RET-CLIP: A Retinal Image Foundation Model Pre-trained with Clinical Diagnostic Reports

0
🖼️
Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🖼️

0
RET-CLIP: A Retinal Image Foundation Model Pre-trained with Clinical Diagnostic Reports
Jiawei Du, Jia Guo, Weihang Zhang, Shengzhu Yang, Hanruo Liu, Huiqi Li, Ningli Wang
The Vision-Language Foundation model is increasingly investigated in the fields of computer vision and natural language processing, yet its exploration in ophthalmology and broader medical applications remains limited. The challenge is the lack of labeled data for the training of foundation model. To handle this issue, a CLIP-style retinal image foundation model is developed in this paper. Our foundation model, RET-CLIP, is specifically trained on a dataset of 193,865 patients to extract general features of color fundus photographs (CFPs), employing a tripartite optimization strategy to focus on left eye, right eye, and patient level to reflect real-world clinical scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RET-CLIP outperforms existing benchmarks across eight diverse datasets spanning four critical diagnostic categories: diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, multiple disease diagnosis, and multi-label classification of multiple diseases, which demonstrate the performance and generality of our foundation model. The sourse code and pre-trained model are available at https://github.com/sStonemason/RET-CLIP.
Read more8/20/2024
📈

0
EyeCLIP: A visual-language foundation model for multi-modal ophthalmic image analysis
Danli Shi, Weiyi Zhang, Jiancheng Yang, Siyu Huang, Xiaolan Chen, Mayinuer Yusufu, Kai Jin, Shan Lin, Shunming Liu, Qing Zhang, Mingguang He
Early detection of eye diseases like glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy is crucial for preventing vision loss. While artificial intelligence (AI) foundation models hold significant promise for addressing these challenges, existing ophthalmic foundation models primarily focus on a single modality, whereas diagnosing eye diseases requires multiple modalities. A critical yet often overlooked aspect is harnessing the multi-view information across various modalities for the same patient. Additionally, due to the long-tail nature of ophthalmic diseases, standard fully supervised or unsupervised learning approaches often struggle. Therefore, it is essential to integrate clinical text to capture a broader spectrum of diseases. We propose EyeCLIP, a visual-language foundation model developed using over 2.77 million multi-modal ophthalmology images with partial text data. To fully leverage the large multi-modal unlabeled and labeled data, we introduced a pretraining strategy that combines self-supervised reconstructions, multi-modal image contrastive learning, and image-text contrastive learning to learn a shared representation of multiple modalities. Through evaluation using 14 benchmark datasets, EyeCLIP can be transferred to a wide range of downstream tasks involving ocular and systemic diseases, achieving state-of-the-art performance in disease classification, visual question answering, and cross-modal retrieval. EyeCLIP represents a significant advancement over previous methods, especially showcasing few-shot, even zero-shot capabilities in real-world long-tail scenarios.
Read more9/12/2024

0
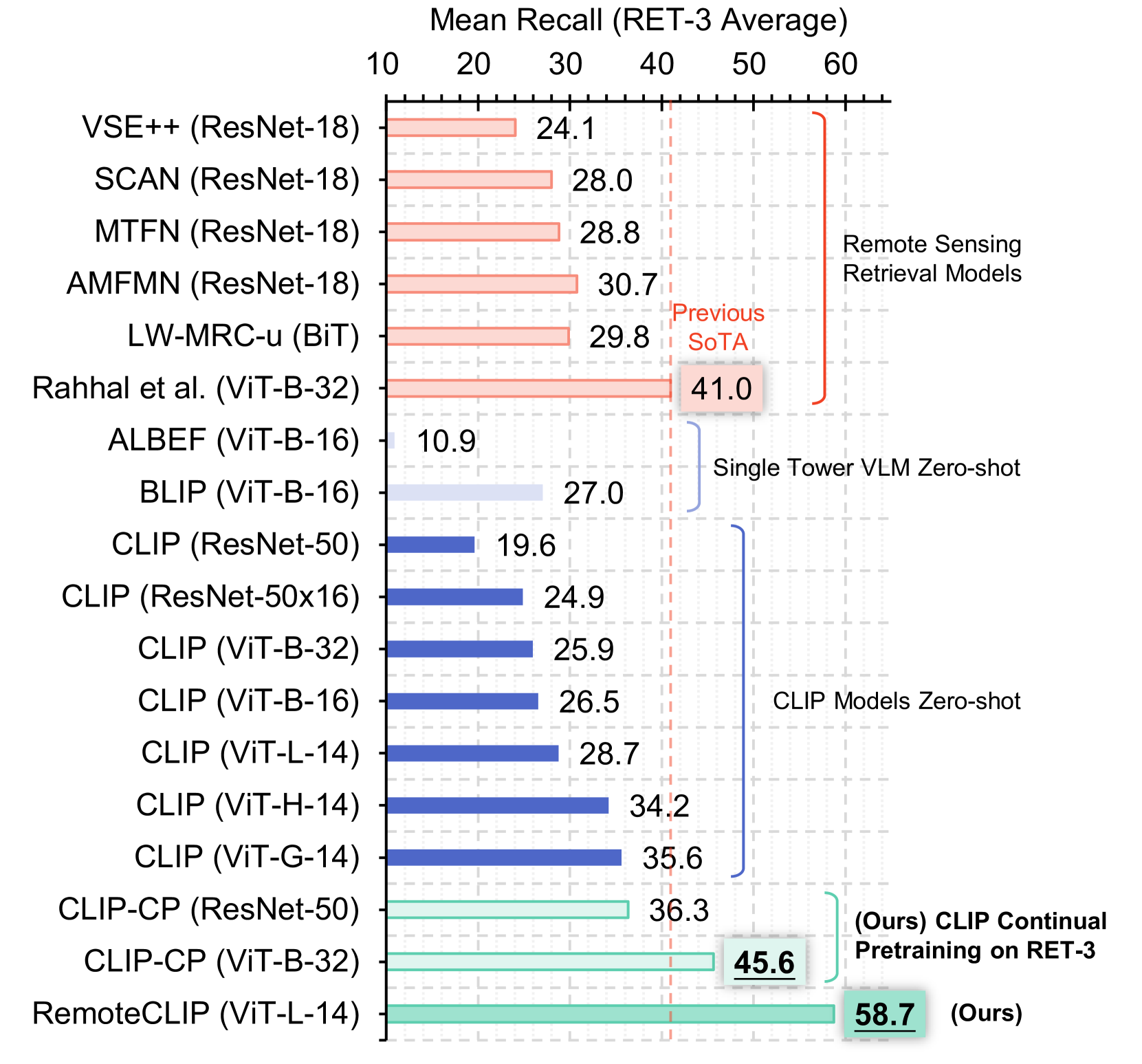
RemoteCLIP: A Vision Language Foundation Model for Remote Sensing
Fan Liu, Delong Chen, Zhangqingyun Guan, Xiaocong Zhou, Jiale Zhu, Qiaolin Ye, Liyong Fu, Jun Zhou
General-purpose foundation models have led to recent breakthroughs in artificial intelligence. In remote sensing, self-supervised learning (SSL) and Masked Image Modeling (MIM) have been adopted to build foundation models. However, these models primarily learn low-level features and require annotated data for fine-tuning. Moreover, they are inapplicable for retrieval and zero-shot applications due to the lack of language understanding. To address these limitations, we propose RemoteCLIP, the first vision-language foundation model for remote sensing that aims to learn robust visual features with rich semantics and aligned text embeddings for seamless downstream application. To address the scarcity of pre-training data, we leverage data scaling which converts heterogeneous annotations into a unified image-caption data format based on Box-to-Caption (B2C) and Mask-to-Box (M2B) conversion. By further incorporating UAV imagery, we produce a 12 $times$ larger pretraining dataset than the combination of all available datasets. RemoteCLIP can be applied to a variety of downstream tasks, including zero-shot image classification, linear probing, $textit{k}$-NN classification, few-shot classification, image-text retrieval, and object counting in remote sensing images. Evaluation on 16 datasets, including a newly introduced RemoteCount benchmark to test the object counting ability, shows that RemoteCLIP consistently outperforms baseline foundation models across different model scales. Impressively, RemoteCLIP beats the state-of-the-art method by 9.14% mean recall on the RSITMD dataset and 8.92% on the RSICD dataset. For zero-shot classification, our RemoteCLIP outperforms the CLIP baseline by up to 6.39% average accuracy on 12 downstream datasets. Project website: https://github.com/ChenDelong1999/RemoteCLIP
Read more4/17/2024
🏋️

0
Training a high-performance retinal foundation model with half-the-data and 400 times less compute
Justin Engelmann, Miguel O. Bernabeu
Artificial Intelligence holds tremendous potential in medicine, but is traditionally limited by the lack of massive datasets to train models on. Foundation models, pre-trained models that can be adapted to downstream tasks with small datasets, could alleviate this problem. Researchers at Moorfields Eye Hospital (MEH) proposed RETFound-MEH, a foundation model for retinal imaging that was trained on 900,000 images, including private hospital data. Recently, data-efficient DERETFound was proposed that provides comparable performance while being trained on only 150,000 images that are all publicly available. However, both these models required very substantial resources to train initially and are resource-intensive in downstream use. We propose a novel Token Reconstruction objective that we use to train RETFound-Green, a retinal foundation model trained using only 75,000 publicly available images and 400 times less compute. We estimate the cost of training RETFound-MEH and DERETFound at $10,000 and $14,000, respectively, while RETFound-Green could be trained for less than $100, with equally reduced environmental impact. RETFound-Green is also far more efficient in downstream use: it can be downloaded 14 times faster, computes vector embeddings 2.7 times faster which then require 2.6 times less storage space. Despite this, RETFound-Green does not perform systematically worse. In fact, it performs best on 14 tasks, compared to six for DERETFound and two for RETFound-MEH. Our results suggest that RETFound-Green is a very efficient, high-performance retinal foundation model. We anticipate that our Token Reconstruction objective could be scaled up for even higher performance and be applied to other domains beyond retinal imaging.
Read more5/2/2024