XHand: Real-time Expressive Hand Avatar

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents XHand, a real-time expressive hand avatar system.
- XHand can reconstruct 3D hand poses from images and generate animated hand avatars.
- The system leverages the MANO hand model to represent and animate the hand.
Plain English Explanation
XHand: Real-time Expressive Hand Avatar is a system that allows you to create and control a digital hand avatar in real-time. It can take images or video of a person's hand and reconstruct a 3D model of the hand's shape and movement.
This 3D hand model is based on the MANO hand model, which is a standard way to mathematically represent the structure and movement of the human hand. Using this model, the XHand system can then animate the digital hand avatar to match the motions and expressions of the real hand.
The key innovation of XHand is its ability to do this reconstruction and animation in real-time, allowing the hand avatar to move and gesture naturally along with the user's actual hand movements. This could have applications in areas like virtual reality, video conferencing, and human-computer interaction, where having a realistic and responsive hand avatar is important.
Technical Explanation
The paper describes how XHand works under the hood. It uses a deep learning model to take 2D images or video frames as input and estimate the 3D pose of the hand. This 3D pose information is then mapped onto the MANO hand model to generate the animated hand avatar.
The deep learning model is trained on a large dataset of hand images labeled with the corresponding 3D hand poses. This allows the model to learn the visual patterns associated with different hand configurations. During runtime, the model can take a new image as input and quickly output the estimated 3D hand pose.
The paper also discusses how XHand handles hand occlusions, where parts of the hand may be hidden from view. It uses an attention mechanism to focus the model on the visible parts of the hand and fill in the occluded regions based on the learned hand structure.
Additionally, the system incorporates real-time adaptation to adjust the hand avatar to better match the user's specific hand shape and movement patterns. This personalization helps ensure the avatar looks and behaves as realistically as possible.
Critical Analysis
The paper does a good job of highlighting the key capabilities and innovations of the XHand system. However, it does not go into extensive detail on the exact model architecture or training process. More information on these technical aspects would be helpful for researchers looking to build upon this work.
The paper also acknowledges some limitations of the current system, such as the need for a single, unoccluded view of the hand. Handling more complex hand poses and occlusions could be an area for future improvement.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss the potential privacy and ethical implications of a system that can reconstruct and animate highly personal hand movements. As this technology becomes more advanced and widespread, these societal considerations will be important to address.
Overall, the XHand system represents a promising step forward in real-time hand avatar generation, with applications in various interactive and immersive technologies. Further research and development in this area could lead to even more realistic and expressive digital hand representations.
Conclusion
XHand is a novel system that can reconstruct 3D hand poses from 2D images and generate animated hand avatars in real-time. By leveraging the MANO hand model, the system can create visually realistic and responsive hand avatars that can mimic the user's actual hand movements.
This technology could enable more natural and intuitive interactions in virtual environments, video conferencing, and other human-computer interface applications. As the field of 3D hand reconstruction and animation continues to evolve, the XHand approach demonstrates the potential for highly expressive and personalized digital hand representations.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
XHand: Real-time Expressive Hand Avatar
Qijun Gan, Zijie Zhou, Jianke Zhu
Hand avatars play a pivotal role in a wide array of digital interfaces, enhancing user immersion and facilitating natural interaction within virtual environments. While previous studies have focused on photo-realistic hand rendering, little attention has been paid to reconstruct the hand geometry with fine details, which is essential to rendering quality. In the realms of extended reality and gaming, on-the-fly rendering becomes imperative. To this end, we introduce an expressive hand avatar, named XHand, that is designed to comprehensively generate hand shape, appearance, and deformations in real-time. To obtain fine-grained hand meshes, we make use of three feature embedding modules to predict hand deformation displacements, albedo, and linear blending skinning weights, respectively. To achieve photo-realistic hand rendering on fine-grained meshes, our method employs a mesh-based neural renderer by leveraging mesh topological consistency and latent codes from embedding modules. During training, a part-aware Laplace smoothing strategy is proposed by incorporating the distinct levels of regularization to effectively maintain the necessary details and eliminate the undesired artifacts. The experimental evaluations on InterHand2.6M and DeepHandMesh datasets demonstrate the efficacy of XHand, which is able to recover high-fidelity geometry and texture for hand animations across diverse poses in real-time. To reproduce our results, we will make the full implementation publicly available at https://github.com/agnJason/XHand.
Read more7/31/2024

0
4DHands: Reconstructing Interactive Hands in 4D with Transformers
Dixuan Lin, Yuxiang Zhang, Mengcheng Li, Yebin Liu, Wei Jing, Qi Yan, Qianying Wang, Hongwen Zhang
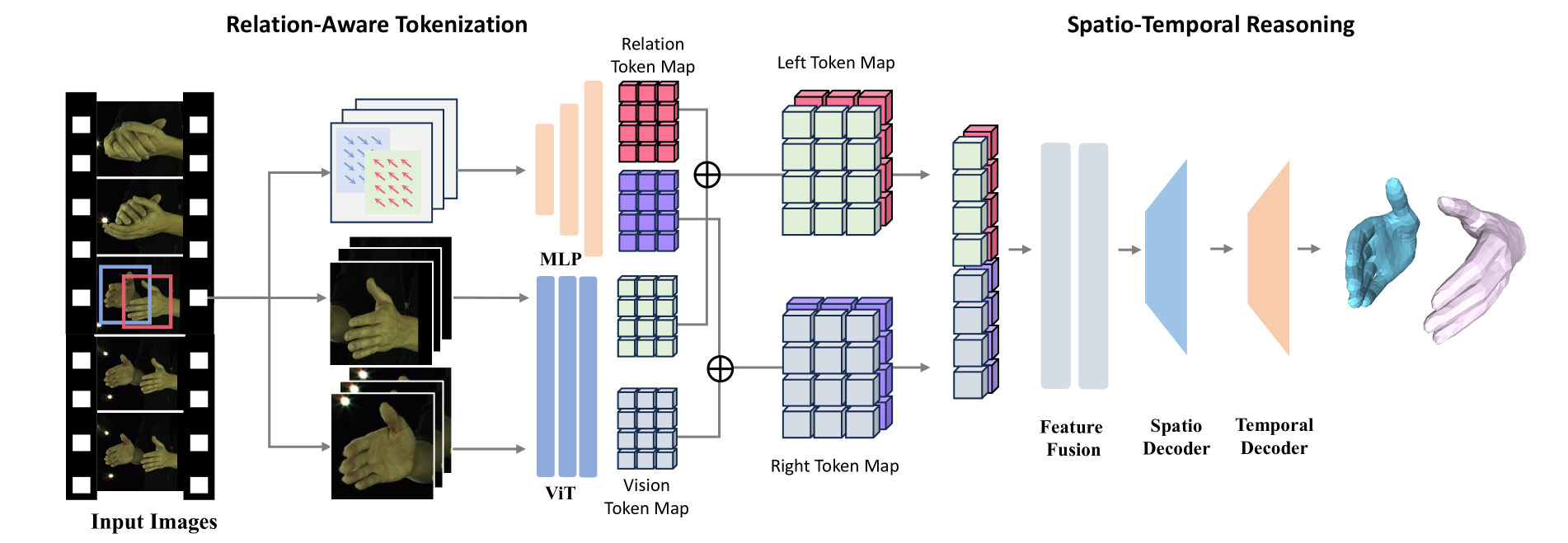
In this paper, we introduce 4DHands, a robust approach to recovering interactive hand meshes and their relative movement from monocular inputs. Our approach addresses two major limitations of previous methods: lacking a unified solution for handling various hand image inputs and neglecting the positional relationship of two hands within images. To overcome these challenges, we develop a transformer-based architecture with novel tokenization and feature fusion strategies. Specifically, we propose a Relation-aware Two-Hand Tokenization (RAT) method to embed positional relation information into the hand tokens. In this way, our network can handle both single-hand and two-hand inputs and explicitly leverage relative hand positions, facilitating the reconstruction of intricate hand interactions in real-world scenarios. As such tokenization indicates the relative relationship of two hands, it also supports more effective feature fusion. To this end, we further develop a Spatio-temporal Interaction Reasoning (SIR) module to fuse hand tokens in 4D with attention and decode them into 3D hand meshes and relative temporal movements. The efficacy of our approach is validated on several benchmark datasets. The results on in-the-wild videos and real-world scenarios demonstrate the superior performances of our approach for interactive hand reconstruction. More video results can be found on the project page: https://4dhands.github.io.
Read more6/3/2024


0
HanDiffuser: Text-to-Image Generation With Realistic Hand Appearances
Supreeth Narasimhaswamy, Uttaran Bhattacharya, Xiang Chen, Ishita Dasgupta, Saayan Mitra, Minh Hoai
Text-to-image generative models can generate high-quality humans, but realism is lost when generating hands. Common artifacts include irregular hand poses, shapes, incorrect numbers of fingers, and physically implausible finger orientations. To generate images with realistic hands, we propose a novel diffusion-based architecture called HanDiffuser that achieves realism by injecting hand embeddings in the generative process. HanDiffuser consists of two components: a Text-to-Hand-Params diffusion model to generate SMPL-Body and MANO-Hand parameters from input text prompts, and a Text-Guided Hand-Params-to-Image diffusion model to synthesize images by conditioning on the prompts and hand parameters generated by the previous component. We incorporate multiple aspects of hand representation, including 3D shapes and joint-level finger positions, orientations and articulations, for robust learning and reliable performance during inference. We conduct extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments and perform user studies to demonstrate the efficacy of our method in generating images with high-quality hands.
Read more4/23/2024


0
PhysHand: A Hand Simulation Model with Physiological Geometry, Physical Deformation, and Accurate Contact Handling
Mingyang Sun, Dongliang Kou, Ruisheng Yuan, Dingkang Yang, Peng Zhai, Xiao Zhao, Yang Jiang, Xiong Li, Jingchen Li, Lihua Zhang
In virtual Hand-Object Interaction (HOI) scenarios, the authenticity of the hand's deformation is important to immersive experience, such as natural manipulation or tactile feedback. Unrealistic deformation arises from simplified hand geometry, neglect of the different physics attributes of the hand, and penetration due to imprecise contact handling. To address these problems, we propose PhysHand, a novel hand simulation model, which enhances the realism of deformation in HOI. First, we construct a physiologically plausible geometry, a layered mesh with a skin-flesh-skeleton structure. Second, to satisfy the distinct physics features of different soft tissues, a constraint-based dynamics framework is adopted with carefully designed layer-corresponding constraints to maintain flesh attached and skin smooth. Finally, we employ an SDF-based method to eliminate the penetration caused by contacts and enhance its accuracy by introducing a novel multi-resolution querying strategy. Extensive experiments have been conducted to demonstrate the outstanding performance of PhysHand in calculating deformations and handling contacts. Compared to existing methods, our PhysHand: 1) can compute both physiologically and physically plausible deformation; 2) significantly reduces the depth and count of penetration in HOI.
Read more9/10/2024