Transformer based neural networks for emotion recognition in conversations
2405.11222

0
0

Abstract
This paper outlines the approach of the ISDS-NLP team in the SemEval 2024 Task 10: Emotion Discovery and Reasoning its Flip in Conversation (EDiReF). For Subtask 1 we obtained a weighted F1 score of 0.43 and placed 12 in the leaderboard. We investigate two distinct approaches: Masked Language Modeling (MLM) and Causal Language Modeling (CLM). For MLM, we employ pre-trained BERT-like models in a multilingual setting, fine-tuning them with a classifier to predict emotions. Experiments with varying input lengths, classifier architectures, and fine-tuning strategies demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach. Additionally, we utilize Mistral 7B Instruct V0.2, a state-of-the-art model, applying zero-shot and few-shot prompting techniques. Our findings indicate that while Mistral shows promise, MLMs currently outperform them in sentence-level emotion classification.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents the ISDS-NLP team's approach to the SemEval-2024 Task 10: Emotion Recognition in Conversations.
- The team used transformer-based neural networks to tackle the challenge of emotion recognition in dialogues.
- Key techniques employed include fine-tuning pre-trained language models and incorporating conversational context information.
Plain English Explanation
The ISDS-NLP team took on the task of recognizing emotions in conversations, which can be a tricky challenge. They used a type of artificial intelligence called transformer-based neural networks to try to solve this problem. These networks are good at understanding language and can be trained on large amounts of data.
The team's approach involved taking a pre-trained language model and fine-tuning it, which means they adapted it to work better for the specific task of emotion recognition. They also incorporated information about the context of the conversation, not just the individual messages, to help the model understand the emotions better.
Overall, the ISDS-NLP team used state-of-the-art techniques in natural language processing to tackle this challenging problem of recognizing emotions in dialogues. Their work could help advance the field of emotion analysis and have applications in areas like customer service, mental health support, and more.
Technical Explanation
The ISDS-NLP team approached the SemEval-2024 Task 10 on Emotion Recognition in Conversations by leveraging transformer-based neural network architectures. They fine-tuned pre-trained language models, such as BERT and RoBERTa, to adapt them to the specific task of emotion classification in dialogue contexts.
To incorporate conversational context, the team explored different strategies, including concatenating the current message with previous messages in the dialogue, as well as using hierarchical transformer models that can capture the structure of the conversation. They also experimented with various input representations, such as incorporating speaker information and timestamps.
The team's models were trained and evaluated on the provided dataset for the SemEval-2024 Task 10. They measured performance using standard metrics such as accuracy, F1-score, and macro-averaged F1-score, comparing their results to other participating teams.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the ISDS-NLP team's approach to the emotion recognition task, highlighting their use of transformer-based models and their efforts to incorporate conversational context. However, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific architectural choices, hyperparameter tuning, or ablation studies that were conducted to arrive at the final model configurations.
Additionally, the paper could benefit from a more detailed discussion of the challenges and limitations encountered during the research, such as the inherent complexities of emotion recognition in dialogues, the potential biases in the dataset, or the generalizability of the proposed solutions.
It would also be valuable to see a comparative analysis of the ISDS-NLP approach with other participating teams, such as IITK-AT-SEMEVAL-2024-TASK-10-WHO, LYS-AT-SEMEVAL-2024-TASK-3-EARLY, PETKAZ-AT-SEMEVAL-2024-TASK-3-ADVANCING, or SAMSUNG-RESEARCH-CHINA-BEIJING-AT-SEMEVAL-2024, to better understand the relative strengths and weaknesses of the ISDS-NLP approach.
Conclusion
The ISDS-NLP team's work on emotion recognition in conversations using transformer-based neural networks is a valuable contribution to the field of natural language processing. Their approach of fine-tuning pre-trained language models and incorporating conversational context information demonstrates the potential of such techniques for tackling the complex challenge of emotion analysis in dialogues.
While the paper provides a solid technical overview, further exploration of the limitations, comparative analysis, and potential areas for improvement could strengthen the research and its impact. Nonetheless, the ISDS-NLP team's work highlights the ongoing advancements in the field and the promising applications of these techniques in various domains, such as customer service, mental health support, and beyond.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

IITK at SemEval-2024 Task 10: Who is the speaker? Improving Emotion Recognition and Flip Reasoning in Conversations via Speaker Embeddings
Shubham Patel, Divyaksh Shukla, Ashutosh Modi

0
0
This paper presents our approach for the SemEval-2024 Task 10: Emotion Discovery and Reasoning its Flip in Conversations. For the Emotion Recognition in Conversations (ERC) task, we utilize a masked-memory network along with speaker participation. We propose a transformer-based speaker-centric model for the Emotion Flip Reasoning (EFR) task. We also introduce Probable Trigger Zone, a region of the conversation that is more likely to contain the utterances causing the emotion to flip. For sub-task 3, the proposed approach achieves a 5.9 (F1 score) improvement over the task baseline. The ablation study results highlight the significance of various design choices in the proposed method.
4/9/2024
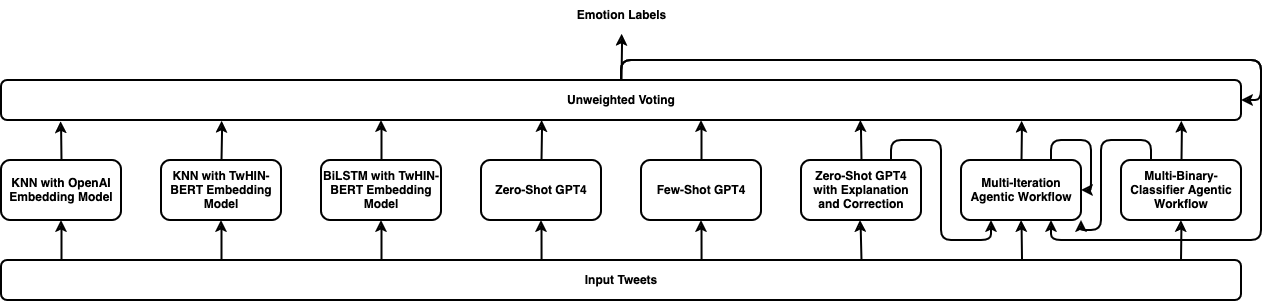
TEII: Think, Explain, Interact and Iterate with Large Language Models to Solve Cross-lingual Emotion Detection
Long Cheng, Qihao Shao, Christine Zhao, Sheng Bi, Gina-Anne Levow

0
0
Cross-lingual emotion detection allows us to analyze global trends, public opinion, and social phenomena at scale. We participated in the Explainability of Cross-lingual Emotion Detection (EXALT) shared task, achieving an F1-score of 0.6046 on the evaluation set for the emotion detection sub-task. Our system outperformed the baseline by more than 0.16 F1-score absolute, and ranked second amongst competing systems. We conducted experiments using fine-tuning, zero-shot learning, and few-shot learning for Large Language Model (LLM)-based models as well as embedding-based BiLSTM and KNN for non-LLM-based techniques. Additionally, we introduced two novel methods: the Multi-Iteration Agentic Workflow and the Multi-Binary-Classifier Agentic Workflow. We found that LLM-based approaches provided good performance on multilingual emotion detection. Furthermore, ensembles combining all our experimented models yielded higher F1-scores than any single approach alone.
5/28/2024
🛠️
New!MasonTigers at SemEval-2024 Task 10: Emotion Discovery and Flip Reasoning in Conversation with Ensemble of Transformers and Prompting
Al Nahian Bin Emran, Amrita Ganguly, Sadiya Sayara Chowdhury Puspo, Nishat Raihan, Dhiman Goswami

0
0
In this paper, we present MasonTigers' participation in SemEval-2024 Task 10, a shared task aimed at identifying emotions and understanding the rationale behind their flips within monolingual English and Hindi-English code-mixed dialogues. This task comprises three distinct subtasks - emotion recognition in conversation for Hindi-English code-mixed dialogues, emotion flip reasoning for Hindi-English code-mixed dialogues, and emotion flip reasoning for English dialogues. Our team, MasonTigers, contributed to each subtask, focusing on developing methods for accurate emotion recognition and reasoning. By leveraging our approaches, we attained impressive F1-scores of 0.78 for the first task and 0.79 for both the second and third tasks. This performance not only underscores the effectiveness of our methods across different aspects of the task but also secured us the top rank in the first and third subtasks, and the 2nd rank in the second subtask. Through extensive experimentation and analysis, we provide insights into our system's performance and contributions to each subtask.
7/2/2024
🔄
LyS at SemEval-2024 Task 3: An Early Prototype for End-to-End Multimodal Emotion Linking as Graph-Based Parsing
Ana Ezquerro, David Vilares

0
0
This paper describes our participation in SemEval 2024 Task 3, which focused on Multimodal Emotion Cause Analysis in Conversations. We developed an early prototype for an end-to-end system that uses graph-based methods from dependency parsing to identify causal emotion relations in multi-party conversations. Our model comprises a neural transformer-based encoder for contextualizing multimodal conversation data and a graph-based decoder for generating the adjacency matrix scores of the causal graph. We ranked 7th out of 15 valid and official submissions for Subtask 1, using textual inputs only. We also discuss our participation in Subtask 2 during post-evaluation using multi-modal inputs.
5/13/2024