Solid Waste Detection, Monitoring and Mapping in Remote Sensing Images: A Survey

0
✨
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Detecting and characterizing illegal solid waste disposal sites is critical for environmental protection
- Improper landfill management can contaminate soil and groundwater, harming animals and humans
- Traditional inspection methods are time-consuming and expensive
- Remote sensing using Earth Observation (EO) satellites can cost-effectively identify and monitor solid waste sites over broad areas and long time periods
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses how detecting and analyzing illegal dumping sites is important for protecting the environment, particularly by mitigating pollution and health risks. Improperly managed landfills can contaminate the soil and groundwater, which can harm both animals and people. Traditional methods of finding these sites, like sending inspectors to check locations, take a lot of time and money.
In contrast, the researchers explain that using satellites to remotely sense the Earth's surface is a more cost-effective way to identify and monitor solid waste disposal sites over large areas and long time periods. Satellites equipped with various sensors can provide high-resolution data that researchers can analyze to detect illegal dumping, track changes at existing landfills, and find good locations for new waste management facilities.
Technical Explanation
The paper reviews specialized techniques that leverage remote sensing imagery from Earth Observation (EO) satellites to perform a range of tasks related to solid waste sites, including detection, monitoring, and site suitability assessment. The authors describe and compare the different approaches, techniques, and data sources used in this research.
Since the data sources are crucial for developing effective solid waste detection models, the paper also provides a comprehensive overview of the available satellite platforms and publicly accessible data sets.
Finally, the paper identifies open issues in the current state-of-the-art and discusses relevant research directions for reducing costs and improving the effectiveness of novel solid waste detection methods.
Critical Analysis
The paper acknowledges some limitations of the existing remote sensing approaches, such as the need to further improve the accuracy and automation of waste site detection. It also highlights the importance of developing techniques that can provide more detailed information about the characteristics and contents of the detected sites.
One potential concern not addressed in the paper is the availability and quality of ground truth data for training and validating the remote sensing-based models. Obtaining reliable information about the location and nature of illegal dumping sites can be challenging, which could affect the performance of the detection algorithms.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into the potential privacy and ethical considerations around using satellite imagery and other remote sensing data for monitoring waste management activities. As these technologies become more advanced, it will be important to carefully consider any unintended consequences or misuse of the collected data.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the state-of-the-art in using remote sensing techniques, particularly satellite imagery, for the detection and monitoring of solid waste disposal sites. The researchers highlight the advantages of this approach over traditional inspection methods, such as broader coverage and lower costs.
The insights from this work could help inform the development of more effective and efficient waste management strategies, contributing to environmental protection and public health. However, future research should also address the remaining challenges and potential ethical considerations to ensure these technologies are deployed responsibly and for the benefit of society.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
✨

0
Solid Waste Detection, Monitoring and Mapping in Remote Sensing Images: A Survey
Piero Fraternali, Luca Morandini, Sergio Luis Herrera Gonz'alez
The detection and characterization of illegal solid waste disposal sites are essential for environmental protection, particularly for mitigating pollution and health hazards. Improperly managed landfills contaminate soil and groundwater via rainwater infiltration, posing threats to both animals and humans. Traditional landfill identification approaches, such as on-site inspections, are time-consuming and expensive. Remote sensing is a cost-effective solution for the identification and monitoring of solid waste disposal sites that enables broad coverage and repeated acquisitions over time. Earth Observation (EO) satellites, equipped with an array of sensors and imaging capabilities, have been providing high-resolution data for several decades. Researchers proposed specialized techniques that leverage remote sensing imagery to perform a range of tasks such as waste site detection, dumping site monitoring, and assessment of suitable locations for new landfills. This review aims to provide a detailed illustration of the most relevant proposals for the detection and monitoring of solid waste sites by describing and comparing the approaches, the implemented techniques, and the employed data. Furthermore, since the data sources are of the utmost importance for developing an effective solid waste detection model, a comprehensive overview of the satellites and publicly available data sets is presented. Finally, this paper identifies the open issues in the state-of-the-art and discusses the relevant research directions for reducing the costs and improving the effectiveness of novel solid waste detection methods.
Read more8/29/2024


0
Super-Resolution Analysis for Landfill Waste Classification
Matias Molina, Rita P. Ribeiro, Bruno Veloso, Jo~ao Gama
Illegal landfills are a critical issue due to their environmental, economic, and public health impacts. This study leverages aerial imagery for environmental crime monitoring. While advances in artificial intelligence and computer vision hold promise, the challenge lies in training models with high-resolution literature datasets and adapting them to open-access low-resolution images. Considering the substantial quality differences and limited annotation, this research explores the adaptability of models across these domains. Motivated by the necessity for a comprehensive evaluation of waste detection algorithms, it advocates cross-domain classification and super-resolution enhancement to analyze the impact of different image resolutions on waste classification as an evaluation to combat the proliferation of illegal landfills. We observed performance improvements by enhancing image quality but noted an influence on model sensitivity, necessitating careful threshold fine-tuning.
Read more4/3/2024
📉

0
Enhancing Environmental Monitoring through Multispectral Imaging: The WasteMS Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Lakeside Waste
Qinfeng Zhu, Ningxin Weng, Lei Fan, Yuanzhi Cai
Environmental monitoring of lakeside green areas is crucial for environmental protection. Compared to manual inspections, computer vision technologies offer a more efficient solution when deployed on-site. Multispectral imaging provides diverse information about objects under different spectrums, aiding in the differentiation between waste and lakeside lawn environments. This study introduces WasteMS, the first multispectral dataset established for the semantic segmentation of lakeside waste. WasteMS includes a diverse range of waste types in lawn environments, captured under various lighting conditions. We implemented a rigorous annotation process to label waste in images. Representative semantic segmentation frameworks were used to evaluate segmentation accuracy using WasteMS. Challenges encountered when using WasteMS for segmenting waste on lakeside lawns were discussed. The WasteMS dataset is available at https://github.com/zhuqinfeng1999/WasteMS.
Read more7/26/2024

0
Deep Learning Innovations for Underwater Waste Detection: An In-Depth Analysis
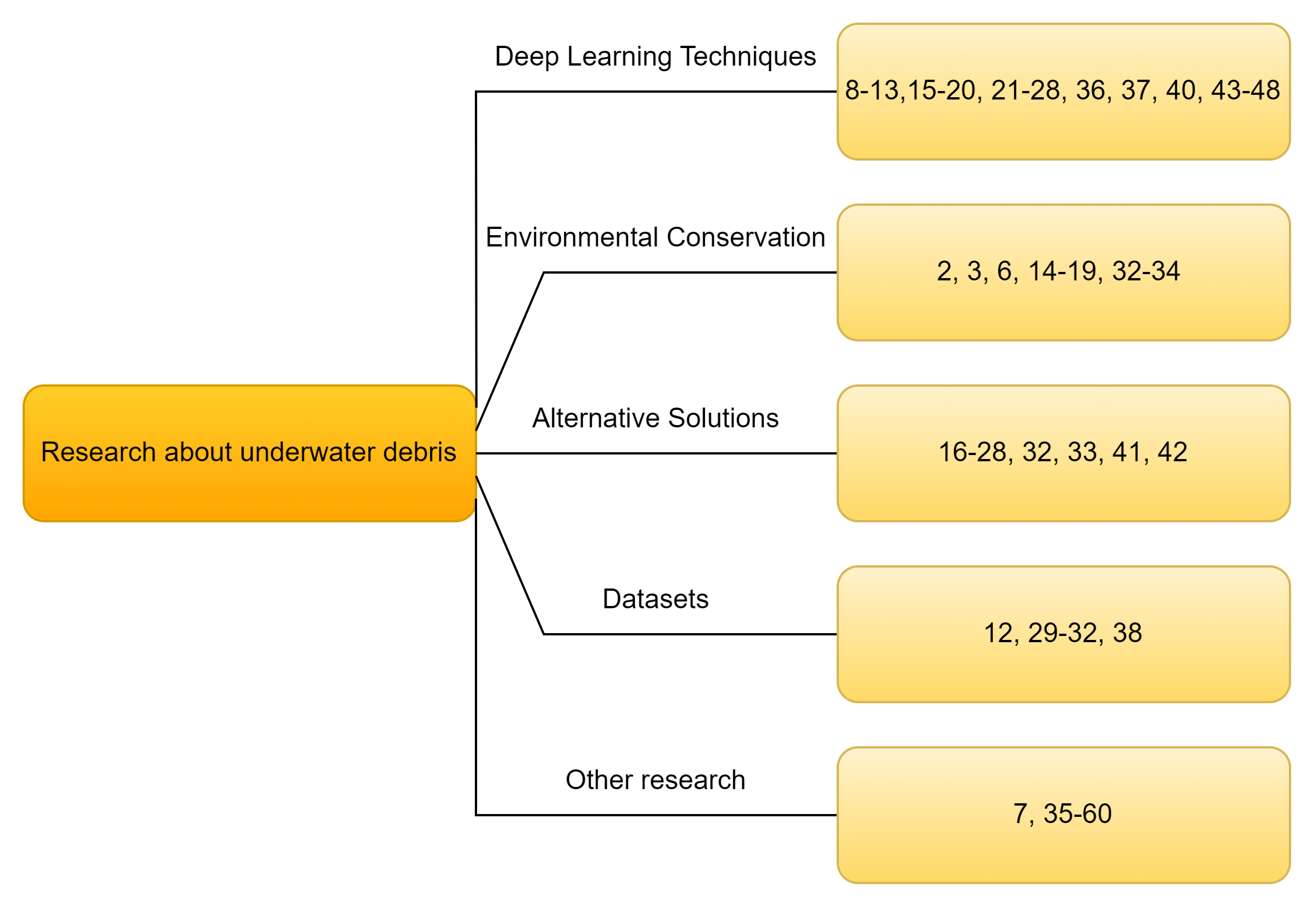
Jaskaran Singh Walia, Pavithra L K
Addressing the issue of submerged underwater trash is crucial for safeguarding aquatic ecosystems and preserving marine life. While identifying debris present on the surface of water bodies is straightforward, assessing the underwater submerged waste is a challenge due to the image distortions caused by factors such as light refraction, absorption, suspended particles, color shifts, and occlusion. This paper conducts a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art architectures and on the existing datasets to establish a baseline for submerged waste and trash detection. The primary goal remains to establish the benchmark of the object localization techniques to be leveraged by advanced underwater sensors and autonomous underwater vehicles. The ultimate objective is to explore the underwater environment, to identify, and remove underwater debris. The absence of benchmarks (dataset or algorithm) in many researches emphasizes the need for a more robust algorithmic solution. Through this research, we aim to give performance comparative analysis of various underwater trash detection algorithms.
Read more8/16/2024