AI-Assisted Writing in Education: Ecosystem Risks and Mitigations
2404.10281

0
0
🤔
Abstract
While the excitement around the capabilities of technological advancements is giving rise to new AI-based writing assistants, the overarching ecosystem plays a crucial role in how they are adopted in educational practice. In this paper, we point to key ecological aspects for consideration. We draw insights from extensive research integrated with practice on a writing feedback tool over 9 years at a university, and we highlight potential risks when these are overlooked. It informs the design of educational writing support tools to be better aligned within broader contexts to balance innovation with practical impact.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper explores the important role that the broader ecosystem plays in how AI-based writing assistants are adopted in educational practice.
- The authors draw insights from 9 years of research and experience with a writing feedback tool at a university, highlighting potential risks that can arise when key ecological aspects are overlooked.
- The findings inform the design of educational writing support tools to better align them within the broader context and balance innovation with practical impact.
Plain English Explanation
The excitement around the capabilities of new AI-based writing assistants is undeniable. However, these AI models are not operating in a vacuum – the overall ecosystem in which they are introduced plays a crucial role in how they are actually adopted and used in educational settings.
This paper draws insights from the authors' extensive research and practical experience with a writing feedback tool over the course of 9 years at a university. They highlight important ecological factors that need to be considered when designing and deploying these types of AI-powered writing assistance tools.
By overlooking these key contextual elements, there is a risk of unintended consequences that can undermine the intended benefits of the technology. For example, issues around trust, agency, and responsibility between students, teachers, and the AI system.
The insights from this research can help guide the design of educational writing support tools to ensure they are better aligned with the broader context in which they will be used. This can help strike a balance between innovative technology and practical, beneficial impact.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a case study based on 9 years of research and experience with a writing feedback tool deployed at a university. The authors examine the broader ecosystem in which the AI-powered tool is integrated, focusing on factors that influence its adoption and use in educational practice.
Through this longitudinal study, the researchers identified key ecological aspects that need to be considered, such as the roles and dynamics between students, instructors, and the AI system, as well as institutional policies, pedagogical approaches, and technological infrastructure.
The findings suggest that overlooking these contextual elements can lead to unintended consequences that undermine the intended benefits of the writing assistance tool. For example, issues around trust, agency, and responsibility, as well as tensions between innovation and practicality.
The authors propose that the design of educational writing support tools should be guided by a nuanced understanding of the broader ecosystem, ensuring better alignment and a balanced approach that maximizes the positive impact of the technology.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a valuable perspective by highlighting the importance of considering the broader ecosystem when introducing AI-based writing assistants in educational settings. The longitudinal case study approach allows the researchers to uncover insights that may be missed in shorter-term evaluations.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific ecological factors identified or provide a comprehensive framework for analyzing the broader context. Additionally, while the paper acknowledges potential risks and unintended consequences, it could have explored these issues in greater detail, particularly around the ethical and societal implications of AI-powered writing tools in education.
Further research could investigate how different educational institutions, pedagogical approaches, and student demographics might influence the adoption and use of these AI-based writing assistance tools. Exploring the perspectives of various stakeholders, including students, instructors, and policymakers, could also shed light on the nuances of the ecosystem and inform the design of more effective and responsible writing support systems.
Conclusion
This paper underscores the crucial role that the broader ecosystem plays in the adoption and use of AI-based writing assistants in educational practice. By drawing insights from a 9-year case study, the authors emphasize the need to consider key ecological factors, such as stakeholder dynamics, institutional policies, and technological infrastructure, when designing and deploying these types of writing support tools.
The findings suggest that overlooking these contextual elements can lead to unintended consequences that undermine the intended benefits of the technology. To address this, the paper proposes that the design of educational writing support tools should be guided by a nuanced understanding of the broader ecosystem, ensuring better alignment and a balanced approach that maximizes the positive impact of the technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
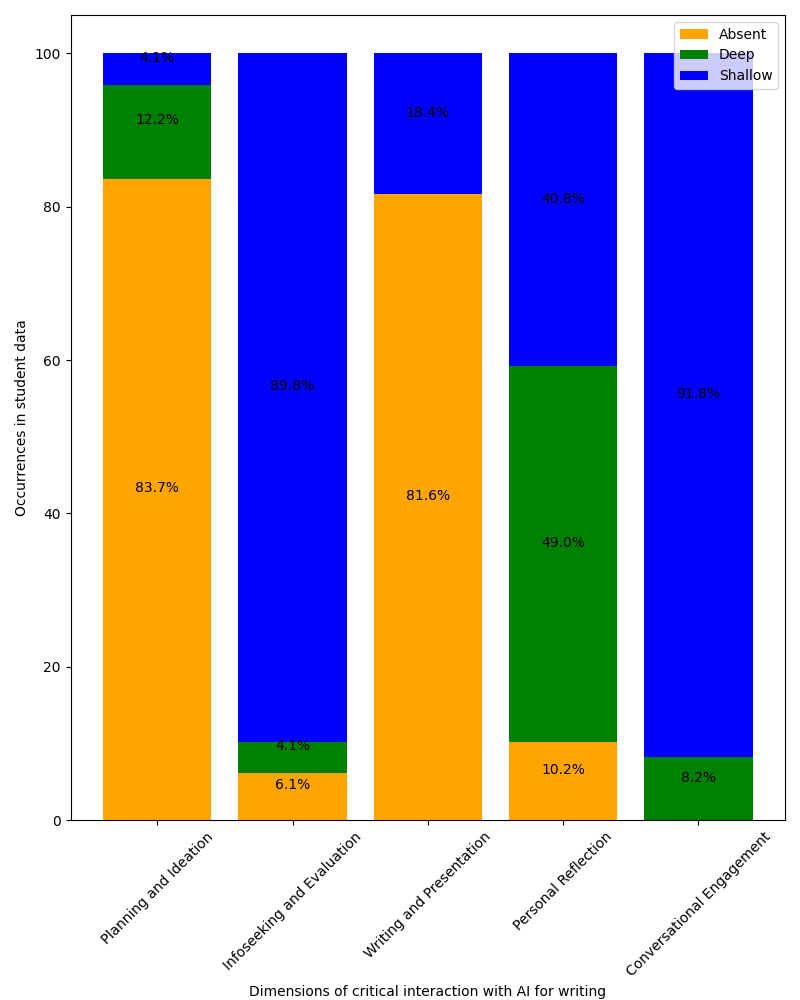
Untangling Critical Interaction with AI in Students Written Assessment
Antonette Shibani, Simon Knight, Kirsty Kitto, Ajanie Karunanayake, Simon Buckingham Shum

0
0
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a ubiquitous part of society, but a key challenge exists in ensuring that humans are equipped with the required critical thinking and AI literacy skills to interact with machines effectively by understanding their capabilities and limitations. These skills are particularly important for learners to develop in the age of generative AI where AI tools can demonstrate complex knowledge and ability previously thought to be uniquely human. To activate effective human-AI partnerships in writing, this paper provides a first step toward conceptualizing the notion of critical learner interaction with AI. Using both theoretical models and empirical data, our preliminary findings suggest a general lack of Deep interaction with AI during the writing process. We believe that the outcomes can lead to better task and tool design in the future for learners to develop deep, critical thinking when interacting with AI.
4/11/2024
🤖
Augmenting the Author: Exploring the Potential of AI Collaboration in Academic Writing
Joseph Tu, Hilda Hadan, Derrick M. Wang, Sabrina A Sgandurra, Reza Hadi Mogavi, Lennart E. Nacke

0
0
This workshop paper presents a critical examination of the integration of Generative AI (Gen AI) into the academic writing process, focusing on the use of AI as a collaborative tool. It contrasts the performance and interaction of two AI models, Gemini and ChatGPT, through a collaborative inquiry approach where researchers engage in facilitated sessions to design prompts that elicit specific AI responses for crafting research outlines. This case study highlights the importance of prompt design, output analysis, and recognizing the AI's limitations to ensure responsible and effective AI integration in scholarly work. Preliminary findings suggest that prompt variation significantly affects output quality and reveals distinct capabilities and constraints of each model. The paper contributes to the field of Human-Computer Interaction by exploring effective prompt strategies and providing a comparative analysis of Gen AI models, ultimately aiming to enhance AI-assisted academic writing and prompt a deeper dialogue within the HCI community.
4/26/2024
🗣️
The Dearth of the Author in AI-Supported Writing
Max Kreminski

0
0
We diagnose and briefly discuss the dearth of the author: a condition that arises when AI-based creativity support tools for writing allow users to produce large amounts of text without making a commensurate number of creative decisions, resulting in output that is sparse in expressive intent. We argue that the dearth of the author helps to explain a number of recurring difficulties and anxieties around AI-based writing support tools, but that it also suggests an ambitious new goal for AI-based CSTs.
4/17/2024
Holding the Line: A Study of Writers' Attitudes on Co-creativity with AI
Morteza Behrooz, Yuandong Tian, William Ngan, Yael Yungster, Justin Wong, David Zax

0
0
Generative AI has put many professional writers on the defensive; a major negotiation point of the recent Writers Guild of America's strike concerned use of AI. However, must AI threaten writers, their livelihoods or their creativity? And under what conditions, if any, might AI assistance be invited by different types of writers (from the amateur to the professional, from the screenwriter to the novelist)? To explore these questions, we conducted a qualitative study with 37 writers. We found that most writing occurs across five stages and within one of three modes; we additionally map openness to AI assistance to each intersecting stage-mode. We found that most writers were interested in AI assistance to some degree, but some writers felt drawing firm boundaries with an AI was key to their comfort using such systems. Designers can leverage these insights to build agency-respecting AI products for writers.
4/23/2024