Signaling Rate and Performance of RIS Reconfiguration and Handover Management in Next Generation Mobile Networks

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explains signaling rate and performance of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) reconfiguration and handover management in next-generation mobile networks
- Analyzes how RIS reconfiguration and handover affect network performance and signaling overhead
- Provides insights to help optimize RIS deployment and management for 5G and beyond networks
Plain English Explanation
The paper examines how the reconfiguration and handover processes in reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) can impact the performance and signaling overhead in next-generation mobile networks like 5G and beyond. RIS is an emerging technology that can dynamically control the wireless environment to improve network coverage and capacity.
The researchers analyze the tradeoffs between the frequency of RIS reconfigurations, which can enhance the wireless channel, and the associated signaling overhead required to coordinate these changes. They also look at how handover procedures - when a mobile device switches between network access points - interact with RIS reconfiguration.
The findings provide guidance on optimizing RIS deployment and management to balance performance gains and signaling costs. This can help network operators better harness RIS technology to deliver reliable, high-speed connectivity in 5G and future mobile networks.
Technical Explanation
The paper Signaling Rate and Performance of RIS Reconfiguration and Handover Management in Next Generation Mobile Networks investigates the interplay between reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) reconfiguration and handover management in 5G and beyond mobile networks.
The authors develop an analytical framework to model the signaling overhead and network performance impact of RIS reconfiguration and handover procedures. Key aspects include:
- RIS Reconfiguration: The researchers analyze how frequently RIS elements should be reconfigured to optimize the wireless channel, while considering the associated signaling overhead.
- Handover Management: The paper examines how RIS reconfiguration interacts with user equipment (UE) handover between network access points, and the resulting performance tradeoffs.
- Performance Metrics: Metrics evaluated include achievable data rate, signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR), and handover success probability.
Through analysis and simulations, the authors provide insights on:
- The optimal RIS reconfiguration rate to balance performance gains and signaling costs
- The impact of RIS reconfiguration on handover success probability and UE experience
- Guidelines for RIS deployment and management in future mobile networks
These findings can help network operators effectively incorporate RIS technology to enhance coverage, capacity, and reliability in 5G and beyond.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a detailed analytical and simulation-based study of the tradeoffs involved in RIS reconfiguration and handover management in next-generation mobile networks. The authors have identified and modeled key factors influencing performance, signaling overhead, and user experience.
One limitation is the use of simplified channel and mobility models, which may not fully capture the complexity of real-world propagation and user dynamics. Additionally, the analysis focuses on a single-cell scenario, whereas practical deployments would involve multi-cell coordination.
Further research could investigate more sophisticated RIS control algorithms, consider heterogeneous RIS deployments, and explore the implications of imperfect RIS state information. Integrating these aspects could provide a more comprehensive understanding of RIS-enabled network optimization.
Overall, the paper offers valuable insights to guide the development of efficient RIS management strategies for 5G and beyond. The findings can inform both network planning and dynamic RIS control to unlock the full potential of this emerging technology.
Conclusion
This paper provides a detailed analysis of the signaling rate and performance implications of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) management in next-generation mobile networks. The researchers have developed an analytical framework to study the tradeoffs between RIS reconfiguration, handover procedures, and network metrics such as data rate, SINR, and handover success probability.
The key takeaways include guidelines for optimizing the RIS reconfiguration rate to balance performance gains and signaling overhead, as well as insights on how RIS can be effectively integrated with handover management to enhance user experience. These insights can help network operators and researchers unlock the full potential of RIS technology in 5G and beyond, paving the way for reliable, high-performance wireless communication systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Signaling Rate and Performance of RIS Reconfiguration and Handover Management in Next Generation Mobile Networks
Mounir Bensalem, Admela Jukan
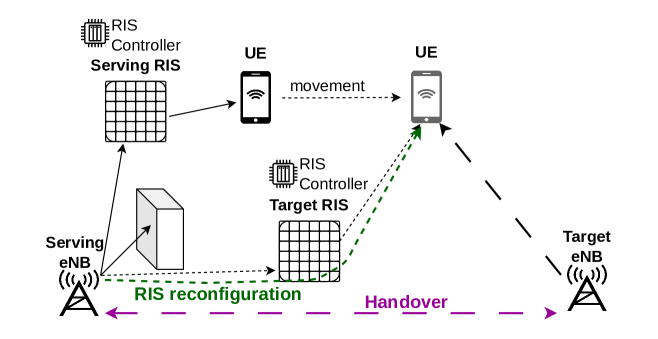
We consider the problem of signaling rate and performance for an efficient control and management of RIS reconfigurations and handover in next generation mobile networks. To this end, we first analytically determine the rates of RIS reconfigurations and handover using a stochastic geometry network model. We derive closed-form expressions of these rates while taking into account static obstacles (both known and unknown), self-blockage, RIS location density, and variations in the angle and direction of user mobility. Based on the rates derived, we analyze the signaling rates of a sample novel signaling protocol, which we propose as an extension of an handover signaling protocol standard in mobile networks. The results quantify the impact of known and unknown obstacles on the RIS and handover reconfiguration rate as function of device density and mobility. We use the proposed analysis to evaluate the signaling overhead due to RIS reconfigurations, as well as to dimension the related RIS control plane server capacity in the network management system. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first analytical model to derive the closed form expressions of RIS reconfiguration rates, along with handover rates, and relate its statistical properties to the signaling rate and performance in next generation mobile networks.
Read more7/26/2024
🎲

0
Outage Probability Analysis of Wireless Paths with Faulty Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Mounir Bensalem, Admela Jukan
We consider a next generation wireless network incorporating a base station a set of typically low-cost and faulty Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs). The base station needs to select the path including the RIS to provide the maximum signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) to the user. We study the effect of the number of elements, distance and RIS hardware failure on the path outage probability, and based on the known signal propagation model at high frequencies, derive the closed-form expression for the said probability of outage. Numerical results show the path outage likelihood as function of the probability of hardware failure of RIS elements, the number of elements, and the distance between mobile users and the RIS.
Read more4/24/2024
📶

0
RIS in Cellular Networks -- Challenges and Issues
Magnus {AA}strom, Philipp Gentner, Omer Haliloglu, Behrooz Makki, Ola Tageman
Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) has been suggested to be a key 6G feature and was suggested to be considered as a study-item in both 3GPP Releases 18 and 19. However, in both releases, it has been decided not to continue with it as a study-item, and to leave it for possible future specification. In this paper, we present the rationale for such a decision. Particularly, we demonstrate the practical issues which may affect the feasibility or usefulness of RIS in cellular networks, and present open problems to be addressed before RIS can be used in practice. Moreover, we compare the performance of RIS with network-controlled repeater, the node with the most similar characteristics to RIS and which has been standardized in 3GPP Release 18. Finally, different simulations are presented to evaluate the performance of RIS-assisted networks.
Read more4/9/2024
✅

0
Multi-hop Multi-RIS Wireless Communication Systems: Multi-reflection Path Scheduling and Beamforming
Xiaoyan Ma, Haixia Zhang, Xianhao Chen, Yuguang Fangmand Dongfeng Yuan
Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) provides a promising way to proactively augment propagation environments for better transmission performance in wireless communications. Existing multi-RIS works mainly focus on link-level optimization with predetermined transmission paths, which cannot be directly extended to system-level management, since they neither consider the interference caused by undesired scattering of RISs, nor the performance balancing between different transmission paths. To address this, we study an innovative multi-hop multi-RIS communication system, where a base station (BS) transmits information to a set of distributed users over multi-RIS configuration space in a multi-hop manner. The signals for each user are subsequently reflected by the selected RISs via multi-reflection line-of-sight (LoS) links. To ensure that all users have fair access to the system to avoid excessive number of RISs serving one user, we aim to find the optimal beam reflecting path for each user, while judiciously determining the path scheduling strategies with the corresponding beamforming design to ensure the fairness. Due to the presence of interference caused by undesired scattering of RISs, it is highly challenging to solve the formulated multi-RIS multi-path beamforming optimization problem. To solve it, we first derive the optimal RISs' phase shifts and the corresponding reflecting path selection for each user based on its practical deployment location. With the optimized multi-reflection paths, we obtain a feasible user grouping pattern for effective interference mitigation by constructing the maximum independent sets (MISs). Finally, we propose a joint heuristic algorithm to iteratively update the beamforming vectors and the group scheduling policies to maximize the minimum equivalent data rate of all users.
Read more5/22/2024