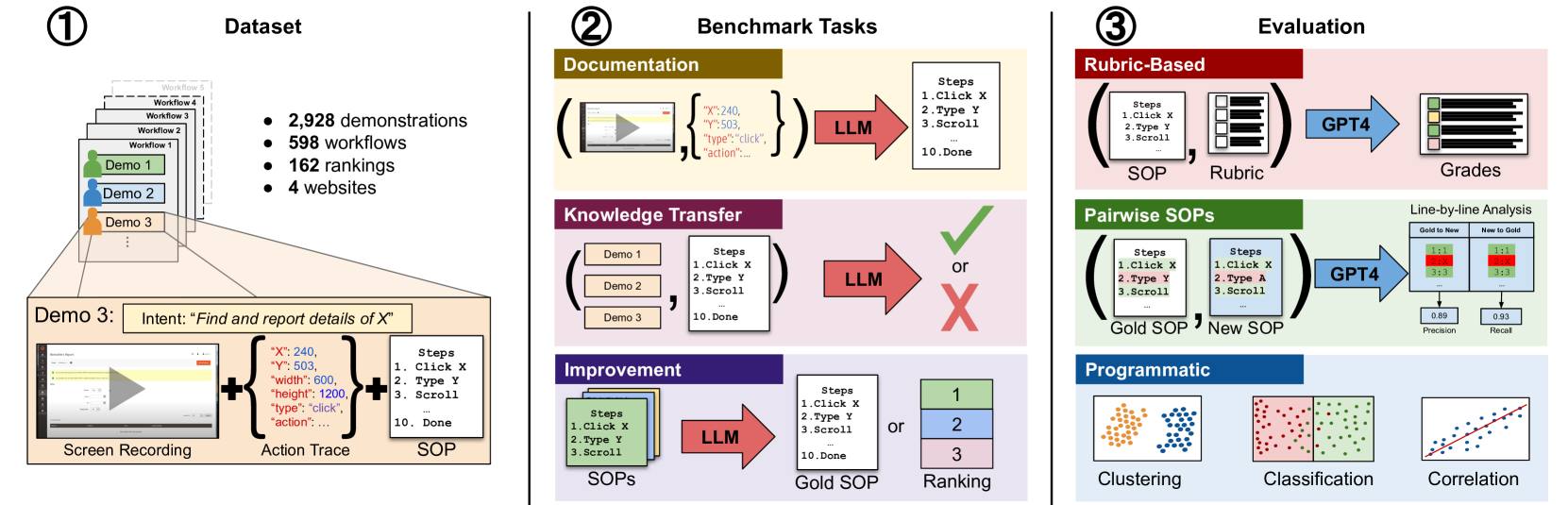
Do Multimodal Foundation Models Understand Enterprise Workflows? A Benchmark for Business Process Management Tasks
Michael Wornow, Avanika Narayan, Ben Viggiano, Ishan S. Khare, Tathagat Verma, Tibor Thompson, Miguel Angel Fuentes Hernandez, Sudharsan Sundar, Chloe Trujillo, Krrish Chawla, Rongfei Lu, Justin Shen, Divya Nagaraj, Joshua Martinez, Vardhan Agrawal, Althea Hudson, Nigam H. Shah, Christopher Re

0
0
Existing ML benchmarks lack the depth and diversity of annotations needed for evaluating models on business process management (BPM) tasks. BPM is the practice of documenting, measuring, improving, and automating enterprise workflows. However, research has focused almost exclusively on one task - full end-to-end automation using agents based on multimodal foundation models (FMs) like GPT-4. This focus on automation ignores the reality of how most BPM tools are applied today - simply documenting the relevant workflow takes 60% of the time of the typical process optimization project. To address this gap we present WONDERBREAD, the first benchmark for evaluating multimodal FMs on BPM tasks beyond automation. Our contributions are: (1) a dataset containing 2928 documented workflow demonstrations; (2) 6 novel BPM tasks sourced from real-world applications ranging from workflow documentation to knowledge transfer to process improvement; and (3) an automated evaluation harness. Our benchmark shows that while state-of-the-art FMs can automatically generate documentation (e.g. recalling 88% of the steps taken in a video demonstration of a workflow), they struggle to re-apply that knowledge towards finer-grained validation of workflow completion (F1 < 0.3). We hope WONDERBREAD encourages the development of more human-centered AI tooling for enterprise applications and furthers the exploration of multimodal FMs for the broader universe of BPM tasks. We publish our dataset and experiments here: https://github.com/HazyResearch/wonderbread
6/21/2024
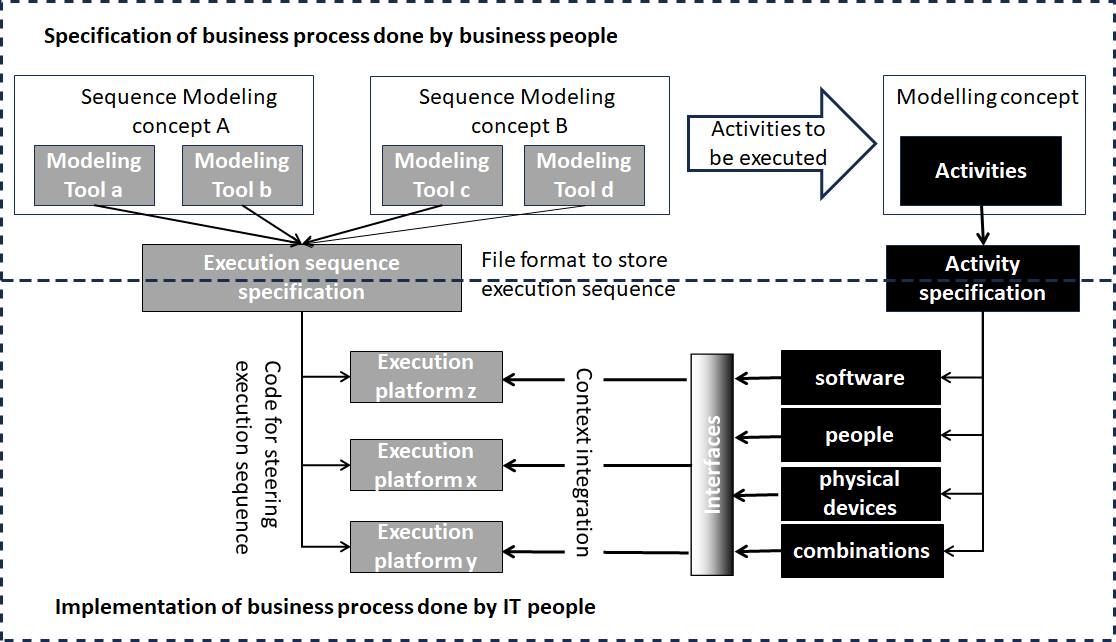
A Step Towards a Universal Method for Modeling and Implementing Cross-Organizational Business Processes
Gerhard Zeisler, Tim Tobias Braunauer, Albert Fleischmann, Robert Singer

0
0
The widely adopted Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a cornerstone of industry standards for business process modeling. However, its ambiguous execution semantics often result in inconsistent interpretations, depending on the software used for implementation. In response, the Process Specification Language (PASS) provides formally defined semantics to overcome these interpretational challenges. Despite its clear advantages, PASS has not reached the same level of industry penetration as BPMN. This feasibility study proposes using PASS as an intermediary framework to translate and execute BPMN models. It describes the development of a prototype translator that converts specific BPMN elements into a format compatible with PASS. These models are then transformed into source code and executed in a bespoke workflow environment, marking a departure from traditional BPMN implementations. Our findings suggest that integrating PASS enhances compatibility across different modeling and execution tools and offers a more robust methodology for implementing business processes across organizations. This study lays the groundwork for more accurate and unified business process model executions, potentially transforming industry standards for process modeling and execution.
6/19/2024