Resource Management for Low-latency Cooperative Fine-tuning of Foundation Models at the Network Edge

0

Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Resource Management for Low-latency Cooperative Fine-tuning of Foundation Models at the Network Edge
Hai Wu, Xu Chen, Kaibin Huang
The emergence of large-scale foundation models (FoMo's) that can perform human-like intelligence motivates their deployment at the network edge for devices to access state-of-the-art artificial intelligence. For better user experiences, the pre-trained FoMo's need to be adapted to specialized downstream tasks through fine-tuning techniques. To transcend a single device's memory and computation limitations, we advocate multi-device cooperation within the device-edge cooperative fine-tuning (DEFT) paradigm, where edge devices cooperate to simultaneously optimize different parts of fine-tuning parameters within a FoMo. However, the parameter blocks reside at different depths within a FoMo architecture, leading to varied computation latency-and-memory cost due to gradient backpropagation-based calculations. The heterogeneous on-device computation and memory capacities and channel conditions necessitate an integrated communication-and-computation allocation of local computation loads and communication resources to achieve low-latency (LoLa) DEFT. To this end, we consider the depth-ware DEFT block allocation problem. The involved optimal block-device matching is tackled by the proposed low-complexity Cutting-RecoUNting-CHecking (CRUNCH) algorithm, which is designed by exploiting the monotone-increasing property between block depth and computation latency-and-memory cost. Next, the joint bandwidth-and-block allocation makes the problem more sophisticated. We observe a splittable Lagrangian expression through the transformation and analysis of the original problem, where the variables indicating device involvement are introduced. Then, the dual ascent method is employed to tackle this problem iteratively. Through extensive experiments conducted on the GLUE benchmark, our results demonstrate significant latency reduction achievable by LoLa DEFT for fine-tuning a RoBERTa model.
Read more7/16/2024


0
Fine-Tuning and Deploying Large Language Models Over Edges: Issues and Approaches
Yanjie Dong, Xiaoyi Fan, Fangxin Wang, Chengming Li, Victor C. M. Leung, Xiping Hu
Since the invention of GPT2--1.5B in 2019, large language models (LLMs) have transitioned from specialized models to versatile foundation models. The LLMs exhibit impressive zero-shot ability, however, require fine-tuning on local datasets and significant resources for deployment. Traditional fine-tuning techniques with the first-order optimizers require substantial GPU memory that exceeds mainstream hardware capability. Therefore, memory-efficient methods are motivated to be investigated. Model compression techniques can reduce energy consumption, operational costs, and environmental impact so that to support sustainable artificial intelligence advancements. Additionally, large-scale foundation models have expanded to create images, audio, videos, and multi-modal contents, further emphasizing the need for efficient deployment. Therefore, we are motivated to present a comprehensive overview of the prevalent memory-efficient fine-tuning methods over the network edge. We also review the state-of-the-art literatures on model compression to provide a vision on deploying LLMs over the network edge.
Read more8/21/2024

0
Federated Fine-Tuning of LLMs on the Very Edge: The Good, the Bad, the Ugly
Herbert Woisetschlager, Alexander Isenko, Shiqiang Wang, Ruben Mayer, Hans-Arno Jacobsen
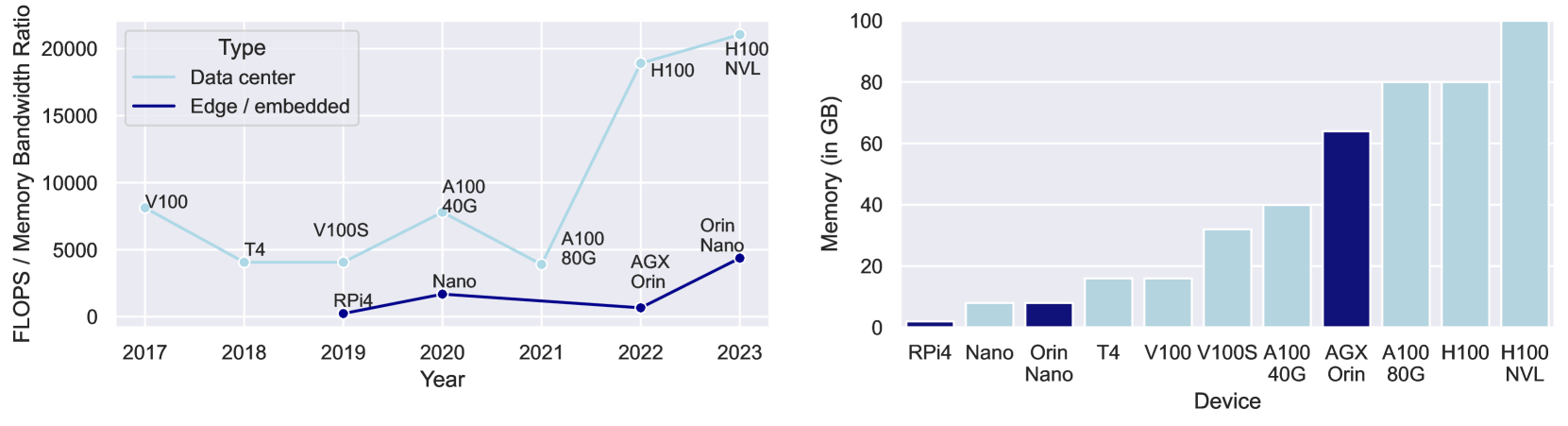
Large Language Models (LLM) and foundation models are popular as they offer new opportunities for individuals and businesses to improve natural language processing, interact with data, and retrieve information faster. However, training or fine-tuning LLMs requires a vast amount of data, which can be challenging to access due to legal or technical restrictions and may require private computing resources. Federated Learning (FL) is a solution designed to overcome these challenges and expand data access for deep learning applications. This paper takes a hardware-centric approach to explore how LLMs can be brought to modern edge computing systems. Our study fine-tunes the FLAN-T5 model family, ranging from 80M to 3B parameters, using FL for a text summarization task. We provide a micro-level hardware benchmark, compare the model FLOP utilization to a state-of-the-art data center GPU, and study the network utilization in realistic conditions. Our contribution is twofold: First, we evaluate the current capabilities of edge computing systems and their potential for LLM FL workloads. Second, by comparing these systems with a data-center GPU, we demonstrate the potential for improvement and the next steps toward achieving greater computational efficiency at the edge.
Read more5/3/2024

0
DLoRA: Distributed Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Solution for Large Language Model
Chao Gao, Sai Qian Zhang
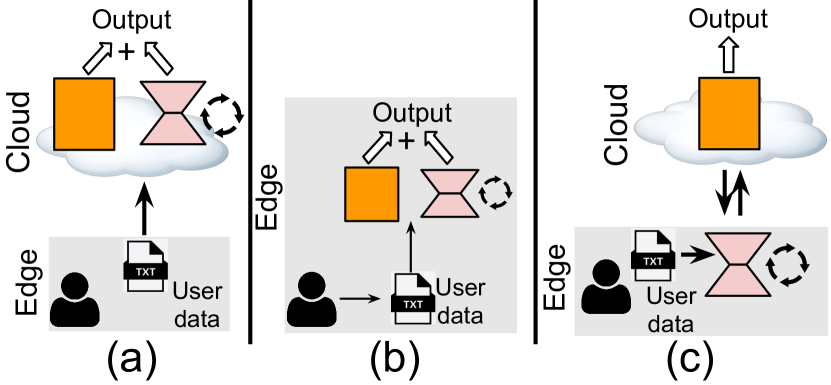
To enhance the performance of large language models (LLM) on downstream tasks, one solution is to fine-tune certain LLM parameters and make it better align with the characteristics of the training dataset. This process is commonly known as parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). Due to the scale of LLM, PEFT operations are usually executed in the public environment (e.g., cloud server). This necessitates the sharing of sensitive user data across public environments, thereby raising potential privacy concerns. To tackle these challenges, we propose a distributed PEFT framework called DLoRA. DLoRA enables scalable PEFT operations to be performed collaboratively between the cloud and user devices. Coupled with the proposed Kill and Revive algorithm, the evaluation results demonstrate that DLoRA can significantly reduce the computation and communication workload over the user devices while achieving superior accuracy and privacy protection.
Read more4/9/2024