Tracking the perspectives of interacting language models
2406.11938

0
0
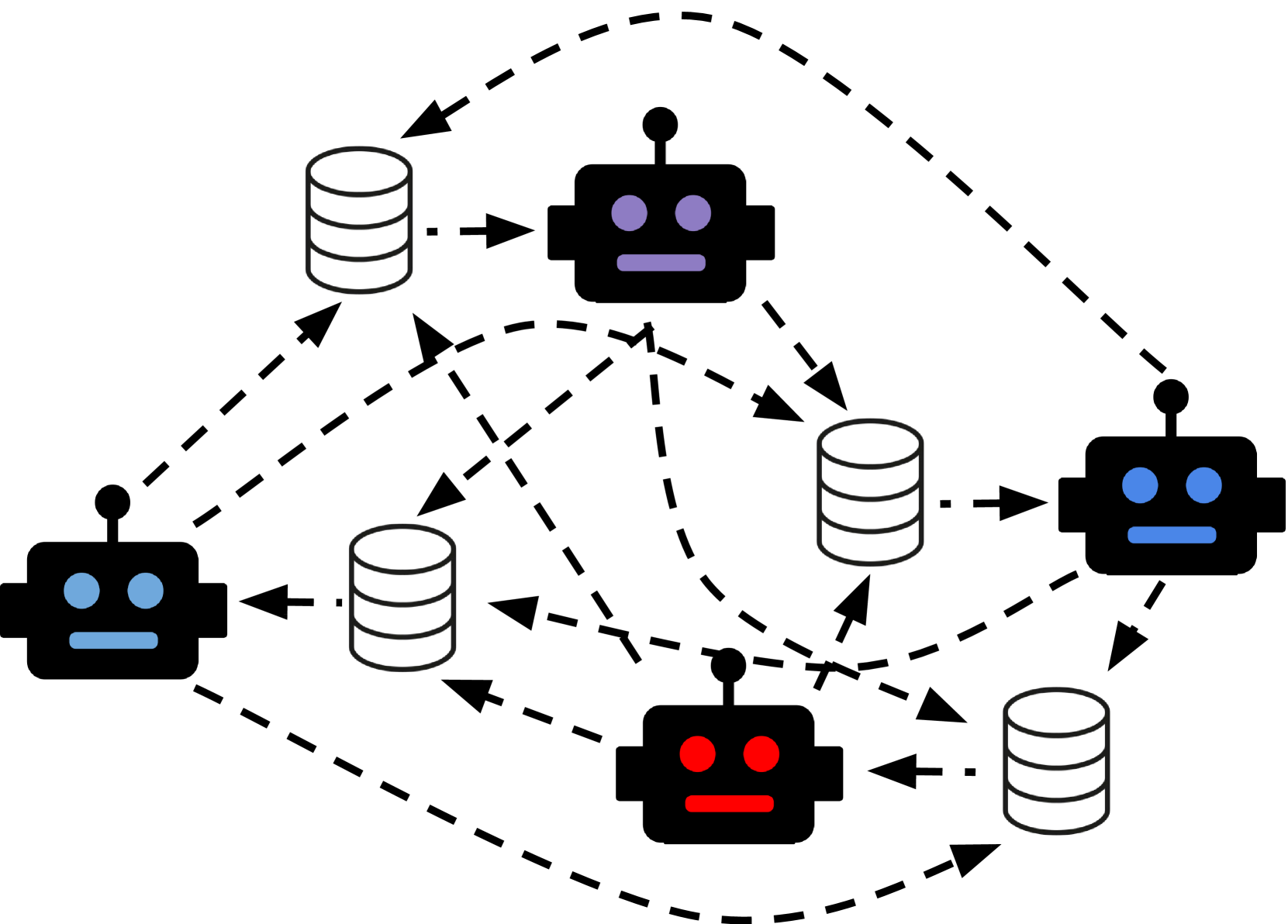
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) are capable of producing high quality information at unprecedented rates. As these models continue to entrench themselves in society, the content they produce will become increasingly pervasive in databases that are, in turn, incorporated into the pre-training data, fine-tuning data, retrieval data, etc. of other language models. In this paper we formalize the idea of a communication network of LLMs and introduce a method for representing the perspective of individual models within a collection of LLMs. Given these tools we systematically study information diffusion in the communication network of LLMs in various simulated settings.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the perspectives and interactions of large language models (LLMs) in a communication network.
- The researchers define a "perspective extraction" technique to track the evolving viewpoints of LLMs as they engage in dialogue.
- The paper examines how LLMs' perspectives shift and converge over the course of a conversation, providing insights into the underlying mechanisms of these complex systems.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 and DALL-E have become increasingly powerful at generating human-like text and images. However, as these models become more advanced, it's important to understand how they form and change their perspectives during interactions.
In this paper, the researchers propose a technique called "perspective extraction" to track the evolving viewpoints of LLMs as they engage in dialogue. By monitoring how an LLM's opinions and beliefs shift over the course of a conversation, the researchers can gain insights into the underlying mechanisms driving these complex systems.
For example, imagine two LLMs discussing a controversial topic. As they exchange ideas, their perspectives may start to converge or diverge, reflecting the nuanced ways these models process and respond to information. By analyzing these perspective changes, we can better understand how LLMs form and adapt their views, which has important implications for the use of LLMs in education and other domains.
Technical Explanation
The researchers first establish a communication network of LLMs, where multiple models can interact with each other through a series of text exchanges. They then define a "perspective extraction" technique that involves tracking the evolution of an LLM's opinions, beliefs, and stances over the course of a conversation.
This technique involves several key steps:
- Representing the LLM's perspectives as high-dimensional vectors, capturing the model's beliefs and attitudes on a range of topics.
- Monitoring how these perspective vectors change as the LLMs engage in dialogue, using techniques like cosine similarity to quantify the shifts.
- Analyzing the patterns and trends in perspective changes, such as convergence, divergence, or the emergence of new viewpoints.
By applying this approach to various LLM interactions, the researchers were able to uncover insights about the underlying cognitive processes driving these models. For example, they observed that LLMs can sometimes develop shared perspectives through iterative exchanges, while in other cases, their viewpoints may become increasingly polarized.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a novel and promising approach for studying the evolving perspectives of interacting LLMs. However, it's important to note that this research is still in its early stages, and there are several limitations and areas for further exploration:
- The perspective extraction technique relies on certain assumptions and simplifications, which may not fully capture the nuanced ways LLMs form and update their beliefs.
- The paper focuses on relatively simple dialogues, and it's unclear how well the approach would scale to more complex, open-ended conversations.
- The researchers acknowledge that their analysis does not directly shed light on the interpretability or "inner workings" of LLMs, which is a critical area for further research on these models.
Nevertheless, this work represents an important step towards understanding the dynamic and interactive nature of LLMs, which will be crucial as these technologies become more prevalent in various applications, from natural language processing to content generation. By continuing to study the perspectives and interactions of LLMs, researchers can work towards developing more transparent, accountable, and ethical AI systems.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach for tracking the evolving perspectives of interacting large language models (LLMs). By defining a "perspective extraction" technique, the researchers were able to monitor how an LLM's opinions and beliefs shift during a conversation, providing insights into the underlying cognitive processes driving these complex systems.
While the research is still in its early stages, this work represents an important step towards understanding the dynamic and interactive nature of LLMs. As these technologies become increasingly prevalent in various applications, from natural language processing to content generation, it will be crucial to continue studying their perspectives and interactions, in order to develop more transparent, accountable, and ethical AI systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
Exploring the landscape of large language models: Foundations, techniques, and challenges
Milad Moradi, Ke Yan, David Colwell, Matthias Samwald, Rhona Asgari

0
0
In this review paper, we delve into the realm of Large Language Models (LLMs), covering their foundational principles, diverse applications, and nuanced training processes. The article sheds light on the mechanics of in-context learning and a spectrum of fine-tuning approaches, with a special focus on methods that optimize efficiency in parameter usage. Additionally, it explores how LLMs can be more closely aligned with human preferences through innovative reinforcement learning frameworks and other novel methods that incorporate human feedback. The article also examines the emerging technique of retrieval augmented generation, integrating external knowledge into LLMs. The ethical dimensions of LLM deployment are discussed, underscoring the need for mindful and responsible application. Concluding with a perspective on future research trajectories, this review offers a succinct yet comprehensive overview of the current state and emerging trends in the evolving landscape of LLMs, serving as an insightful guide for both researchers and practitioners in artificial intelligence.
4/19/2024
💬
Large Language Models as Instruments of Power: New Regimes of Autonomous Manipulation and Control
Yaqub Chaudhary, Jonnie Penn

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) can reproduce a wide variety of rhetorical styles and generate text that expresses a broad spectrum of sentiments. This capacity, now available at low cost, makes them powerful tools for manipulation and control. In this paper, we consider a set of underestimated societal harms made possible by the rapid and largely unregulated adoption of LLMs. Rather than consider LLMs as isolated digital artefacts used to displace this or that area of work, we focus on the large-scale computational infrastructure upon which they are instrumentalised across domains. We begin with discussion on how LLMs may be used to both pollute and uniformize information environments and how these modalities may be leveraged as mechanisms of control. We then draw attention to several areas of emerging research, each of which compounds the capabilities of LLMs as instruments of power. These include (i) persuasion through the real-time design of choice architectures in conversational interfaces (e.g., via AI personas), (ii) the use of LLM-agents as computational models of human agents (e.g., silicon subjects), (iii) the use of LLM-agents as computational models of human agent populations (e.g., silicon societies) and finally, (iv) the combination of LLMs with reinforcement learning to produce controllable and steerable strategic dialogue models. We draw these strands together to discuss how these areas may be combined to build LLM-based systems that serve as powerful instruments of individual, social and political control via the simulation and disingenuous prediction of human behaviour, intent, and action.
5/8/2024

Large Knowledge Model: Perspectives and Challenges
Huajun Chen

0
0
Humankind's understanding of the world is fundamentally linked to our perception and cognition, with emph{human languages} serving as one of the major carriers of emph{world knowledge}. In this vein, emph{Large Language Models} (LLMs) like ChatGPT epitomize the pre-training of extensive, sequence-based world knowledge into neural networks, facilitating the processing and manipulation of this knowledge in a parametric space. This article explores large models through the lens of knowledge. We initially investigate the role of symbolic knowledge such as Knowledge Graphs (KGs) in enhancing LLMs, covering aspects like knowledge-augmented language model, structure-inducing pre-training, knowledgeable prompts, structured CoT, knowledge editing, semantic tools for LLM and knowledgeable AI agents. Subsequently, we examine how LLMs can boost traditional symbolic knowledge bases, encompassing aspects like using LLM as KG builder and controller, structured knowledge pretraining, and LLM-enhanced symbolic reasoning. Considering the intricate nature of human knowledge, we advocate for the creation of emph{Large Knowledge Models} (LKM), specifically engineered to manage diversified spectrum of knowledge structures. This promising undertaking would entail several key challenges, such as disentangling knowledge base from language models, cognitive alignment with human knowledge, integration of perception and cognition, and building large commonsense models for interacting with physical world, among others. We finally propose a five-A principle to distinguish the concept of LKM.
6/27/2024
💬
A Philosophical Introduction to Language Models - Part II: The Way Forward
Raphael Milli`ere, Cameron Buckner

0
0
In this paper, the second of two companion pieces, we explore novel philosophical questions raised by recent progress in large language models (LLMs) that go beyond the classical debates covered in the first part. We focus particularly on issues related to interpretability, examining evidence from causal intervention methods about the nature of LLMs' internal representations and computations. We also discuss the implications of multimodal and modular extensions of LLMs, recent debates about whether such systems may meet minimal criteria for consciousness, and concerns about secrecy and reproducibility in LLM research. Finally, we discuss whether LLM-like systems may be relevant to modeling aspects of human cognition, if their architectural characteristics and learning scenario are adequately constrained.
5/7/2024