Research, Applications and Prospects of Event-Based Pedestrian Detection: A Survey

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive survey of event-based pedestrian detection, covering research, applications, and future prospects.
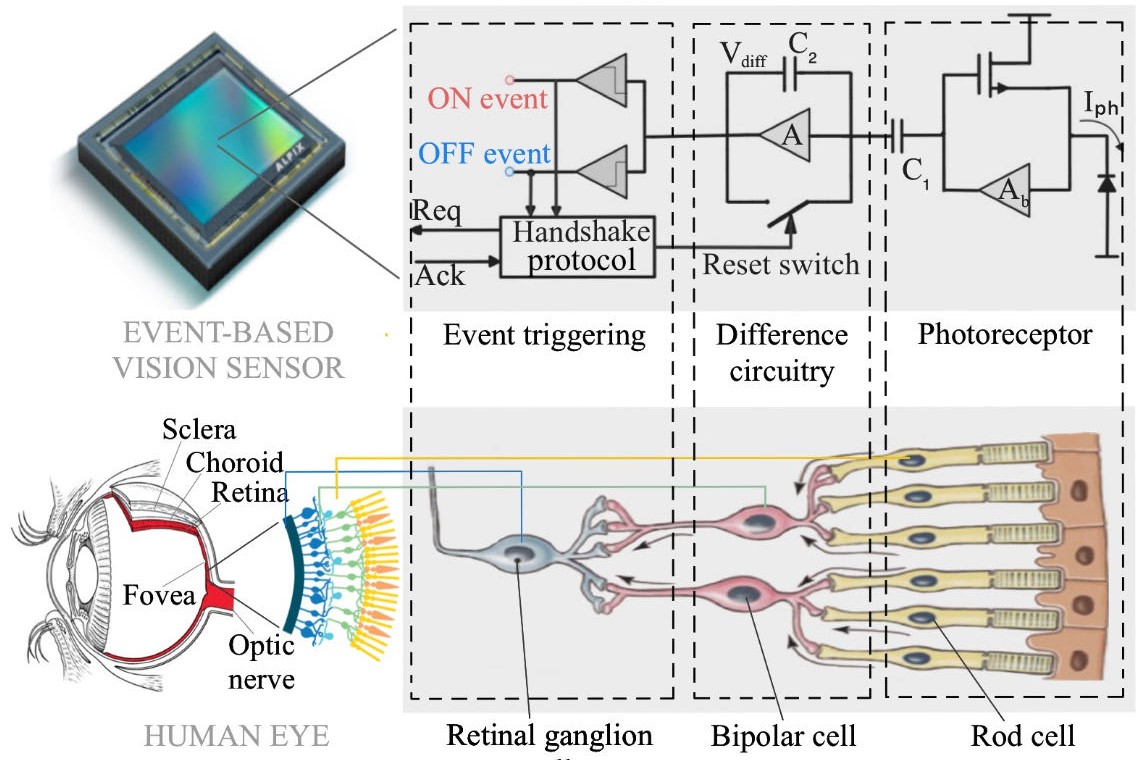
- Event-based cameras, also known as dynamic vision sensors (DVS) or event-based vision sensors (EVS), capture changes in light intensity rather than full image frames.
- Pedestrian detection is a crucial task in intelligent transportation systems (ITS) and autonomous vehicles, and event-based approaches offer advantages over traditional frame-based methods.
Plain English Explanation
Event-based cameras are a type of sensor that work differently from regular cameras. Instead of capturing full images, they only detect changes in light intensity. This allows them to capture information more quickly and efficiently.
Pedestrian detection is an important task for things like self-driving cars and intelligent transportation systems. It's how these systems identify people walking around so they can avoid collisions and operate safely.
Traditional cameras capture full images and then have to process all that data to identify pedestrians. Event-based cameras, on the other hand, only detect changes in the scene. This means they can focus on the moving objects, like people, and ignore the stationary background. This makes pedestrian detection faster and more accurate.
The paper looks at the research, real-world applications, and future potential of using event-based cameras for pedestrian detection. It covers the key advantages of this approach and how it is being used today, as well as areas for further development.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides a comprehensive survey of event-based pedestrian detection, which leverages event-based cameras, also known as dynamic vision sensors (DVS) or event-based vision sensors (EVS). These sensors capture changes in light intensity over time rather than full image frames, offering advantages over traditional frame-based methods for tasks like pedestrian detection in intelligent transportation systems (ITS) and autonomous vehicles.
The authors first present a taxonomy of event-based pedestrian detection approaches, categorizing them based on the sensor type (e.g., DVS, DAVIS), the detection algorithm (e.g., background subtraction, deep learning), and the application domain (e.g., urban traffic monitoring, assistive technology). They then provide a detailed review of the state-of-the-art research in this field, discussing the key techniques, architectures, and insights.
The paper also examines real-world applications of event-based pedestrian detection, highlighting use cases in intelligent transportation, surveillance, and assistive technologies. It explores the advantages of this approach, such as fast processing, low power consumption, and robustness to lighting changes, as well as the remaining challenges and areas for future development.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and up-to-date overview of the research, applications, and prospects of event-based pedestrian detection. The authors thoroughly cover the technical details, including the sensor types, detection algorithms, and system architectures, while also discussing the practical implications and potential use cases.
One potential limitation of the survey is that it may not be fully comprehensive, as the field of event-based vision is rapidly evolving, and new developments could have occurred since the paper's publication. Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the limitations and potential pitfalls of event-based pedestrian detection, such as issues with object occlusion, environmental factors, or the need for specialized hardware.
Overall, the paper provides a valuable and well-researched introduction to the topic, but readers may need to consult additional sources to gain a more complete understanding of the challenges and tradeoffs involved in implementing event-based pedestrian detection systems in real-world scenarios.
Conclusion
This comprehensive survey paper examines the research, applications, and future prospects of event-based pedestrian detection. Event-based cameras, which capture changes in light intensity rather than full image frames, offer several advantages over traditional frame-based approaches for tasks like pedestrian detection in intelligent transportation systems and autonomous vehicles.
The paper provides a detailed taxonomy of event-based pedestrian detection techniques and reviews the state-of-the-art research in this field. It also explores real-world applications of this technology, highlighting its potential benefits in areas such as traffic monitoring, surveillance, and assistive technologies.
While the paper presents a thorough overview of the current state of the art, it acknowledges the need for further research to address remaining challenges and fully realize the potential of event-based pedestrian detection. Overall, this survey serves as a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and practitioners interested in exploring the frontiers of event-based vision and its applications in the realm of intelligent transportation and beyond.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Research, Applications and Prospects of Event-Based Pedestrian Detection: A Survey
Han Wang, Yuman Nie, Yun Li, Hongjie Liu, Min Liu, Wen Cheng, Yaoxiong Wang
Event-based cameras, inspired by the biological retina, have evolved into cutting-edge sensors distinguished by their minimal power requirements, negligible latency, superior temporal resolution, and expansive dynamic range. At present, cameras used for pedestrian detection are mainly frame-based imaging sensors, which have suffered from lethargic response times and hefty data redundancy. In contrast, event-based cameras address these limitations by eschewing extraneous data transmissions and obviating motion blur in high-speed imaging scenarios. On pedestrian detection via event-based cameras, this paper offers an exhaustive review of research and applications particularly in the autonomous driving context. Through methodically scrutinizing relevant literature, the paper outlines the foundational principles, developmental trajectory, and the comparative merits and demerits of eventbased detection relative to traditional frame-based methodologies. This review conducts thorough analyses of various event stream inputs and their corresponding network models to evaluate their applicability across diverse operational environments. It also delves into pivotal elements such as crucial datasets and data acquisition techniques essential for advancing this technology, as well as advanced algorithms for processing event stream data. Culminating with a synthesis of the extant landscape, the review accentuates the unique advantages and persistent challenges inherent in event-based pedestrian detection, offering a prognostic view on potential future developments in this fast-progressing field.
Read more7/8/2024


0
Recent Event Camera Innovations: A Survey
Bharatesh Chakravarthi, Aayush Atul Verma, Kostas Daniilidis, Cornelia Fermuller, Yezhou Yang
Event-based vision, inspired by the human visual system, offers transformative capabilities such as low latency, high dynamic range, and reduced power consumption. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of event cameras, tracing their evolution over time. It introduces the fundamental principles of event cameras, compares them with traditional frame cameras, and highlights their unique characteristics and operational differences. The survey covers various event camera models from leading manufacturers, key technological milestones, and influential research contributions. It explores diverse application areas across different domains and discusses essential real-world and synthetic datasets for research advancement. Additionally, the role of event camera simulators in testing and development is discussed. This survey aims to consolidate the current state of event cameras and inspire further innovation in this rapidly evolving field. To support the research community, a GitHub page (https://github.com/chakravarthi589/Event-based-Vision_Resources) categorizes past and future research articles and consolidates valuable resources.
Read more8/28/2024
🤿

0
Deep Learning for Event-based Vision: A Comprehensive Survey and Benchmarks
Xu Zheng, Yexin Liu, Yunfan Lu, Tongyan Hua, Tianbo Pan, Weiming Zhang, Dacheng Tao, Lin Wang
Event cameras are bio-inspired sensors that capture the per-pixel intensity changes asynchronously and produce event streams encoding the time, pixel position, and polarity (sign) of the intensity changes. Event cameras possess a myriad of advantages over canonical frame-based cameras, such as high temporal resolution, high dynamic range, low latency, etc. Being capable of capturing information in challenging visual conditions, event cameras have the potential to overcome the limitations of frame-based cameras in the computer vision and robotics community. In very recent years, deep learning (DL) has been brought to this emerging field and inspired active research endeavors in mining its potential. However, there is still a lack of taxonomies in DL techniques for event-based vision. We first scrutinize the typical event representations with quality enhancement methods as they play a pivotal role as inputs to the DL models. We then provide a comprehensive survey of existing DL-based methods by structurally grouping them into two major categories: 1) image/video reconstruction and restoration; 2) event-based scene understanding and 3D vision. We conduct benchmark experiments for the existing methods in some representative research directions, i.e., image reconstruction, deblurring, and object recognition, to identify some critical insights and problems. Finally, we have discussions regarding the challenges and provide new perspectives for inspiring more research studies.
Read more4/12/2024


0
Deep Event-based Object Detection in Autonomous Driving: A Survey
Bingquan Zhou, Jie Jiang
Object detection plays a critical role in autonomous driving, where accurately and efficiently detecting objects in fast-moving scenes is crucial. Traditional frame-based cameras face challenges in balancing latency and bandwidth, necessitating the need for innovative solutions. Event cameras have emerged as promising sensors for autonomous driving due to their low latency, high dynamic range, and low power consumption. However, effectively utilizing the asynchronous and sparse event data presents challenges, particularly in maintaining low latency and lightweight architectures for object detection. This paper provides an overview of object detection using event data in autonomous driving, showcasing the competitive benefits of event cameras.
Read more5/8/2024