On the stability of Lipschitz continuous control problems and its application to reinforcement learning
2404.13316

0
0

Abstract
We address the crucial yet underexplored stability properties of the Hamilton--Jacobi--Bellman (HJB) equation in model-free reinforcement learning contexts, specifically for Lipschitz continuous optimal control problems. We bridge the gap between Lipschitz continuous optimal control problems and classical optimal control problems in the viscosity solutions framework, offering new insights into the stability of the value function of Lipschitz continuous optimal control problems. By introducing structural assumptions on the dynamics and reward functions, we further study the rate of convergence of value functions. Moreover, we introduce a generalized framework for Lipschitz continuous control problems that incorporates the original problem and leverage it to propose a new HJB-based reinforcement learning algorithm. The stability properties and performance of the proposed method are tested with well-known benchmark examples in comparison with existing approaches.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
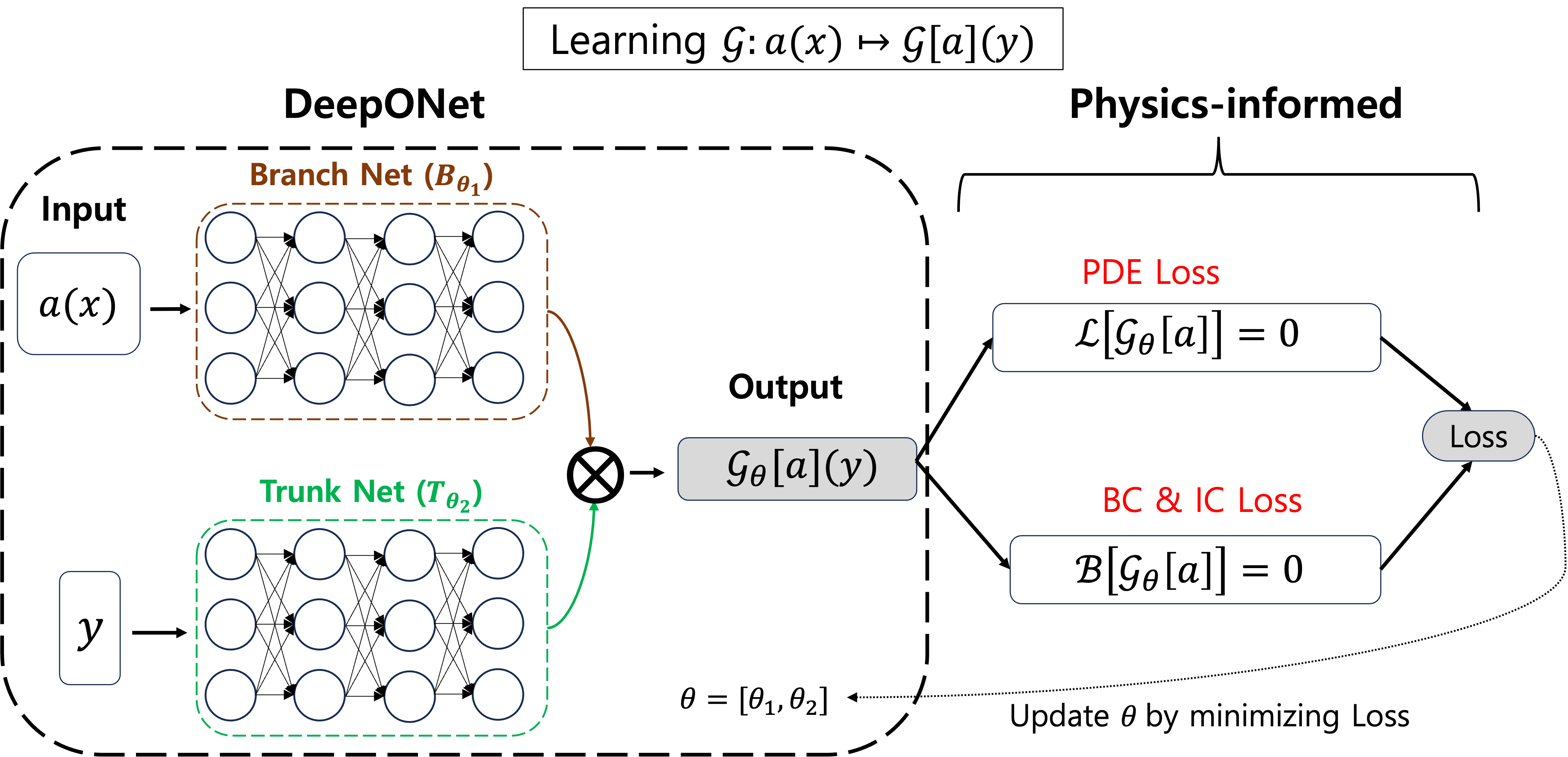
Hamilton-Jacobi Based Policy-Iteration via Deep Operator Learning
Jae Yong Lee, Yeoneung Kim

0
0
The framework of deep operator network (DeepONet) has been widely exploited thanks to its capability of solving high dimensional partial differential equations. In this paper, we incorporate DeepONet with a recently developed policy iteration scheme to numerically solve optimal control problems and the corresponding Hamilton--Jacobi--Bellman (HJB) equations. A notable feature of our approach is that once the neural network is trained, the solution to the optimal control problem and HJB equations with different terminal functions can be inferred quickly thanks to the unique feature of operator learning. Furthermore, a quantitative analysis of the accuracy of the algorithm is carried out via comparison principles of viscosity solutions. The effectiveness of the method is verified with various examples, including 10-dimensional linear quadratic regulator problems (LQRs).
6/18/2024
🌿
Leveraging Hamilton-Jacobi PDEs with time-dependent Hamiltonians for continual scientific machine learning
Paula Chen, Tingwei Meng, Zongren Zou, J'er^ome Darbon, George Em Karniadakis

0
0
We address two major challenges in scientific machine learning (SciML): interpretability and computational efficiency. We increase the interpretability of certain learning processes by establishing a new theoretical connection between optimization problems arising from SciML and a generalized Hopf formula, which represents the viscosity solution to a Hamilton-Jacobi partial differential equation (HJ PDE) with time-dependent Hamiltonian. Namely, we show that when we solve certain regularized learning problems with integral-type losses, we actually solve an optimal control problem and its associated HJ PDE with time-dependent Hamiltonian. This connection allows us to reinterpret incremental updates to learned models as the evolution of an associated HJ PDE and optimal control problem in time, where all of the previous information is intrinsically encoded in the solution to the HJ PDE. As a result, existing HJ PDE solvers and optimal control algorithms can be reused to design new efficient training approaches for SciML that naturally coincide with the continual learning framework, while avoiding catastrophic forgetting. As a first exploration of this connection, we consider the special case of linear regression and leverage our connection to develop a new Riccati-based methodology for solving these learning problems that is amenable to continual learning applications. We also provide some corresponding numerical examples that demonstrate the potential computational and memory advantages our Riccati-based approach can provide.
5/8/2024
📊
Value Approximation for Two-Player General-Sum Differential Games with State Constraints
Lei Zhang, Mukesh Ghimire, Wenlong Zhang, Zhe Xu, Yi Ren

0
0
Solving Hamilton-Jacobi-Isaacs (HJI) PDEs numerically enables equilibrial feedback control in two-player differential games, yet faces the curse of dimensionality (CoD). While physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) have shown promise in alleviating CoD in solving PDEs, vanilla PINNs fall short in learning discontinuous solutions due to their sampling nature, leading to poor safety performance of the resulting policies when values are discontinuous due to state or temporal logic constraints. In this study, we explore three potential solutions to this challenge: (1) a hybrid learning method that is guided by both supervisory equilibria and the HJI PDE, (2) a value-hardening method where a sequence of HJIs are solved with increasing Lipschitz constant on the constraint violation penalty, and (3) the epigraphical technique that lifts the value to a higher dimensional state space where it becomes continuous. Evaluations through 5D and 9D vehicle and 13D drone simulations reveal that the hybrid method outperforms others in terms of generalization and safety performance by taking advantage of both the supervisory equilibrium values and costates, and the low cost of PINN loss gradients.
5/8/2024
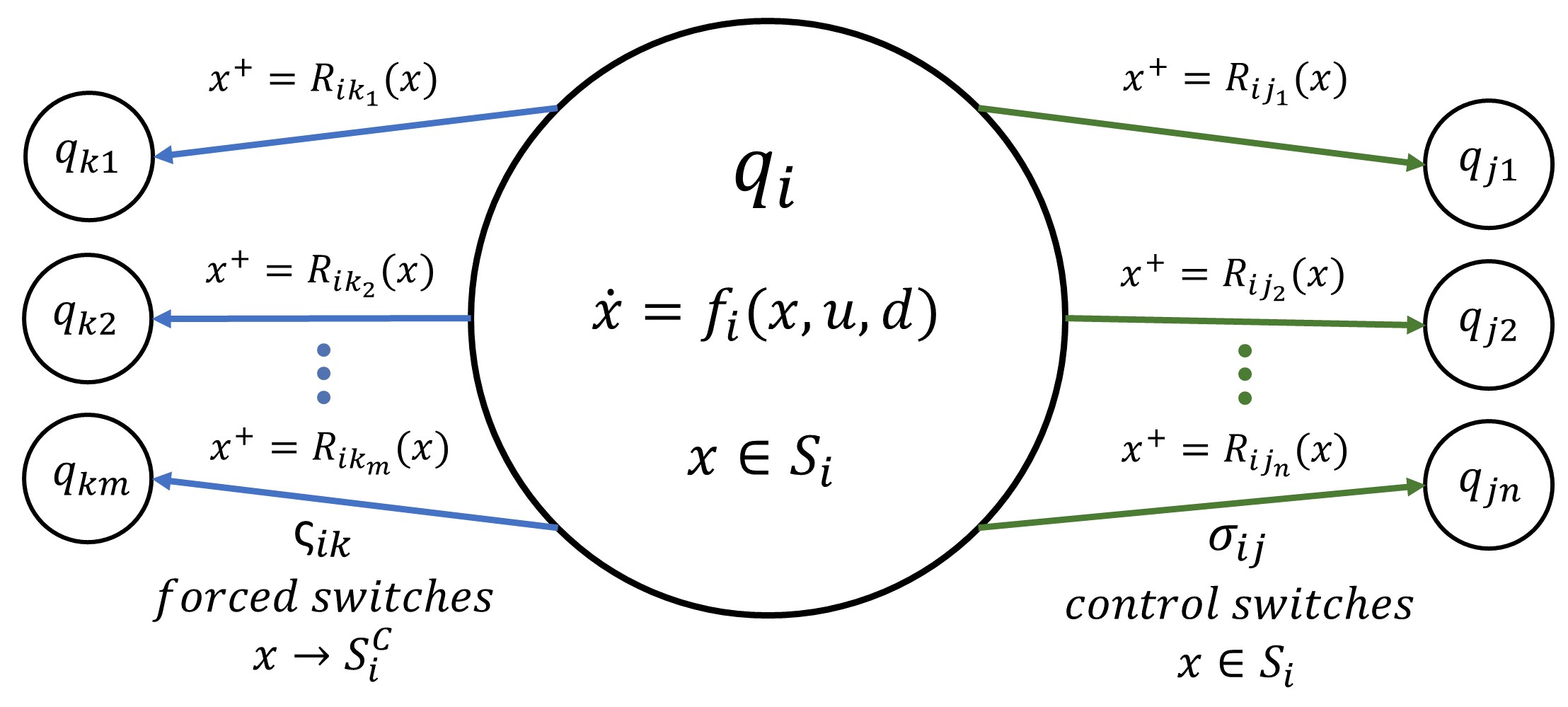
Hamilton-Jacobi Reachability Analysis for Hybrid Systems with Controlled and Forced Transitions
Javier Borquez, Shuang Peng, Yiyu Chen, Quan Nguyen, Somil Bansal

0
0
Hybrid dynamical systems with nonlinear dynamics are one of the most general modeling tools for representing robotic systems, especially contact-rich systems. However, providing guarantees regarding the safety or performance of nonlinear hybrid systems remains a challenging problem because it requires simultaneous reasoning about continuous state evolution and discrete mode switching. In this work, we address this problem by extending classical Hamilton-Jacobi (HJ) reachability analysis, a formal verification method for continuous-time nonlinear dynamical systems, to hybrid dynamical systems. We characterize the reachable sets for hybrid systems through a generalized value function defined over discrete and continuous states of the hybrid system. We also provide a numerical algorithm to compute this value function and obtain the reachable set. Our framework can compute reachable sets for hybrid systems consisting of multiple discrete modes, each with its own set of nonlinear continuous dynamics, discrete transitions that can be directly commanded or forced by a discrete control input, while still accounting for control bounds and adversarial disturbances in the state evolution. Along with the reachable set, the proposed framework also provides an optimal continuous and discrete controller to ensure system safety. We demonstrate our framework in several simulation case studies, as well as on a real-world testbed to solve the optimal mode planning problem for a quadruped with multiple gaits.
6/26/2024