Visual Deformation Detection Using Soft Material Simulation for Pre-training of Condition Assessment Models

0
🔎
Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔎

0
Visual Deformation Detection Using Soft Material Simulation for Pre-training of Condition Assessment Models
Joel Sol, Amir M. Soufi Enayati, Homayoun Najjaran
This paper addresses the challenge of geometric quality assurance in manufacturing, particularly when human assessment is required. It proposes using Blender, an open-source simulation tool, to create synthetic datasets for machine learning (ML) models. The process involves translating expert information into shape key parameters to simulate deformations, generating images for both deformed and non-deformed objects. The study explores the impact of discrepancies between real and simulated environments on ML model performance and investigates the effect of different simulation backgrounds on model sensitivity. Additionally, the study aims to enhance the model's robustness to camera positioning by generating datasets with a variety of randomized viewpoints. The entire process, from data synthesis to model training and testing, is implemented using a Python API interfacing with Blender. An experiment with a soda can object validates the accuracy of the proposed pipeline.
Read more5/27/2024


0
Sim-to-Real Domain Adaptation for Deformation Classification
Joel Sol, Jamil Fayyad, Shadi Alijani, Homayoun Najjaran
Deformation detection is vital for enabling accurate assessment and prediction of structural changes in materials, ensuring timely and effective interventions to maintain safety and integrity. Automating deformation detection through computer vision is crucial for efficient monitoring, but it faces significant challenges in creating a comprehensive dataset of both deformed and non-deformed objects, which can be difficult to obtain in many scenarios. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework for generating controlled synthetic data that simulates deformed objects. This approach allows for the realistic modeling of object deformations under various conditions. Our framework integrates an intelligent adapter network that facilitates sim-to-real domain adaptation, enhancing classification results without requiring real data from deformed objects. We conduct experiments on domain adaptation and classification tasks and demonstrate that our framework improves sim-to-real classification results compared to simulation baseline.
Read more7/16/2024
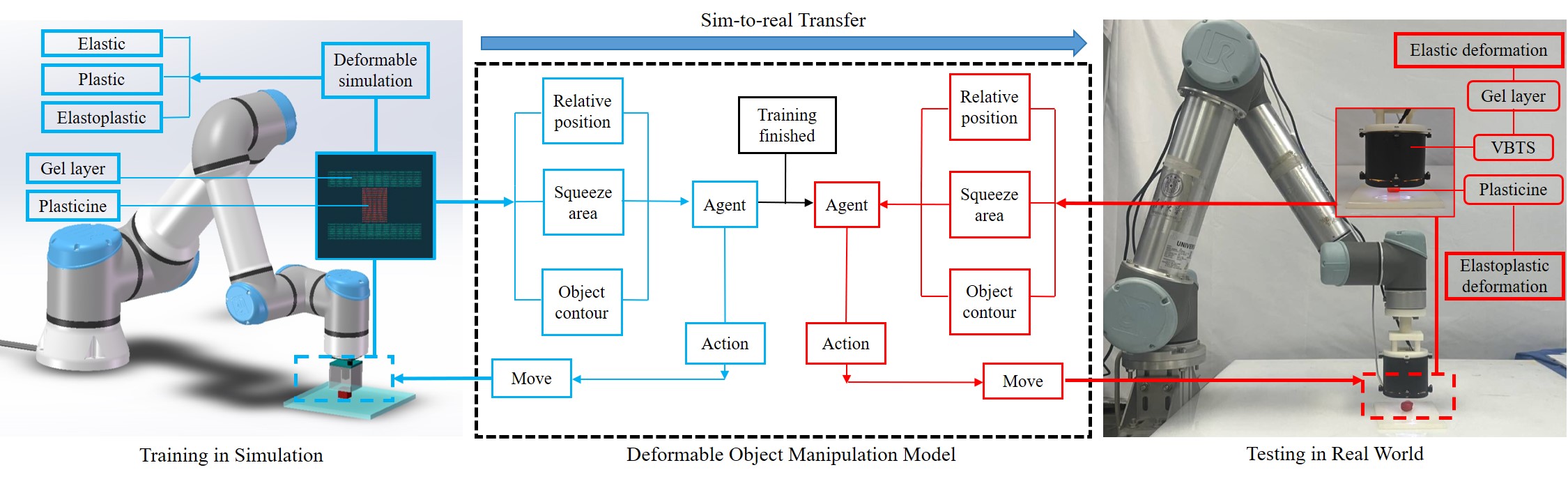

0
Soft Contact Simulation and Manipulation Learning of Deformable Objects with Vision-based Tactile Sensor
Jianhua Shan, Yuhao Sun, Shixin Zhang, Fuchun Sun, Zixi Chen, Zirong Shen, Cesare Stefanini, Yiyong Yang, Shan Luo, Bin Fang
Deformable object manipulation is a classical and challenging research area in robotics. Compared with rigid object manipulation, this problem is more complex due to the deformation properties including elastic, plastic, and elastoplastic deformation. In this paper, we describe a new deformable object manipulation method including soft contact simulation, manipulation learning, and sim-to-real transfer. We propose a novel approach utilizing Vision-Based Tactile Sensors (VBTSs) as the end-effector in simulation to produce observations like relative position, squeezed area, and object contour, which are transferable to real robots. For a more realistic contact simulation, a new simulation environment including elastic, plastic, and elastoplastic deformations is created. We utilize RL strategies to train agents in the simulation, and expert demonstrations are applied for challenging tasks. Finally, we build a real experimental platform to complete the sim-to-real transfer and achieve a 90% success rate on difficult tasks such as cylinder and sphere. To test the robustness of our method, we use plasticine of different hardness and sizes to repeat the tasks including cylinder and sphere. The experimental results show superior performances of deformable object manipulation with the proposed method.
Read more5/14/2024


0
Function based sim-to-real learning for shape control of deformable free-form surfaces
Yingjun Tian, Guoxin Fang, Renbo Su, Weiming Wang, Simeon Gill, Andrew Weightman, Charlie C. L. Wang
For the shape control of deformable free-form surfaces, simulation plays a crucial role in establishing the mapping between the actuation parameters and the deformed shapes. The differentiation of this forward kinematic mapping is usually employed to solve the inverse kinematic problem for determining the actuation parameters that can realize a target shape. However, the free-form surfaces obtained from simulators are always different from the physically deformed shapes due to the errors introduced by hardware and the simplification adopted in physical simulation. To fill the gap, we propose a novel deformation function based sim-to-real learning method that can map the geometric shape of a simulated model into its corresponding shape of the physical model. Unlike the existing sim-to-real learning methods that rely on completely acquired dense markers, our method accommodates sparsely distributed markers and can resiliently use all captured frames -- even for those in the presence of missing markers. To demonstrate its effectiveness, our sim-to-real method has been integrated into a neural network-based computational pipeline designed to tackle the inverse kinematic problem on a pneumatically actuated deformable mannequin.
Read more5/16/2024