Unsupervised Blind Joint Dereverberation and Room Acoustics Estimation with Diffusion Models

0

Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Unsupervised Blind Joint Dereverberation and Room Acoustics Estimation with Diffusion Models
Jean-Marie Lemercier, Eloi Moliner, Simon Welker, Vesa Valimaki, Timo Gerkmann
This paper presents an unsupervised method for single-channel blind dereverberation and room impulse response (RIR) estimation, called BUDDy. The algorithm is rooted in Bayesian posterior sampling: it combines a likelihood model enforcing fidelity to the reverberant measurement, and an anechoic speech prior implemented by an unconditional diffusion model. We design a parametric filter representing the RIR, with exponential decay for each frequency subband. Room acoustics estimation and speech dereverberation are jointly carried out, as the filter parameters are iteratively estimated and the speech utterance refined along the reverse diffusion trajectory. In a blind scenario where the room impulse response is unknown, BUDDy successfully performs speech dereverberation in various acoustic scenarios, significantly outperforming other blind unsupervised baselines. Unlike supervised methods, which often struggle to generalize, BUDDy seamlessly adapts to different acoustic conditions. This paper extends our previous work by offering new experimental results and insights into the algorithm's performance and versatility. We first investigate the robustness of informed dereverberation methods to RIR estimation errors, to motivate the joint acoustic estimation and dereverberation paradigm. Then, we demonstrate the adaptability of our method to high-resolution singing voice dereverberation, study its performance in RIR estimation, and conduct subjective evaluation experiments to validate the perceptual quality of the results, among other contributions. Audio samples and code can be found online.
Read more8/15/2024
🤷

0
BUDDy: Single-Channel Blind Unsupervised Dereverberation with Diffusion Models
Eloi Moliner, Jean-Marie Lemercier, Simon Welker, Timo Gerkmann, Vesa Valimaki
In this paper, we present an unsupervised single-channel method for joint blind dereverberation and room impulse response estimation, based on posterior sampling with diffusion models. We parameterize the reverberation operator using a filter with exponential decay for each frequency subband, and iteratively estimate the corresponding parameters as the speech utterance gets refined along the reverse diffusion trajectory. A measurement consistency criterion enforces the fidelity of the generated speech with the reverberant measurement, while an unconditional diffusion model implements a strong prior for clean speech generation. Without any knowledge of the room impulse response nor any coupled reverberant-anechoic data, we can successfully perform dereverberation in various acoustic scenarios. Our method significantly outperforms previous blind unsupervised baselines, and we demonstrate its increased robustness to unseen acoustic conditions in comparison to blind supervised methods. Audio samples and code are available online.
Read more5/8/2024
🗣️

0
Speech dereverberation constrained on room impulse response characteristics
Louis Bahrman (S2A, IDS), Mathieu Fontaine (S2A, IDS), Jonathan Le Roux (MERL), Gael Richard (S2A, IDS)
Single-channel speech dereverberation aims at extracting a dry speech signal from a recording affected by the acoustic reflections in a room. However, most current deep learning-based approaches for speech dereverberation are not interpretable for room acoustics, and can be considered as black-box systems in that regard. In this work, we address this problem by regularizing the training loss using a novel physical coherence loss which encourages the room impulse response (RIR) induced by the dereverberated output of the model to match the acoustic properties of the room in which the signal was recorded. Our investigation demonstrates the preservation of the original dereverberated signal alongside the provision of a more physically coherent RIR.
Read more7/12/2024
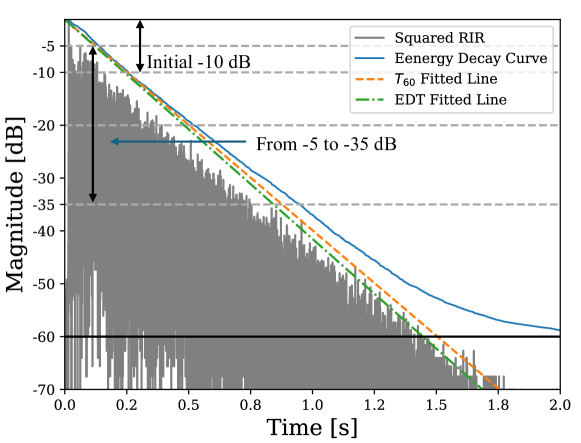

0
BERP: A Blind Estimator of Room Acoustic and Physical Parameters for Single-Channel Noisy Speech Signals
Lijun Wang, Yixian Lu, Ziyan Gao, Kai Li, Jianqiang Huang, Yuntao Kong, Shogo Okada
Room acoustic parameters (RAPs) and room physical parameters ( RPPs) are essential metrics for parameterizing the room acoustical characteristics (RAC) of a sound field around a listener's local environment, offering comprehensive indications for various applications. The current RAPs and RPPs estimation methods either fall short of covering broad real-world acoustic environments in the context of real background noise or lack universal frameworks for blindly estimating RAPs and RPPs from noisy single-channel speech signals, particularly sound source distances, direction-of-arrival (DOA) of sound sources, and occupancy levels. On the other hand, in this paper, we propose a novel universal blind estimation framework called the blind estimator of room acoustical and physical parameters (BERP), by introducing a new stochastic room impulse response (RIR) model, namely, the sparse stochastic impulse response (SSIR) model, and endowing the BERP with a unified encoder and multiple separate predictors to estimate RPPs and SSIR parameters in parallel. This estimation framework enables the computationally efficient and universal estimation of room parameters by solely using noisy single-channel speech signals. Finally, all the RAPs can be simultaneously derived from the RIRs synthesized from SSIR model with the estimated parameters. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed BERP and SSIR models, we compile a task-specific dataset from several publicly available datasets. The results reveal that the BERP achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Moreover, the evaluation results pertaining to the SSIR RIR model also demonstrated its efficacy. The code is available on GitHub.
Read more5/17/2024