Narrative Review of Support for Emotional Expressions in Virtual Reality: Psychophysiology of speech-to-text interfaces
2405.13924

0
0
🏋️
Abstract
This narrative review on emotional expression in Speech-to-Text (STT) interfaces with Virtual Reality (VR) aims to identify advancements, limitations, and research gaps in incorporating emotional expression into transcribed text generated by STT systems. Using a rigorous search strategy, relevant articles published between 2020 and 2024 are extracted and categorized into themes such as communication enhancement technologies, innovations in captioning, emotion recognition in AR and VR, and empathic machines. The findings reveal the evolution of tools and techniques to meet the needs of individuals with hearing impairments, showcasing innovations in live transcription, closed captioning, AR, VR, and emotion recognition technologies. Despite improvements in accessibility, the absence of emotional nuance in transcribed text remains a significant communication challenge. The study underscores the urgency for innovations in STT technology to capture emotional expressions. The research discusses integrating emotional expression into text through strategies like animated text captions, emojilization tools, and models associating emotions with animation properties. Extending these efforts into AR and VR environments opens new possibilities for immersive and emotionally resonant experiences, especially in educational contexts. The study also explores empathic applications in healthcare, education, and human-robot interactions, highlighting the potential for personalized and effective interactions. The multidisciplinary nature of the literature underscores the potential for collaborative and interdisciplinary research.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This narrative review examines advancements, limitations, and research gaps in incorporating emotional expression into transcribed text generated by Speech-to-Text (STT) systems used in Virtual Reality (VR) environments.
- The review covers a range of relevant topics, including communication enhancement technologies, innovations in captioning, emotion recognition in Augmented Reality (AR) and VR, and the potential for empathic machines.
- The findings highlight the evolution of tools and techniques to improve accessibility for individuals with hearing impairments, as well as the ongoing challenge of capturing emotional nuance in transcribed text.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how emotion can be expressed in the text that is generated when speech is converted to text, especially in virtual reality (VR) applications. It reviews the latest research in this area, covering things like:
- New technologies that can enhance communication, such as improved captioning and live transcription
- Innovations in how emotion is recognized in augmented reality (AR) and VR environments
- The potential for "empathic machines" that can understand and respond to human emotions
The key finding is that while accessibility has improved, there is still a significant challenge in capturing the emotional tone and nuance in the text that is generated from speech. The paper discusses ways to address this, such as using animated text captions, emojis, and models that link emotions to animation properties.
Integrating emotional expression into text in AR and VR could lead to more immersive and emotionally impactful experiences, especially in areas like education. The paper also explores how this technology could be used in healthcare, education, and human-robot interactions to enable more personalized and effective interactions.
Overall, the review highlights the importance of this multidisciplinary research area and the potential for collaboration across different fields to address the challenges of capturing emotion in speech-to-text technology.
Technical Explanation
The paper conducts a narrative review of the literature published between 2020 and 2024 on the topic of incorporating emotional expression into transcribed text generated by STT systems used in VR environments. The authors used a rigorous search strategy to identify relevant articles, which were then categorized into themes such as communication enhancement technologies, innovations in captioning, emotion recognition in AR and VR, and empathic machines.
The review reveals advancements in tools and techniques to improve accessibility for individuals with hearing impairments, including innovations in live transcription, closed captioning, AR, VR, and emotion recognition technologies. However, the absence of emotional nuance in transcribed text remains a significant challenge.
The paper discusses strategies to integrate emotional expression into text, such as animated text captions, emojilization tools, and models that associate emotions with animation properties. Extending these efforts into AR and VR environments opens up new possibilities for immersive and emotionally resonant experiences, particularly in educational contexts.
The review also explores the potential for empathic applications in healthcare, education, and human-robot interactions, highlighting the prospect of personalized and effective interactions. The multidisciplinary nature of the literature underscores the potential for collaborative and interdisciplinary research in this field.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research on incorporating emotional expression into STT interfaces with VR. However, it is important to note that the review is limited to publications between 2020 and 2024, which may exclude earlier or ongoing research in this rapidly evolving field.
While the paper discusses various strategies for integrating emotional expression into transcribed text, such as animated captions and emojilization, it does not provide a detailed evaluation of the effectiveness or feasibility of these approaches. Further research is needed to assess the real-world implementation and user experience of these techniques.
Additionally, the paper does not address potential challenges or limitations in deploying emotion recognition technologies in VR environments, such as the impact of virtual avatars or the influence of immersive experiences on emotional expression. These factors could significantly affect the accuracy and reliability of emotion recognition algorithms in VR contexts.
Finally, the review focuses primarily on the technical aspects of incorporating emotional expression into STT interfaces, but it lacks a deeper discussion of the ethical and societal implications of such technologies. Issues like data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for misuse or manipulation of emotional data should be explored in future research.
Conclusion
This narrative review highlights the ongoing efforts to enhance the emotional expression in transcribed text generated by STT systems used in VR environments. The paper showcases the advancements in communication enhancement technologies, captioning innovations, and the potential of empathic machines to improve accessibility and engagement for individuals with hearing impairments.
While significant progress has been made, the lack of emotional nuance in transcribed text remains a significant challenge. The proposed strategies, such as animated captions and emojilization, offer promising avenues for further development and exploration. Integrating these technologies into AR and VR environments could lead to more immersive and emotionally resonant experiences, particularly in educational and healthcare settings.
The multidisciplinary nature of this research field underscores the need for collaborative efforts across different disciplines to address the complex technical, ethical, and societal implications of incorporating emotional expression into STT interfaces. Continued research and innovation in this area have the potential to enhance communication, foster empathic interactions, and create more inclusive and engaging virtual experiences.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Towards Understanding Emotions for Engaged Mental Health Conversations
Kellie Yu Hui Sim, Kohleen Tijing Fortuno, Kenny Tsu Wei Choo

0
0
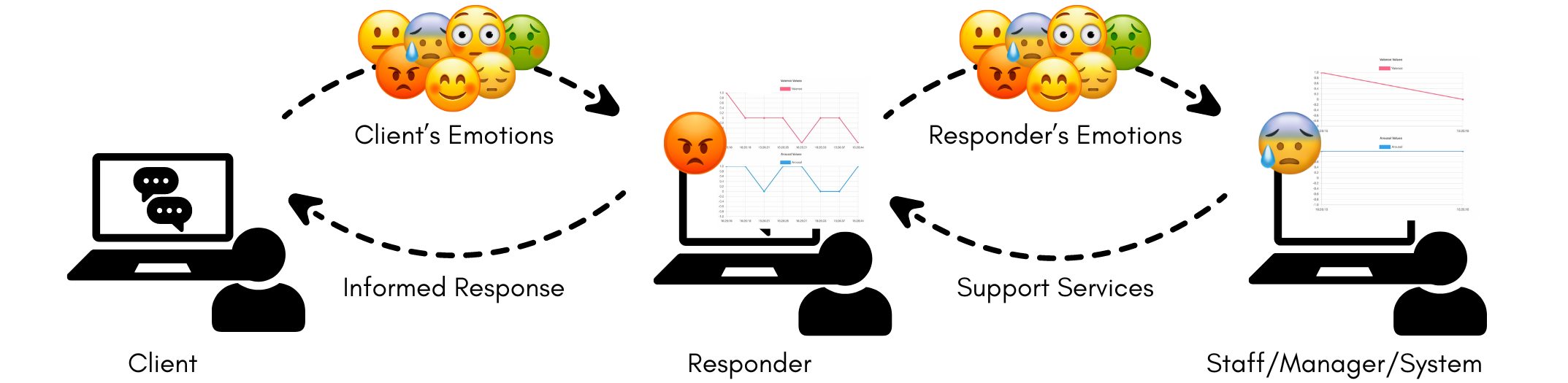
Providing timely support and intervention is crucial in mental health settings. As the need to engage youth comfortable with texting increases, mental health providers are exploring and adopting text-based media such as chatbots, community-based forums, online therapies with licensed professionals, and helplines operated by trained responders. To support these text-based media for mental health--particularly for crisis care--we are developing a system to perform passive emotion-sensing using a combination of keystroke dynamics and sentiment analysis. Our early studies of this system posit that the analysis of short text messages and keyboard typing patterns can provide emotion information that may be used to support both clients and responders. We use our preliminary findings to discuss the way forward for applying AI to support mental health providers in providing better care.
6/18/2024
🤔
Understanding Emotional Hijacking in Metaverse
Syed Ali Asif, Philip Gable, Chien-Chung Shen, Yan-Ming Chiou

0
0
Emotions are an integral part of being human, and experiencing a range of emotions is what makes life rich and vibrant. From basic emotions like anger, fear, happiness, and sadness to more complex ones like excitement and grief, emotions help us express ourselves and connect with the world around us. In recent years, researchers have begun adopting virtual reality (VR) technology to evoke emotions as realistically as possible and quantify the strength of emotions from the electroencephalogram (EEG) signals measured from the brain to understand human emotions in realistic situations better. This is achieved by creating a sense of presence in the virtual environment, the feeling that the user is there. For instance, [6] studied the excitement of a rollercoaster ride in VR, and [5] studied the fear of navigating in a VR cave.
5/10/2024
Controlling Emotion in Text-to-Speech with Natural Language Prompts
Thomas Bott, Florian Lux, Ngoc Thang Vu

0
0
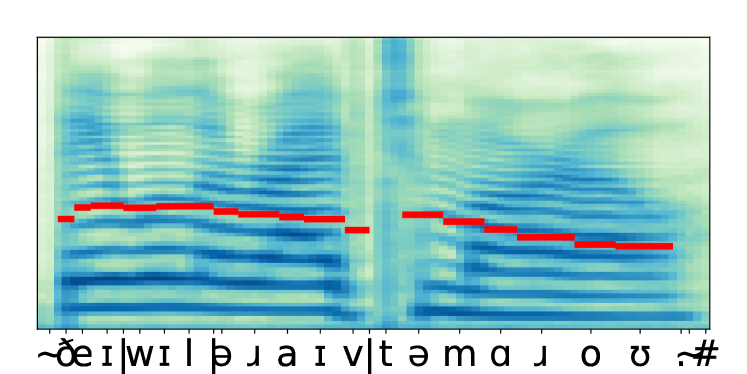
In recent years, prompting has quickly become one of the standard ways of steering the outputs of generative machine learning models, due to its intuitive use of natural language. In this work, we propose a system conditioned on embeddings derived from an emotionally rich text that serves as prompt. Thereby, a joint representation of speaker and prompt embeddings is integrated at several points within a transformer-based architecture. Our approach is trained on merged emotional speech and text datasets and varies prompts in each training iteration to increase the generalization capabilities of the model. Objective and subjective evaluation results demonstrate the ability of the conditioned synthesis system to accurately transfer the emotions present in a prompt to speech. At the same time, precise tractability of speaker identities as well as overall high speech quality and intelligibility are maintained.
6/13/2024
🔎
Empathy Detection from Text, Audiovisual, Audio or Physiological Signals: Task Formulations and Machine Learning Methods
Md Rakibul Hasan, Md Zakir Hossain, Shreya Ghosh, Aneesh Krishna, Tom Gedeon

0
0
Empathy indicates an individual's ability to understand others. Over the past few years, empathy has drawn attention from various disciplines, including but not limited to Affective Computing, Cognitive Science and Psychology. Detecting empathy has potential applications in society, healthcare and education. Despite being a broad and overlapping topic, the avenue of empathy detection leveraging Machine Learning remains underexplored from a systematic literature review perspective. We collected 828 papers from 10 well-known databases, systematically screened them and analysed the final 61 papers. Our analyses reveal several prominent task formulations $-$ including empathy on localised utterances or overall expressions, unidirectional or parallel empathy, and emotional contagion $-$ in monadic, dyadic and group interactions. Empathy detection methods are summarised based on four input modalities $-$ text, audiovisual, audio and physiological signals $-$ thereby presenting modality-specific network architecture design protocols. We discuss challenges, research gaps and potential applications in the Affective Computing-based empathy domain, which can facilitate new avenues of exploration. We further enlist the public availability of datasets and codes. We believe that our work is a stepping stone to developing a robust empathy detection system that can be deployed in practice to enhance the overall well-being of human life.
6/27/2024