Design, Key Techniques and System-Level Simulation for NB-IoT Networks

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a detailed study on the design, key techniques, and system-level simulation for Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) networks.
- NB-IoT is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technology that enables efficient and cost-effective connectivity for IoT devices.
- The paper focuses on the link-level simulator structure, system-level simulation, and key techniques for enhancing NB-IoT performance.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses the development of a comprehensive system for simulating and analyzing NB-IoT networks. NB-IoT is a type of wireless communication technology designed to connect a large number of low-power devices, such as sensors and smart meters, over a wide area.
The researchers created a detailed link-level simulator to model the various components and processes involved in NB-IoT communication. This allows them to study how the system behaves and identify ways to improve its performance. Some of the key techniques they explore include:
- Optimizing the signal processing and resource allocation algorithms to enhance the efficiency and reliability of NB-IoT transmissions.
- Developing advanced interference management strategies to mitigate the impact of other wireless signals on the NB-IoT network.
- Implementing smart power management schemes to extend the battery life of NB-IoT devices.
By using this comprehensive simulation system, the researchers were able to gain insights into the real-world challenges and limitations of deploying NB-IoT networks. This knowledge can help guide the development of more robust and effective NB-IoT solutions in the future.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a detailed link-level simulator for Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) networks. The simulator models the various components and processes involved in NB-IoT communication, including the physical layer, medium access control (MAC) layer, and higher-level protocols.
The link-level simulator is designed to be highly configurable, allowing researchers to explore the impact of different parameters and techniques on NB-IoT performance. This includes the ability to simulate various deployment scenarios, channel models, and device characteristics.
One of the key features of the simulator is its support for advanced interference management strategies. The researchers developed algorithms to mitigate the impact of other wireless signals, such as those from nearby cellular networks or Wi-Fi devices, on the NB-IoT network. This is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient NB-IoT communications in dense urban environments.
The simulator also incorporates power management schemes to optimize the energy consumption of NB-IoT devices. This is critical for IoT applications, where devices are often battery-powered and need to operate for extended periods without the need for manual recharging or replacement.
Using this comprehensive simulation system, the researchers were able to explore a range of key techniques for enhancing NB-IoT performance, including:
- Optimized signal processing algorithms to improve the reliability and efficiency of NB-IoT transmissions.
- Advanced resource allocation strategies to ensure fair and efficient utilization of the available spectrum.
- Intelligent interference management techniques to mitigate the impact of other wireless signals on the NB-IoT network.
- Power-efficient communication protocols to extend the battery life of NB-IoT devices.
The insights and findings from this simulation-based study can inform the design and implementation of more robust and effective NB-IoT networks in the future.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and well-structured approach to simulating and analyzing NB-IoT networks. The link-level simulator developed by the researchers appears to be a powerful tool for exploring the various challenges and trade-offs associated with NB-IoT deployment.
One potential limitation of the study is the reliance on simulation-based analysis, which may not fully capture the complexities and idiosyncrasies of real-world NB-IoT deployments. While the researchers have made efforts to model realistic scenarios, there may be additional factors that are not accounted for in the simulation environment.
Moreover, the paper does not provide extensive validation of the simulator's accuracy and fidelity against empirical data or field trials. It would be valuable to see how the simulation results align with observations from actual NB-IoT networks, which could help strengthen the confidence in the conclusions drawn from this study.
Additionally, the paper focuses primarily on the technical aspects of NB-IoT design and simulation, with limited discussion of the broader economic, social, or environmental implications of this technology. Considering these wider perspectives could offer a more holistic understanding of the role of NB-IoT in the evolving IoT landscape.
Despite these potential areas for further exploration, the paper represents a significant contribution to the understanding of NB-IoT network design and optimization. The insights and techniques presented in this work can serve as a valuable foundation for future research and development in this important field.
Conclusion
This paper presents a comprehensive study on the design, key techniques, and system-level simulation for Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) networks. The researchers have developed a detailed link-level simulator that allows for the exploration of various aspects of NB-IoT performance, including signal processing, resource allocation, interference management, and power optimization.
The simulation-based analysis provides valuable insights into the challenges and trade-offs associated with NB-IoT deployment, which can inform the development of more robust and effective NB-IoT solutions. While the reliance on simulation may limit the generalizability of the findings, the techniques and insights presented in this work can serve as a valuable foundation for future research and real-world NB-IoT implementations.
Overall, this paper contributes to the growing body of knowledge on the design and optimization of low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technologies, which are expected to play a critical role in the ongoing expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Design, Key Techniques and System-Level Simulation for NB-IoT Networks
Shutao Zhang, Wenkun Wen, Peiran Wu, Hongqing Huang, Liya Zhu, Yijia Guo, Tingting Yang, Minghua Xia
Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) is a technology specifically designated by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) to meet the explosive demand for massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and it is evolving to RedCap. Industrial companies have increasingly adopted NB-IoT as the solution for mMTC due to its lightweight design and comprehensive technical specifications released by 3GPP. This paper presents a system-level simulation framework for NB-IoT networks to evaluate their performance. The system-level simulator is structured into four parts: initialization, pre-generation, main simulation loop, and post-processing. Additionally, three essential features are investigated to enhance coverage, support massive connections, and ensure low power consumption, respectively. Simulation results demonstrate that the cumulative distribution function curves of the signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio fully comply with industrial standards. Furthermore, the throughput performance explains how NB-IoT networks realize massive connections at the cost of data rate. This work highlights its practical utility and paves the way for developing NB-IoT networks.
Read more8/15/2024
🎯

0
Narrowband-IoT (NB-IoT) and IoT Use Cases in Universities, Campuses, and Educational Institutions: A Research Analysis
Lyberius Ennio F. Taruc, Arvin R. De La Cruz
The main objective of this research paper is to analyze the available use cases of Narrowband-IoT and IoT in universities, campuses, and educational institutions. A literature review was conducted using multiple databases such as IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, and Scopus. The study explores the benefits of IoT adoption in higher education. Various use cases of NB-IoT in educational institutions were analyzed, including smart campus management, asset tracking, monitoring, and safety and security systems. Of the six use cases assessed, three focused on the deployment of IoT Things, while three focused on NB-IoT Connectivity. The research paper concludes that NB-IoT technology has significant potential to enhance various aspects of educational institutions, from smart campus management to improving safety and security systems. The study recommends further exploration and implementation of NB-IoT technology in educational settings to improve efficiency, security, and overall campus management. The research highlights the potential applications of NB-IoT in universities and educational institutions, paving the way for future studies in this area. The social implications of this research could involve enhancing the overall learning experience for students, improving campus safety, and promoting technological advancements in educational settings. Keywords: narrowband-IoT, Internet-of-Things, smart campus, smart institutions
Read more8/7/2024


0
DEEP-IoT: Downlink-Enhanced Efficient-Power Internet of Things
Yulin Shao
At the heart of the Internet of Things (IoT) -- a domain witnessing explosive growth -- the imperative for energy efficiency and the extension of device lifespans has never been more pressing. This paper presents DEEP-IoT, an innovative communication paradigm poised to redefine how IoT devices communicate. Through a pioneering feedback channel coding strategy, DEEP-IoT challenges and transforms the traditional transmitter (IoT devices)-centric communication model to one where the receiver (the access point) play a pivotal role, thereby cutting down energy use and boosting device longevity. We not only conceptualize DEEP-IoT but also actualize it by integrating deep learning-enhanced feedback channel codes within a narrow-band system. Simulation results show a significant enhancement in the operational lifespan of IoT cells -- surpassing traditional systems using Turbo and Polar codes by up to 52.71%. This leap signifies a paradigm shift in IoT communications, setting the stage for a future where IoT devices boast unprecedented efficiency and durability.
Read more9/10/2024

0
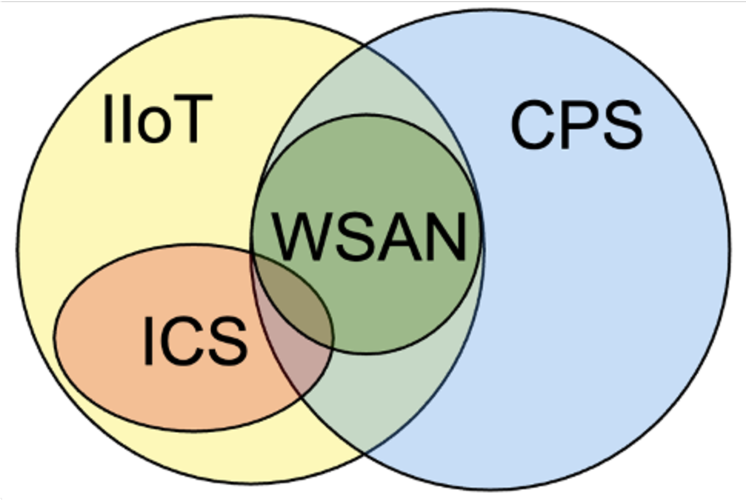
A Survey on Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Testbeds for Connectivity Research
Tianyu Zhang, Chuanyu Xue, Jiachen Wang, Zelin Yun, Natong Lin, Song Han
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies have revolutionized industrial processes, enabling smart automation, real-time data analytics, and improved operational efficiency across diverse industry sectors. IIoT testbeds play a critical role in advancing IIoT research and development (R&D) to provide controlled environments for technology evaluation before their real-world deployment. In this article, we conduct a comprehensive literature review on existing IIoT testbeds, aiming to identify benchmark performance, research gaps and explore emerging trends in IIoT systems. We first review the state-of-the-art resource management solutions proposed for IIoT applications. We then categorize the reviewed testbeds according to their deployed communication protocols (including TSN, IEEE 802.15.4, IEEE 802.11 and 5G) and discuss the design and usage of each testbed. Driven by the knowledge gained during this study, we present suggestions and good practices for researchers and practitioners who are planning to design and develop IIoT testbeds for connectivity research.
Read more7/2/2024