WaterMamba: Visual State Space Model for Underwater Image Enhancement

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
• This paper introduces WaterMamba, a visual state space model for enhancing underwater images. The key ideas include:
- Developing a state space model to capture the complex underwater image formation process
- Leveraging this model to effectively restore the original scene colors and details in degraded underwater images
- Achieving high-quality results with low computational cost, making it suitable for real-time applications
Plain English Explanation
WaterMamba is a new technique for improving the quality of underwater images. Underwater photos often look hazy, dull, and lacking in detail due to the effects of water on light. WaterMamba uses a mathematical model called a "state space model" to understand how these underwater effects distort the original image.
By learning this model, WaterMamba can then reverse the distortions and recover the true colors and details of the scene, producing much clearer and more vibrant underwater images. Importantly, WaterMamba can do this very efficiently, requiring only a small amount of computational power. This makes it practical for real-time applications like underwater robotics or live video feeds.
Technical Explanation
The core of WaterMamba is a state space model that captures the complex underwater image formation process. This model represents the original scene's colors and details as "hidden states" that are gradually distorted by factors like light scattering and absorption as the light travels through the water.
By learning this state space model from training data, WaterMamba can then infer the original hidden states from an observed degraded underwater image. This allows it to restore the true scene colors and details in a computationally efficient way.
The authors also introduce several key innovations, including a selective state space model that focuses on the most important color channels, and a fusion strategy that combines information from multiple input frames. These techniques enable WaterMamba to achieve high-quality results while remaining lightweight and suitable for real-time applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough technical explanation of the WaterMamba system and demonstrates its effectiveness through extensive experiments. However, the authors acknowledge some limitations:
- The model assumes a static underwater environment, so it may not perform as well on scenes with significant motion or changing lighting conditions.
- The training process requires a dataset of paired degraded and ground truth underwater images, which can be challenging to obtain in practice.
- While computationally efficient, WaterMamba may still not be lightweight enough for some resource-constrained applications like low-power underwater drones.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the potential negative impacts of enhanced underwater imagery, such as its use for illegal fishing or environmental monitoring. Further research is needed to understand the ethical implications of this technology.
Conclusion
Overall, WaterMamba represents a promising advance in underwater image enhancement, offering a principled and efficient approach to restoring the true colors and details of underwater scenes. Its combination of strong technical performance and real-time capabilities could make it a valuable tool for a variety of underwater applications, from marine research to underwater robotics. As with any powerful technology, however, it will be important to consider potential ethical and societal implications as the research in this area continues to evolve.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
WaterMamba: Visual State Space Model for Underwater Image Enhancement
Meisheng Guan, Haiyong Xu, Gangyi Jiang, Mei Yu, Yeyao Chen, Ting Luo, Yang Song
Underwater imaging often suffers from low quality due to factors affecting light propagation and absorption in water. To improve image quality, some underwater image enhancement (UIE) methods based on convolutional neural networks (CNN) and Transformer have been proposed. However, CNN-based UIE methods are limited in modeling long-range dependencies, and Transformer-based methods involve a large number of parameters and complex self-attention mechanisms, posing efficiency challenges. Considering computational complexity and severe underwater image degradation, a state space model (SSM) with linear computational complexity for UIE, named WaterMamba, is proposed. We propose spatial-channel omnidirectional selective scan (SCOSS) blocks comprising spatial-channel coordinate omnidirectional selective scan (SCCOSS) modules and a multi-scale feedforward network (MSFFN). The SCOSS block models pixel and channel information flow, addressing dependencies. The MSFFN facilitates information flow adjustment and promotes synchronized operations within SCCOSS modules. Extensive experiments showcase WaterMamba's cutting-edge performance with reduced parameters and computational resources, outperforming state-of-the-art methods on various datasets, validating its effectiveness and generalizability. The code will be released on GitHub after acceptance.
Read more5/15/2024


0
O-Mamba: O-shape State-Space Model for Underwater Image Enhancement
Chenyu Dong, Chen Zhao, Weiling Cai, Bo Yang
Underwater image enhancement (UIE) face significant challenges due to complex underwater lighting conditions. Recently, mamba-based methods have achieved promising results in image enhancement tasks. However, these methods commonly rely on Vmamba, which focuses only on spatial information modeling and struggles to deal with the cross-color channel dependency problem in underwater images caused by the differential attenuation of light wavelengths, limiting the effective use of deep networks. In this paper, we propose a novel UIE framework called O-mamba. O-mamba employs an O-shaped dual-branch network to separately model spatial and cross-channel information, utilizing the efficient global receptive field of state-space models optimized for underwater images. To enhance information interaction between the two branches and effectively utilize multi-scale information, we design a Multi-scale Bi-mutual Promotion Module. This branch includes MS-MoE for fusing multi-scale information within branches, Mutual Promotion module for interaction between spatial and channel information across branches, and Cyclic Multi-scale optimization strategy to maximize the use of multi-scale information. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results.The code is available at https://github.com/chenydong/O-Mamba.
Read more8/26/2024

0
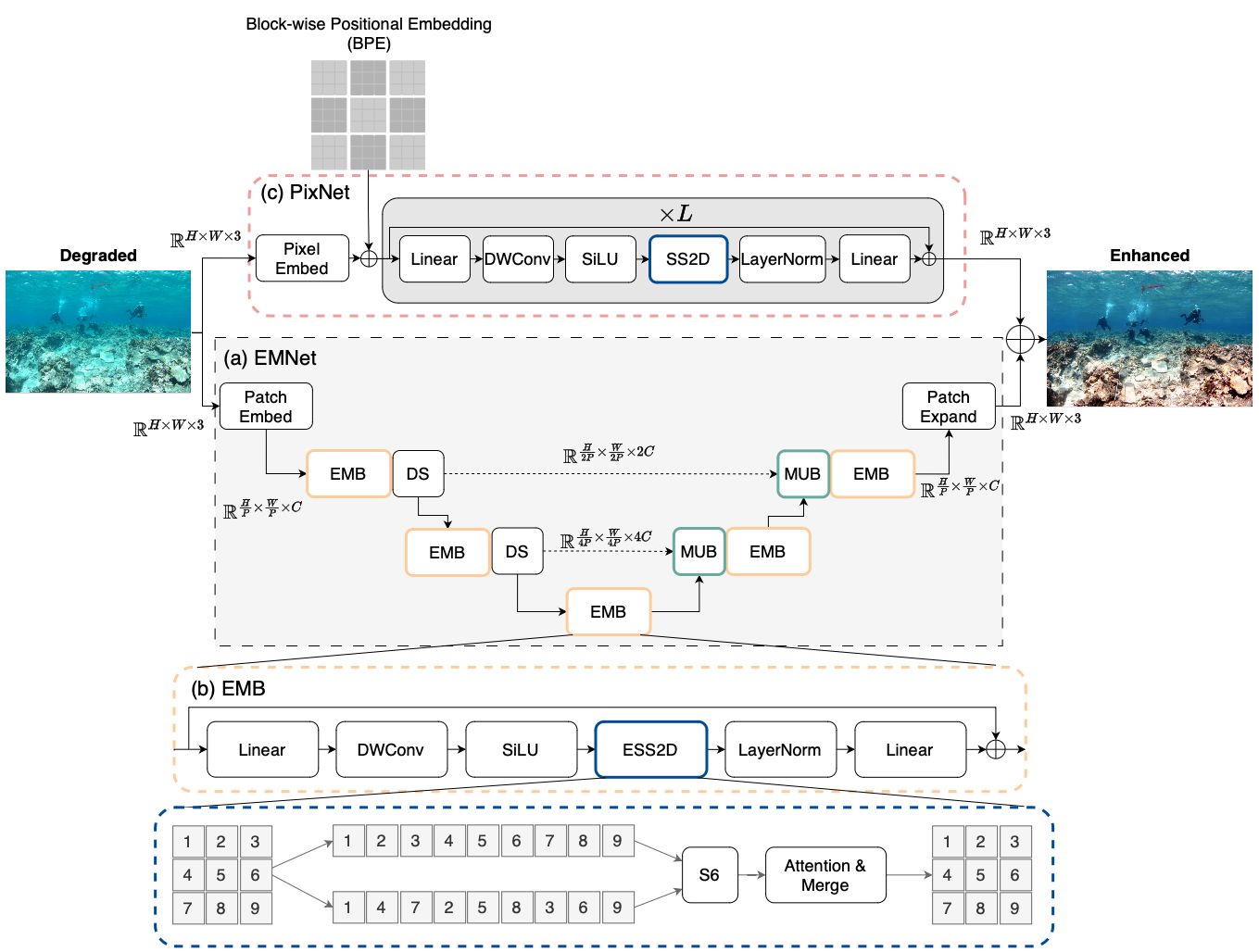
PixMamba: Leveraging State Space Models in a Dual-Level Architecture for Underwater Image Enhancement
Wei-Tung Lin, Yong-Xiang Lin, Jyun-Wei Chen, Kai-Lung Hua
Underwater Image Enhancement (UIE) is critical for marine research and exploration but hindered by complex color distortions and severe blurring. Recent deep learning-based methods have achieved remarkable results, yet these methods struggle with high computational costs and insufficient global modeling, resulting in locally under- or over- adjusted regions. We present PixMamba, a novel architecture, designed to overcome these challenges by leveraging State Space Models (SSMs) for efficient global dependency modeling. Unlike convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with limited receptive fields and transformer networks with high computational costs, PixMamba efficiently captures global contextual information while maintaining computational efficiency. Our dual-level strategy features the patch-level Efficient Mamba Net (EMNet) for reconstructing enhanced image feature and the pixel-level PixMamba Net (PixNet) to ensure fine-grained feature capturing and global consistency of enhanced image that were previously difficult to obtain. PixMamba achieves state-of-the-art performance across various underwater image datasets and delivers visually superior results. Code is available at: https://github.com/weitunglin/pixmamba.
Read more6/13/2024
🤷

0
MambaUIE&SR: Unraveling the Ocean's Secrets with Only 2.8 FLOPs
Zhihao Chen, Yiyuan Ge
Underwater Image Enhancement (UIE) techniques aim to address the problem of underwater image degradation due to light absorption and scattering. In recent years, both Convolution Neural Network (CNN)-based and Transformer-based methods have been widely explored. In addition, combining CNN and Transformer can effectively combine global and local information for enhancement. However, this approach is still affected by the secondary complexity of the Transformer and cannot maximize the performance. Recently, the state-space model (SSM) based architecture Mamba has been proposed, which excels in modeling long distances while maintaining linear complexity. This paper explores the potential of this SSM-based model for UIE from both efficiency and effectiveness perspectives. However, the performance of directly applying Mamba is poor because local fine-grained features, which are crucial for image enhancement, cannot be fully utilized. Specifically, we customize the MambaUIE architecture for efficient UIE. Specifically, we introduce visual state space (VSS) blocks to capture global contextual information at the macro level while mining local information at the micro level. Also, for these two kinds of information, we propose a Dynamic Interaction Block (DIB) and Spatial feed-forward Network (SGFN) for intra-block feature aggregation. MambaUIE is able to efficiently synthesize global and local information and maintains a very small number of parameters with high accuracy. Experiments on UIEB datasets show that our method reduces GFLOPs by 67.4% (2.715G) relative to the SOTA method. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first UIE model constructed based on SSM that breaks the limitation of FLOPs on accuracy in UIE. The official repository of MambaUIE at https://github.com/1024AILab/MambaUIE.
Read more5/27/2024