A Survey of Web Content Control for Generative AI
2404.02309

0
0
Abstract
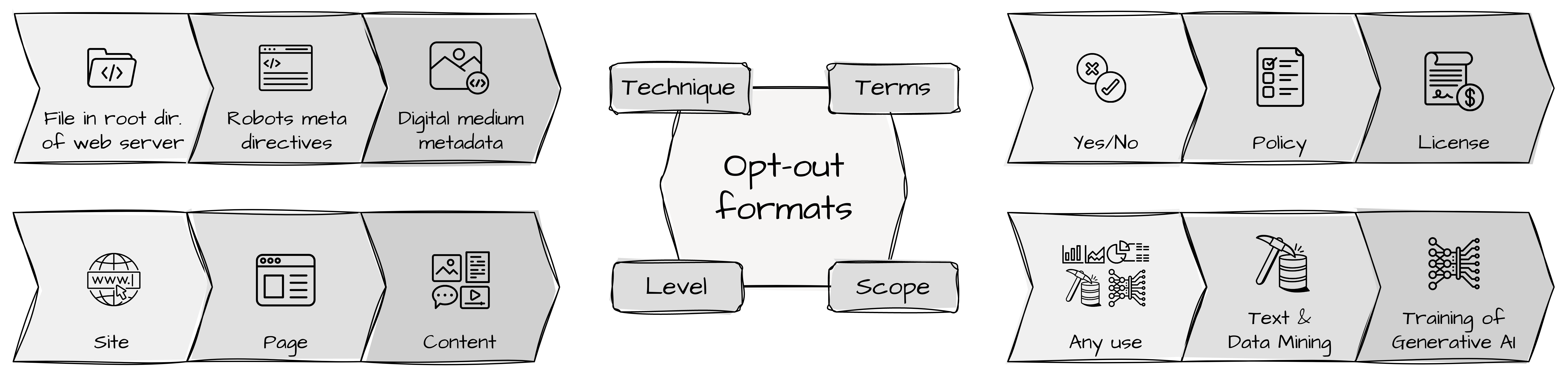
The groundbreaking advancements around generative AI have recently caused a wave of concern culminating in a row of lawsuits, including high-profile actions against Stability AI and OpenAI. This situation of legal uncertainty has sparked a broad discussion on the rights of content creators and publishers to protect their intellectual property on the web. European as well as US law already provides rough guidelines, setting a direction for technical solutions to regulate web data use. In this course, researchers and practitioners have worked on numerous web standards and opt-out formats that empower publishers to keep their data out of the development of generative AI models. The emerging AI/ML opt-out protocols are valuable in regards to data sovereignty, but again, it creates an adverse situation for a site owners who are overwhelmed by the multitude of recent ad hoc standards to consider. In our work, we want to survey the different proposals, ideas and initiatives, and provide a comprehensive legal and technical background in the context of the current discussion on web publishers control.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive survey of the legal and technical challenges around controlling web content generated by AI systems.
- It examines key issues related to intellectual property, privacy, and content moderation that content creators and platform owners must navigate.
- The paper also reviews various technical approaches for monitoring and filtering AI-generated content, highlighting their strengths and limitations.
Plain English Explanation
This paper looks at the complex legal and technical questions that arise as AI systems become more capable of generating content that can be published on the web. When an AI system creates content like text, images, or videos, it raises tricky issues around who owns the intellectual property rights to that content. There are also concerns about protecting people's privacy if the AI uses personal data to generate new content.
Another major challenge is how to effectively moderate all the content being produced by AI models to ensure it doesn't contain harmful, illegal, or inappropriate material. The paper examines different technical methods that companies and platforms could use to try to identify and filter out problematic AI-generated content. However, each approach has its own limitations and tradeoffs.
Overall, the paper emphasizes that as generative AI capabilities continue to advance, there will be growing pressure to develop robust legal frameworks and technical systems to responsibly control the deluge of AI-created web content. Balancing openness, creativity, and innovation with legitimate concerns around rights, privacy, and safety will be an ongoing challenge.
Technical Explanation
The paper first provides background on the key legal issues at play, focusing on intellectual property rights and privacy concerns. It notes that AI-generated content complicates traditional notions of authorship and ownership, as the human role shifts from direct content creation to model training. The paper also highlights privacy risks if AI models leverage personal data to produce new content without consent.
The core of the paper then reviews various technical approaches for monitoring and filtering AI-generated web content. These include:
- Content detection models that attempt to classify whether content was created by an AI
- Watermarking techniques to embed digital identifiers in AI-generated media
- Querying models to understand their training data and biases
- Proactive content moderation systems to screen material before publication
The paper analyzes the strengths and weaknesses of each method, noting tradeoffs around accuracy, computational cost, and user privacy. It emphasizes that a combination of legal, technical, and policy solutions will likely be needed to adequately address the challenges posed by the rise of generative AI.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and balanced overview of the complex challenges in this domain. It rightly identifies the key legal and technical issues that must be grappled with, acknowledging that there are no easy solutions.
One potential limitation is that the analysis of technical approaches is relatively high-level, and does not delve into the nuanced tradeoffs and limitations of each method in great depth. Readers may desire more granular insights into the capabilities and shortcomings of the various detection, watermarking, and moderation techniques discussed.
Additionally, the paper could have explored some of the broader societal implications and ethical considerations around the use of generative AI for web content. For instance, it does not address how these technologies could be leveraged to spread misinformation, infringe on creative rights, or erode trust online.
Overall, though, this is a valuable contribution that lays important groundwork for further research and policymaking in this rapidly evolving space. The authors provide a solid foundation for understanding the multifaceted challenges that must be addressed as generative AI becomes more prevalent on the web.
Conclusion
This comprehensive survey underscores the complex legal and technical landscape that content creators, platform owners, and policymakers must navigate as generative AI becomes increasingly capable of producing web content. The paper highlights the core issues around intellectual property, privacy, and content moderation, while also reviewing various technical approaches for identifying and filtering AI-generated material.
As the authors note, there will be an ongoing need to develop robust yet adaptable solutions that can keep pace with the rapid advancement of these AI technologies. Balancing innovation, openness, and creativity with legitimate concerns around rights, safety, and trust will be a major challenge. But the insights provided in this paper offer a solid starting point for further research and dialogue on this consequential topic.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖
Uncertain Boundaries: Multidisciplinary Approaches to Copyright Issues in Generative AI
Jocelyn Dzuong, Zichong Wang, Wenbin Zhang

0
0
In the rapidly evolving landscape of generative artificial intelligence (AI), the increasingly pertinent issue of copyright infringement arises as AI advances to generate content from scraped copyrighted data, prompting questions about ownership and protection that impact professionals across various careers. With this in mind, this survey provides an extensive examination of copyright infringement as it pertains to generative AI, aiming to stay abreast of the latest developments and open problems. Specifically, it will first outline methods of detecting copyright infringement in mediums such as text, image, and video. Next, it will delve an exploration of existing techniques aimed at safeguarding copyrighted works from generative models. Furthermore, this survey will discuss resources and tools for users to evaluate copyright violations. Finally, insights into ongoing regulations and proposals for AI will be explored and compared. Through combining these disciplines, the implications of AI-driven content and copyright are thoroughly illustrated and brought into question.
4/15/2024
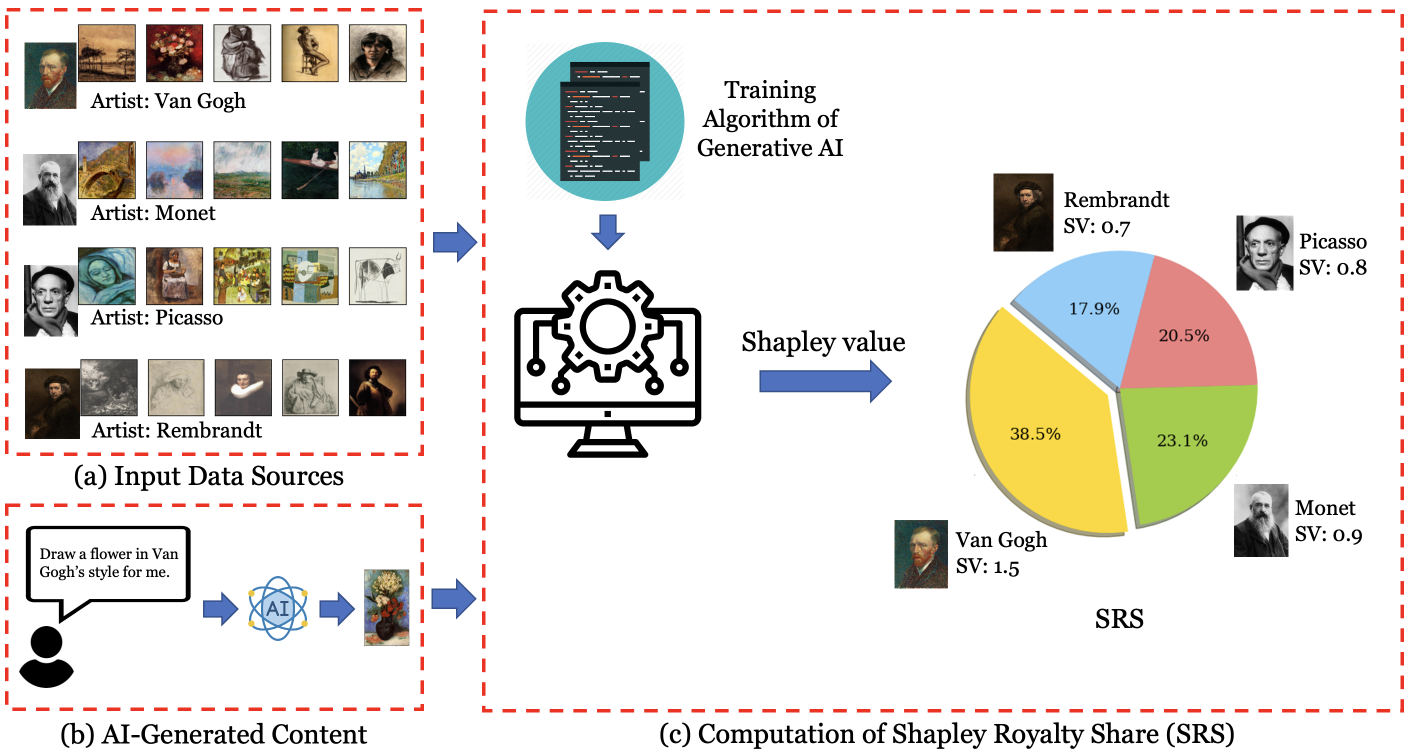
An Economic Solution to Copyright Challenges of Generative AI
Jiachen T. Wang, Zhun Deng, Hiroaki Chiba-Okabe, Boaz Barak, Weijie J. Su

0
0
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) systems are trained on large data corpora to generate new pieces of text, images, videos, and other media. There is growing concern that such systems may infringe on the copyright interests of training data contributors. To address the copyright challenges of generative AI, we propose a framework that compensates copyright owners proportionally to their contributions to the creation of AI-generated content. The metric for contributions is quantitatively determined by leveraging the probabilistic nature of modern generative AI models and using techniques from cooperative game theory in economics. This framework enables a platform where AI developers benefit from access to high-quality training data, thus improving model performance. Meanwhile, copyright owners receive fair compensation, driving the continued provision of relevant data for generative model training. Experiments demonstrate that our framework successfully identifies the most relevant data sources used in artwork generation, ensuring a fair and interpretable distribution of revenues among copyright owners.
4/24/2024
📊
U Can't Gen This? A Survey of Intellectual Property Protection Methods for Data in Generative AI
Tanja v{S}arv{c}evi'c (SBA Research), Alicja Karlowicz (SBA Research), Rudolf Mayer (SBA Research), Ricardo Baeza-Yates (EAI, Northeastern University), Andreas Rauber (TU Wien)

0
0
Large Generative AI (GAI) models have the unparalleled ability to generate text, images, audio, and other forms of media that are increasingly indistinguishable from human-generated content. As these models often train on publicly available data, including copyrighted materials, art and other creative works, they inadvertently risk violating copyright and misappropriation of intellectual property (IP). Due to the rapid development of generative AI technology and pressing ethical considerations from stakeholders, protective mechanisms and techniques are emerging at a high pace but lack systematisation. In this paper, we study the concerns regarding the intellectual property rights of training data and specifically focus on the properties of generative models that enable misuse leading to potential IP violations. Then we propose a taxonomy that leads to a systematic review of technical solutions for safeguarding the data from intellectual property violations in GAI.
6/26/2024
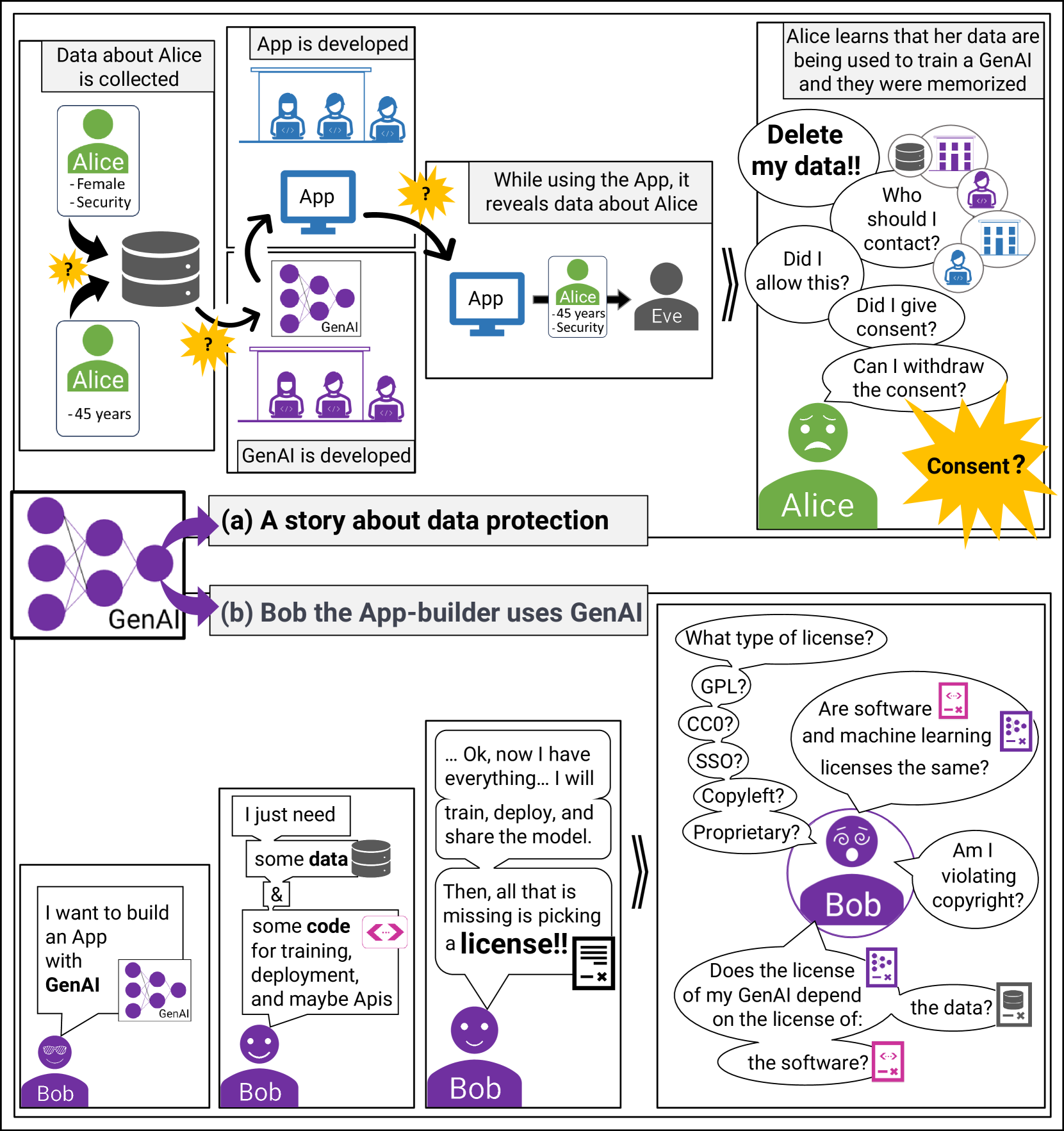
Legal Aspects for Software Developers Interested in Generative AI Applications
Steffen Herbold, Brian Valerius, Anamaria Mojica-Hanke, Isabella Lex, Joel Mittel

0
0
Recent successes in Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) have led to new technologies capable of generating high-quality code, natural language, and images. The next step is to integrate GenAI technology into products, a task typically conducted by software developers. Such product development always comes with a certain risk of liability. Within this article, we want to shed light on the current state of two such risks: data protection and copyright. Both aspects are crucial for GenAI. This technology deals with data for both model training and generated output. We summarize key aspects regarding our current knowledge that every software developer involved in product development using GenAI should be aware of to avoid critical mistakes that may expose them to liability claims.
4/26/2024