WorkArena: How Capable Are Web Agents at Solving Common Knowledge Work Tasks?

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces WorkArena, a new enterprise benchmark for evaluating autonomous agents in a realistic web environment.
- The benchmark aims to move beyond traditional text-based tasks and test agents' abilities to navigate, interact with, and reason about the content and structure of web pages.
- The paper also describes related work in building autonomous agents through large language models and evaluating multimodal agents on open-ended tasks.
Plain English Explanation
The paper introduces a new benchmark called WorkArena that is designed to test the capabilities of autonomous agents in a realistic web environment. Unlike traditional text-based tasks, WorkArena requires agents to navigate, interact with, and reason about the content and structure of web pages.
The goal of this benchmark is to move beyond the limitations of existing tests and better evaluate the abilities of autonomous agents to operate in a more complex, real-world setting. By presenting agents with a diverse range of web-based tasks and challenges, the researchers hope to gain a more nuanced understanding of their strengths and weaknesses.
The paper also discusses related work in the field of autonomous agents, including efforts to leverage large language models to build more capable agents, as well as research into evaluating multimodal agents on open-ended tasks. These related developments provide important context and help situate the WorkArena benchmark within the broader landscape of autonomous agent research.
Technical Explanation
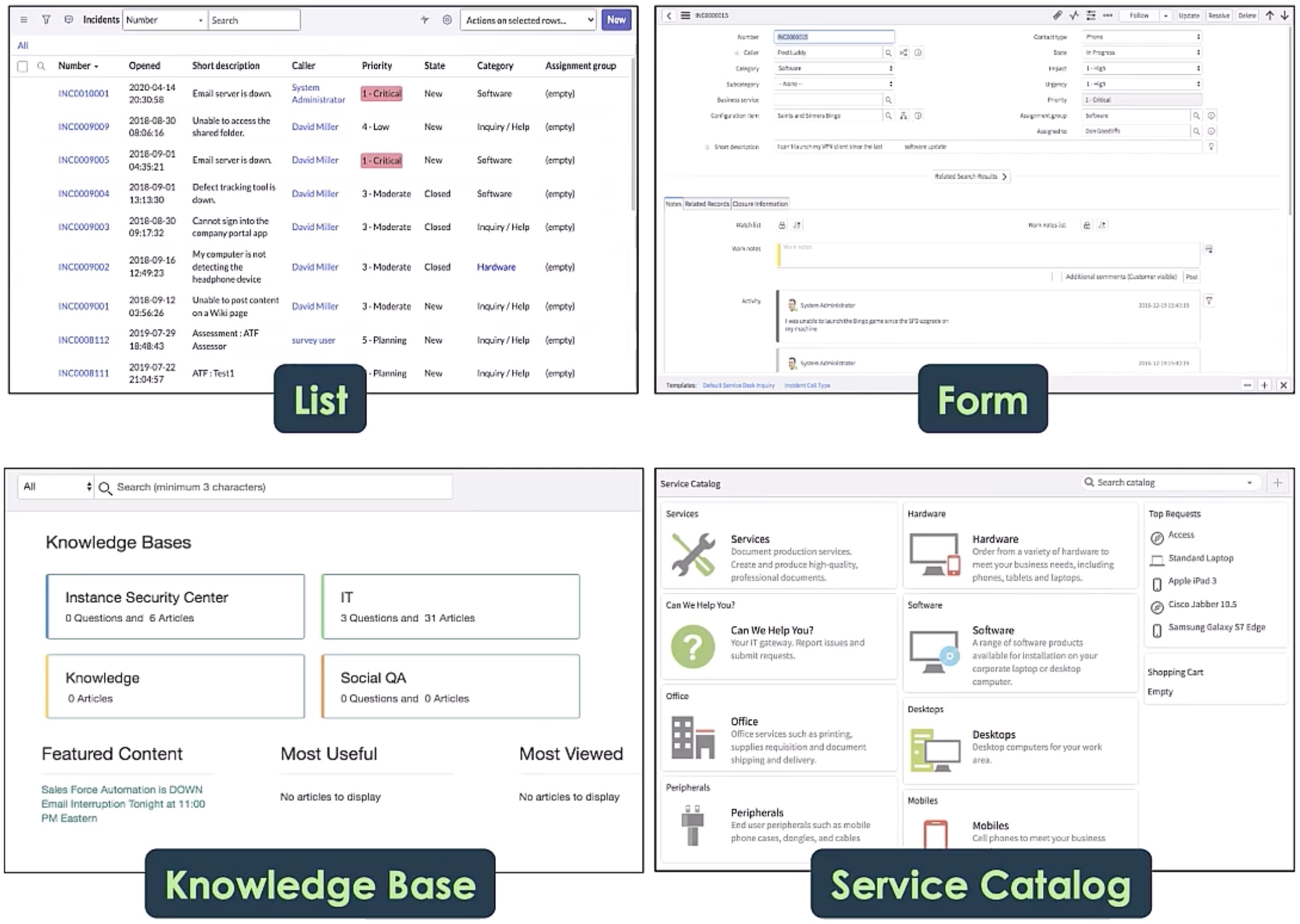
The WorkArena benchmark is designed to assess the performance of autonomous agents in a realistic web environment. It consists of a diverse set of tasks that require agents to navigate, interact with, and reason about the content and structure of web pages.
The tasks are designed to go beyond traditional text-based benchmarks and evaluate agents' abilities to handle more complex, multimodal inputs and outputs. For example, agents may need to extract information from web pages, follow links, fill out forms, and interact with various interactive elements.
The paper also discusses related research in the field of autonomous agents, including efforts to leverage large language models to build more capable agents, as well as work on evaluating multimodal agents on open-ended tasks. These related developments provide important context and help situate the WorkArena benchmark within the broader landscape of autonomous agent research.
Critical Analysis
The WorkArena benchmark represents an important step forward in the evaluation of autonomous agents, as it moves beyond traditional text-based tasks and challenges agents to operate in a more realistic, web-based environment. By incorporating a diverse range of tasks and multimodal inputs, the benchmark aims to provide a more comprehensive assessment of an agent's capabilities.
However, the paper acknowledges several limitations and areas for further research. For example, the tasks in WorkArena may not fully capture the complexity and unpredictability of real-world web interactions, and the evaluation metrics may not adequately capture all aspects of agent performance.
Additionally, the paper does not address potential ethical concerns related to the development and deployment of autonomous agents in web-based environments. Issues such as privacy, security, and the potential for unintended consequences would need to be carefully considered.
Overall, the WorkArena benchmark represents an important step forward in the field of autonomous agent research, but more work is needed to fully address the challenges and potential pitfalls of this emerging technology.
Conclusion
The WorkArena benchmark introduces a new approach to evaluating the capabilities of autonomous agents, moving beyond traditional text-based tasks and into the more complex and realistic domain of web-based interactions. By designing a diverse set of tasks that require agents to navigate, interact with, and reason about web content, the researchers aim to gain a more nuanced understanding of agent performance and capabilities.
This work builds on related research in the field of autonomous agents, including efforts to leverage large language models and evaluate multimodal agents on open-ended tasks. While the WorkArena benchmark represents an important step forward, the paper acknowledges several limitations and areas for further research, such as the need to more fully capture the complexity of real-world web interactions and address potential ethical concerns.
Overall, the WorkArena benchmark represents a significant contribution to the field of autonomous agent research, as it pushes the boundaries of existing evaluation methods and paves the way for a more comprehensive understanding of agent capabilities in realistic, web-based environments.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
WorkArena: How Capable Are Web Agents at Solving Common Knowledge Work Tasks?
Alexandre Drouin, Maxime Gasse, Massimo Caccia, Issam H. Laradji, Manuel Del Verme, Tom Marty, L'eo Boisvert, Megh Thakkar, Quentin Cappart, David Vazquez, Nicolas Chapados, Alexandre Lacoste
We study the use of large language model-based agents for interacting with software via web browsers. Unlike prior work, we focus on measuring the agents' ability to perform tasks that span the typical daily work of knowledge workers utilizing enterprise software systems. To this end, we propose WorkArena, a remote-hosted benchmark of 33 tasks based on the widely-used ServiceNow platform. We also introduce BrowserGym, an environment for the design and evaluation of such agents, offering a rich set of actions as well as multimodal observations. Our empirical evaluation reveals that while current agents show promise on WorkArena, there remains a considerable gap towards achieving full task automation. Notably, our analysis uncovers a significant performance disparity between open and closed-source LLMs, highlighting a critical area for future exploration and development in the field.
Read more7/24/2024
🛸

0
WorkArena++: Towards Compositional Planning and Reasoning-based Common Knowledge Work Tasks
L'eo Boisvert, Megh Thakkar, Maxime Gasse, Massimo Caccia, Thibault Le Sellier De Chezelles, Quentin Cappart, Nicolas Chapados, Alexandre Lacoste, Alexandre Drouin
The ability of large language models (LLMs) to mimic human-like intelligence has led to a surge in LLM-based autonomous agents. Though recent LLMs seem capable of planning and reasoning given user instructions, their effectiveness in applying these capabilities for autonomous task solving remains underexplored. This is especially true in enterprise settings, where automated agents hold the promise of a high impact. To fill this gap, we propose WorkArena++, a novel benchmark consisting of 682 tasks corresponding to realistic workflows routinely performed by knowledge workers. WorkArena++ is designed to evaluate the planning, problem-solving, logical/arithmetic reasoning, retrieval, and contextual understanding abilities of web agents. Our empirical studies across state-of-the-art LLMs and vision-language models (VLMs), as well as human workers, reveal several challenges for such models to serve as useful assistants in the workplace. In addition to the benchmark, we provide a mechanism to effortlessly generate thousands of ground-truth observation/action traces, which can be used for fine-tuning existing models. Overall, we expect this work to serve as a useful resource to help the community progress toward capable autonomous agents. The benchmark can be found at https://github.com/ServiceNow/WorkArena/tree/workarena-plus-plus.
Read more7/9/2024
⚙️

0
WebArena: A Realistic Web Environment for Building Autonomous Agents
Shuyan Zhou, Frank F. Xu, Hao Zhu, Xuhui Zhou, Robert Lo, Abishek Sridhar, Xianyi Cheng, Tianyue Ou, Yonatan Bisk, Daniel Fried, Uri Alon, Graham Neubig
With advances in generative AI, there is now potential for autonomous agents to manage daily tasks via natural language commands. However, current agents are primarily created and tested in simplified synthetic environments, leading to a disconnect with real-world scenarios. In this paper, we build an environment for language-guided agents that is highly realistic and reproducible. Specifically, we focus on agents that perform tasks on the web, and create an environment with fully functional websites from four common domains: e-commerce, social forum discussions, collaborative software development, and content management. Our environment is enriched with tools (e.g., a map) and external knowledge bases (e.g., user manuals) to encourage human-like task-solving. Building upon our environment, we release a set of benchmark tasks focusing on evaluating the functional correctness of task completions. The tasks in our benchmark are diverse, long-horizon, and designed to emulate tasks that humans routinely perform on the internet. We experiment with several baseline agents, integrating recent techniques such as reasoning before acting. The results demonstrate that solving complex tasks is challenging: our best GPT-4-based agent only achieves an end-to-end task success rate of 14.41%, significantly lower than the human performance of 78.24%. These results highlight the need for further development of robust agents, that current state-of-the-art large language models are far from perfect performance in these real-life tasks, and that WebArena can be used to measure such progress.
Read more4/17/2024


0
AssistantBench: Can Web Agents Solve Realistic and Time-Consuming Tasks?
Ori Yoran, Samuel Joseph Amouyal, Chaitanya Malaviya, Ben Bogin, Ofir Press, Jonathan Berant
Language agents, built on top of language models (LMs), are systems that can interact with complex environments, such as the open web. In this work, we examine whether such agents can perform realistic and time-consuming tasks on the web, e.g., monitoring real-estate markets or locating relevant nearby businesses. We introduce AssistantBench, a challenging new benchmark consisting of 214 realistic tasks that can be automatically evaluated, covering different scenarios and domains. We find that AssistantBench exposes the limitations of current systems, including language models and retrieval-augmented language models, as no model reaches an accuracy of more than 25 points. While closed-book LMs perform well, they exhibit low precision since they tend to hallucinate facts. State-of-the-art web agents reach a score of near zero. Additionally, we introduce SeePlanAct (SPA), a new web agent that significantly outperforms previous agents, and an ensemble of SPA and closed-book models reaches the best overall performance. Moreover, we analyze failures of current systems and highlight that web navigation remains a major challenge.
Read more7/23/2024