Toward human-centered shared autonomy AI paradigms for human-robot teaming in healthcare

0
🤖
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Recent advancements in AI and computation have led to the emergence of intelligent paradigms that can empower different fields, such as healthcare robots, with new capabilities.
- Advanced AI robotic algorithms, like reinforcement learning, can be trained to make autonomous decisions to achieve a desired goal.
- However, such independent decision-making might not be ideal for healthcare robots that interact with dynamic end-users or patients.
- In this human-robot interaction (teaming) framework, the dynamic user wants to be involved in decision-making and introduce new goals in real-time.
- To address this challenge, an adaptive shared autonomy AI paradigm is required, with a foundation based on human-centered factors to avoid ethical issues and guarantee no harm to humanity.
Plain English Explanation
In the world of healthcare, robots are increasingly being used to assist patients and medical professionals. These robots are equipped with advanced AI algorithms, like reinforcement learning, which allow them to make decisions and achieve specific goals on their own.
However, when a healthcare robot interacts with a patient, the patient often wants to be involved in the decision-making process and may even introduce new goals during the interaction. This dynamic human-robot interaction can be challenging for a robot that is programmed to make independent decisions.
To address this issue, researchers are developing an adaptive shared autonomy AI paradigm that allows the robot and the human to work together, with the human being able to influence the robot's decisions and goals. This approach is based on human-centered factors to ensure that the robot's actions are ethical and do not harm the patient.
By creating this collaborative relationship between the human and the robot, healthcare robots can be more effective and responsive to the patient's needs, ultimately improving the quality of care.
Technical Explanation
The paper describes the need for an adaptive shared autonomy AI paradigm in healthcare robotics, where the robot and the human user work together to make decisions and achieve goals.
Traditionally, advanced AI robotic algorithms have been trained to make autonomous decisions to achieve a desired and usually fixed goal. However, in the context of healthcare, where the robot interacts with a dynamic end-user or patient, this independent decision-making may not be ideal.
In a human-robot interaction (teaming) framework, the dynamic user continuously wants to be involved in decision-making and may introduce new goals during the real-time interaction. To address this challenge, the researchers propose an adaptive shared autonomy AI paradigm, which is based on human-centered factors to avoid any possible ethical issues and guarantee no harm to the user.
This adaptive shared autonomy approach allows the robot and the human to collaborate, with the human being able to influence the robot's decisions and goals. By creating this strategic opponent modeling between the human and the AI agent, the healthcare robot can be more responsive to the user's needs and preferences, ultimately improving the quality of care.
Critical Analysis
The proposed adaptive shared autonomy AI paradigm for healthcare robots addresses an important challenge in the field of human-robot interaction. By allowing the human user to be involved in the decision-making process and introduce new goals, the robot can be more responsive to the user's needs and preferences.
However, the paper does not provide details on the specific algorithms or implementation of this adaptive shared autonomy approach. It would be helpful to have more information on how the robot and the human user's inputs are integrated, how conflicts are resolved, and how the system ensures that the robot's actions are ethical and do not harm the user.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss the potential limitations or drawbacks of this approach. For example, it is unclear how the system would handle situations where the user's preferences or goals are in conflict with the robot's objectives or the medical professionals' recommendations.
Further research and experimentation would be needed to fully understand the implications of this human-centered automation approach and ensure that it can be safely and effectively implemented in healthcare settings.
Conclusion
The adaptive shared autonomy AI paradigm proposed in this paper represents an important step towards enhancing human-AI collaboration in healthcare robotics. By allowing the human user to be involved in the decision-making process and introduce new goals, the robot can be more responsive to the user's needs and preferences, ultimately improving the quality of care.
However, further research is needed to address the potential limitations and ensure the safe and ethical implementation of this approach in real-world healthcare settings. As AI and robotics continue to advance, the development of human-centered automation solutions will be crucial for empowering healthcare professionals and enhancing patient outcomes.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖

0
Toward human-centered shared autonomy AI paradigms for human-robot teaming in healthcare
Reza Abiri, Ali Rabiee, Sima Ghafoori, Anna Cetera
With recent advancements in AI and computation tools, intelligent paradigms emerged to empower different fields such as healthcare robots with new capabilities. Advanced AI robotic algorithms (e.g., reinforcement learning) can be trained and developed to autonomously make individual decisions to achieve a desired and usually fixed goal. However, such independent decisions and goal achievements might not be ideal for a healthcare robot that usually interacts with a dynamic end-user or a patient. In such a complex human-robot interaction (teaming) framework, the dynamic user continuously wants to be involved in decision-making as well as introducing new goals while interacting with their present environment in real-time. To address this challenge, an adaptive shared autonomy AI paradigm is required to be developed for the two interactive agents (Human & AI agents) with a foundation based on human-centered factors to avoid any possible ethical issues and guarantee no harm to humanity.
Read more7/25/2024


0
Exploring AI-enhanced Shared Control for an Assistive Robotic Arm
Max Pascher, Kirill Kronhardt, Jan Freienstein, Jens Gerken
Assistive technologies and in particular assistive robotic arms have the potential to enable people with motor impairments to live a self-determined life. More and more of these systems have become available for end users in recent years, such as the Kinova Jaco robotic arm. However, they mostly require complex manual control, which can overwhelm users. As a result, researchers have explored ways to let such robots act autonomously. However, at least for this specific group of users, such an approach has shown to be futile. Here, users want to stay in control to achieve a higher level of personal autonomy, to which an autonomous robot runs counter. In our research, we explore how Artifical Intelligence (AI) can be integrated into a shared control paradigm. In particular, we focus on the consequential requirements for the interface between human and robot and how we can keep humans in the loop while still significantly reducing the mental load and required motor skills.
Read more7/19/2024
🔗

0
Towards Human-AI Mutual Learning: A New Research Paradigm
Xiaomei Wang, Xiaoyu Chen
This paper describes a new research paradigm for studying human-AI collaboration, named human-AI mutual learning, defined as the process where humans and AI agents preserve, exchange, and improve knowledge during human-AI collaboration. We describe relevant methodologies, motivations, domain examples, benefits, challenges, and future research agenda under this paradigm.
Read more5/9/2024

0
Deconstructing Human-AI Collaboration: Agency, Interaction, and Adaptation
Steffen Holter, Mennatallah El-Assady
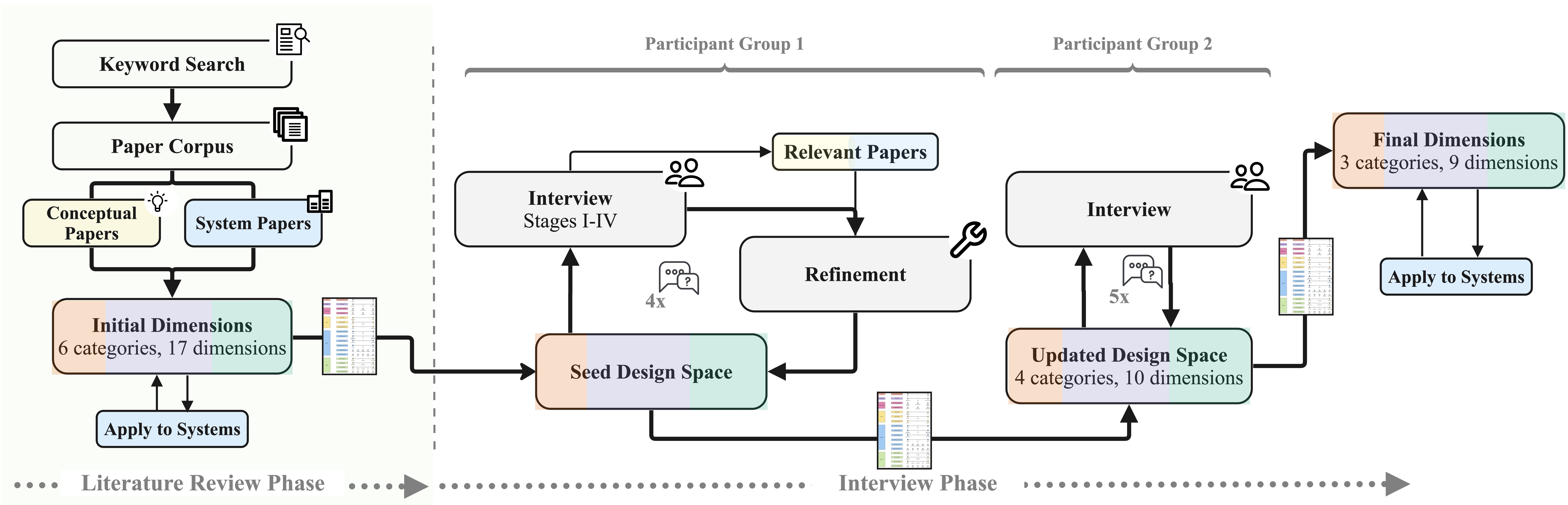
As full AI-based automation remains out of reach in most real-world applications, the focus has instead shifted to leveraging the strengths of both human and AI agents, creating effective collaborative systems. The rapid advances in this area have yielded increasingly more complex systems and frameworks, while the nuance of their characterization has gotten more vague. Similarly, the existing conceptual models no longer capture the elaborate processes of these systems nor describe the entire scope of their collaboration paradigms. In this paper, we propose a new unified set of dimensions through which to analyze and describe human-AI systems. Our conceptual model is centered around three high-level aspects - agency, interaction, and adaptation - and is developed through a multi-step process. Firstly, an initial design space is proposed by surveying the literature and consolidating existing definitions and conceptual frameworks. Secondly, this model is iteratively refined and validated by conducting semi-structured interviews with nine researchers in this field. Lastly, to illustrate the applicability of our design space, we utilize it to provide a structured description of selected human-AI systems.
Read more4/19/2024