Smart Camera Parking System With Auto Parking Spot Detection

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a smart camera parking system with automated parking spot detection.
- The system uses computer vision and deep learning techniques to identify available parking spaces and guide drivers to them.
- The goal is to improve parking efficiency and convenience in crowded urban environments.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers have developed a smart camera system to help drivers find available parking spots more easily. Using advanced computer vision and machine learning algorithms, the system can automatically detect open parking spaces in a lot or garage. It does this by analyzing video feeds from strategically placed cameras.
When a driver needs to park, they can access the system through a mobile app or digital display. The system will guide them to the nearest available spot, saving time and frustration compared to driving around aimlessly. This could be especially helpful in crowded city centers where parking is limited.
The key innovation is the ability to automatically detect free spaces without human intervention. Traditional parking guidance systems often rely on sensors installed in each spot, which can be costly and difficult to maintain. This camera-based approach is more scalable and flexible.
Technical Explanation
The core of the system is a deep learning model that classifies each parking spot as occupied or vacant. This model is trained on a large dataset of annotated parking lot images.
At runtime, the system takes in video feeds from surveillance cameras mounted around the parking facility. It processes these frames using the deep learning model to identify open spaces. The locations of available spots are then communicated to drivers through a mobile app or digital signage.
To further enhance the system, the researchers integrate it with a visual-inertial odometry module. This allows the system to track the movement of vehicles and update the occupancy status of spots in real-time. It also enables the system to provide turn-by-turn navigation guidance to direct drivers to their assigned space.
The overall architecture is designed to be scalable and flexible, allowing it to be deployed in parking lots of various sizes. The researchers evaluate the system's performance on several real-world datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in accurately detecting available spaces.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the smart camera parking system and the technical details of its implementation. The authors have clearly put a lot of effort into developing a robust and practical solution to the problem of parking space allocation.
However, the evaluation of the system is limited to controlled datasets, and it would be valuable to see how it performs in truly complex, real-world parking environments. Additionally, the paper does not address potential privacy concerns that may arise from the extensive use of surveillance cameras and vehicle tracking.
Further research could also explore integrating the system with other smart city initiatives, such as multi-sensor SLAM for comprehensive urban monitoring and planning.
Conclusion
This smart camera parking system represents a significant advancement in the field of automated parking management. By leveraging computer vision and deep learning, the researchers have developed a scalable and flexible solution that can improve parking efficiency and convenience for both drivers and urban planners.
The potential implications of this technology are far-reaching, as it could contribute to the broader vision of smart cities that seamlessly integrate various systems to optimize resource usage and enhance the quality of life for citizens.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Smart Camera Parking System With Auto Parking Spot Detection
Tuan T. Nguyen, Mina Sartipi
Given the rising urban population and the consequential rise in traffic congestion, the implementation of smart parking systems has emerged as a critical matter of concern. Smart parking solutions use cameras, sensors, and algorithms like computer vision to find available parking spaces. This method improves parking place recognition, reduces traffic and pollution, and optimizes travel time. In recent years, computer vision-based approaches have been widely used. However, most existing studies rely on manually labeled parking spots, which has implications for the cost and practicality of implementation. To solve this problem, we propose a novel approach PakLoc, which automatically localize parking spots. Furthermore, we present the PakSke module, which automatically adjust the rotation and the size of detected bounding box. The efficacy of our proposed methodology on the PKLot dataset results in a significant reduction in human labor of 94.25%. Another fundamental aspect of a smart parking system is its capacity to accurately determine and indicate the state of parking spots within a parking lot. The conventional approach involves employing classification techniques to forecast the condition of parking spots based on the bounding boxes derived from manually labeled grids. In this study, we provide a novel approach called PakSta for identifying the state of parking spots automatically. Our method utilizes object detector from PakLoc to simultaneously determine the occupancy status of all parking lots within a video frame. Our proposed method PakSta exhibits a competitive performance on the PKLot dataset when compared to other classification methods.
Read more7/9/2024

0
VIPS-Odom: Visual-Inertial Odometry Tightly-coupled with Parking Slots for Autonomous Parking
Xuefeng Jiang, Fangyuan Wang, Rongzhang Zheng, Han Liu, Yixiong Huo, Jinzhang Peng, Lu Tian, Emad Barsoum
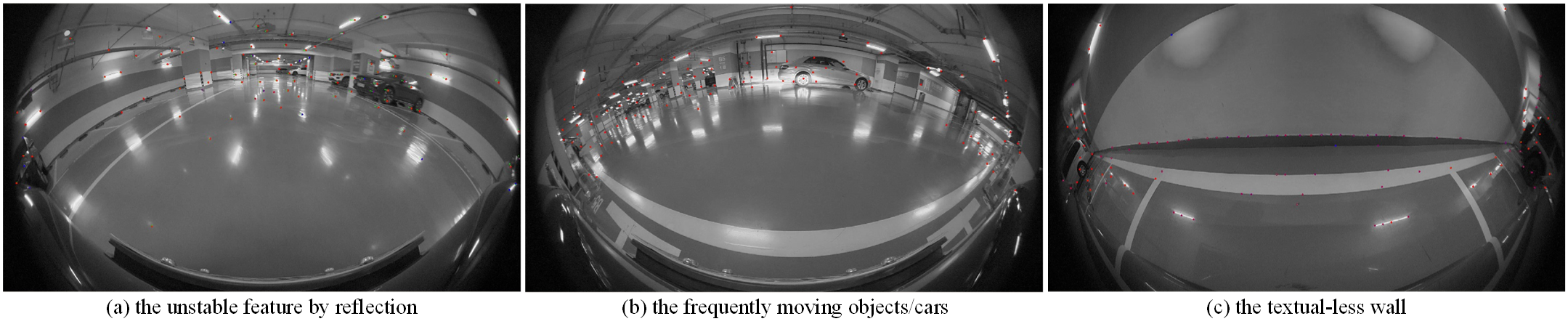
Precise localization is of great importance for autonomous parking task since it provides service for the downstream planning and control modules, which significantly affects the system performance. For parking scenarios, dynamic lighting, sparse textures, and the instability of global positioning system (GPS) signals pose challenges for most traditional localization methods. To address these difficulties, we propose VIPS-Odom, a novel semantic visual-inertial odometry framework for underground autonomous parking, which adopts tightly-coupled optimization to fuse measurements from multi-modal sensors and solves odometry. Our VIPS-Odom integrates parking slots detected from the synthesized bird-eye-view (BEV) image with traditional feature points in the frontend, and conducts tightly-coupled optimization with joint constraints introduced by measurements from the inertial measurement unit, wheel speed sensor and parking slots in the backend. We develop a multi-object tracking framework to robustly track parking slots' states. To prove the superiority of our method, we equip an electronic vehicle with related sensors and build an experimental platform based on ROS2 system. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy and advantages of our method compared with other baselines for parking scenarios.
Read more7/9/2024


0
Enhanced Parking Perception by Multi-Task Fisheye Cross-view Transformers
Antonyo Musabini, Ivan Novikov, Sana Soula, Christel Leonet, Lihao Wang, Rachid Benmokhtar, Fabian Burger, Thomas Boulay, Xavier Perrotton
Current parking area perception algorithms primarily focus on detecting vacant slots within a limited range, relying on error-prone homographic projection for both labeling and inference. However, recent advancements in Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) require interaction with end-users through comprehensive and intelligent Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs). These interfaces should present a complete perception of the parking area going from distinguishing vacant slots' entry lines to the orientation of other parked vehicles. This paper introduces Multi-Task Fisheye Cross View Transformers (MT F-CVT), which leverages features from a four-camera fisheye Surround-view Camera System (SVCS) with multihead attentions to create a detailed Bird-Eye View (BEV) grid feature map. Features are processed by both a segmentation decoder and a Polygon-Yolo based object detection decoder for parking slots and vehicles. Trained on data labeled using LiDAR, MT F-CVT positions objects within a 25m x 25m real open-road scenes with an average error of only 20 cm. Our larger model achieves an F-1 score of 0.89. Moreover the smaller model operates at 16 fps on an Nvidia Jetson Orin embedded board, with similar detection results to the larger one. MT F-CVT demonstrates robust generalization capability across different vehicles and camera rig configurations. A demo video from an unseen vehicle and camera rig is available at: https://streamable.com/jjw54x.
Read more8/23/2024
🏷️

0
BCFPL: Binary classification ConvNet based Fast Parking space recognition with Low resolution image
Shuo Zhang, Xin Chen, Zixuan Wang
The automobile plays an important role in the economic activities of mankind, especially in the metropolis. Under the circumstances, the demand of quick search for available parking spaces has become a major concern for the automobile drivers. Meanwhile, the public sense of privacy is also awaking, the image-based parking space recognition methods lack the attention of privacy protection. In this paper, we proposed a binary convolutional neural network with lightweight design structure named BCFPL, which can be used to train with low-resolution parking space images and offer a reasonable recognition result. The images of parking space were collected from various complex environments, including different weather, occlusion conditions, and various camera angles. We conducted the training and testing progresses among different datasets and partial subsets. The experimental results show that the accuracy of BCFPL does not decrease compared with the original resolution image directly, and can reach the average level of the existing mainstream method. BCFPL also has low hardware requirements and fast recognition speed while meeting the privacy requirements, so it has application potential in intelligent city construction and automatic driving field.
Read more4/23/2024