APISR: Anime Production Inspired Real-World Anime Super-Resolution
2403.01598

0
12
Abstract
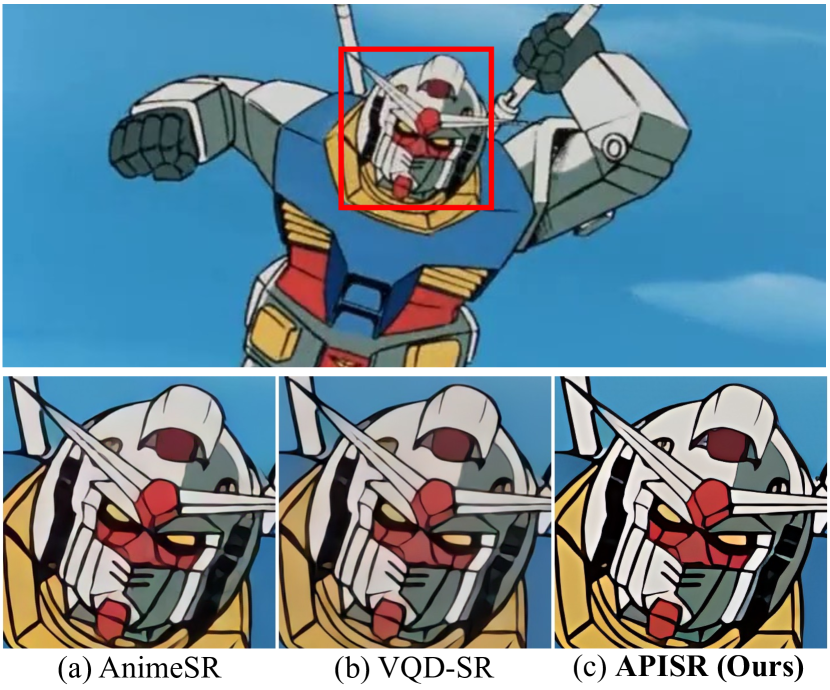
While real-world anime super-resolution (SR) has gained increasing attention in the SR community, existing methods still adopt techniques from the photorealistic domain. In this paper, we analyze the anime production workflow and rethink how to use characteristics of it for the sake of the real-world anime SR. First, we argue that video networks and datasets are not necessary for anime SR due to the repetition use of hand-drawing frames. Instead, we propose an anime image collection pipeline by choosing the least compressed and the most informative frames from the video sources. Based on this pipeline, we introduce the Anime Production-oriented Image (API) dataset. In addition, we identify two anime-specific challenges of distorted and faint hand-drawn lines and unwanted color artifacts. We address the first issue by introducing a prediction-oriented compression module in the image degradation model and a pseudo-ground truth preparation with enhanced hand-drawn lines. In addition, we introduce the balanced twin perceptual loss combining both anime and photorealistic high-level features to mitigate unwanted color artifacts and increase visual clarity. We evaluate our method through extensive experiments on the public benchmark, showing our method outperforms state-of-the-art anime dataset-trained approaches.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Presents a new approach called APISR (Anime Production Inspired Real-World Anime Super-Resolution) for improving the quality of real-world images to look more like high-quality anime art
- Leverages techniques used in anime production to enhance low-resolution real-world images
- Aims to make real-world images have a more stylized, anime-like appearance
Plain English Explanation
The researchers behind this paper have developed a new technique called APISR that can take regular, low-quality photos and make them look more like high-quality anime artwork. They've studied how anime is produced and have found ways to apply those same techniques to real-world images to give them a more stylized, animated appearance.
The key idea is to borrow ideas from the animation industry, where a lot of work goes into making drawings and character designs look visually striking and polished. The researchers have figured out how to essentially "animate" real-world photos, adding in things like bold outlines, simplified color palettes, and exaggerated facial features to make them look more like hand-drawn anime art.
This could have some interesting applications, like allowing people to take mundane photos and turn them into something that looks like it came straight out of an anime series. It's a creative way to bridge the gap between realistic photography and the stylized world of anime. Of course, there are likely some limitations and caveats to this approach that would need to be explored further. But it's an intriguing example of applying ideas from one domain (anime production) to enhance another (real-world images).
Technical Explanation
The APISR approach is built on the idea of leveraging techniques used in the anime production process to improve the quality of real-world images. Specifically, the researchers identified several key elements of anime art that contribute to its distinctive visual style, such as bold outlines, simplified colors, and exaggerated facial features.
They then developed a deep learning architecture that can analyze a low-resolution real-world image and apply these anime-inspired enhancements. This involves a series of neural network models that handle tasks like edge detection, color manipulation, and facial feature augmentation. The end result is a high-quality image that retains the realism of the original photo but has been "animated" to look more like a hand-drawn anime illustration.
The paper presents extensive experiments evaluating APISR's performance on a variety of real-world images, comparing it to other state-of-the-art super-resolution and image-to-image translation techniques. The results demonstrate APISR's ability to generate compelling anime-style renderings while preserving important details and visual fidelity.
Critical Analysis
One potential limitation of the APISR approach is that it may not work as well for certain types of real-world images, such as those with very complex or busy compositions. The anime-inspired enhancements could potentially distort or oversimplify these more intricate scenes. The researchers acknowledge this and suggest that further work is needed to refine the technique for a wider range of input images.
Additionally, while the visual results are impressive, there are some open questions about the broader implications and potential use cases of this technology. For example, there are concerns about the ethical implications of using AI to modify and stylize real-world images in this way. It's important to consider how this type of tool could be abused or misused, and to think carefully about the societal impact of widely disseminating "enhanced" versions of reality.
Overall, the APISR approach is a creative and technically impressive piece of research that demonstrates the potential for cross-pollination between different visual domains. However, as with any powerful AI technology, it will be important to thoughtfully explore both the benefits and potential pitfalls as this line of work continues to evolve.
Conclusion
The APISR paper presents a novel approach to improving the quality and visual style of real-world images by drawing inspiration from the techniques used in anime production. By identifying and applying key elements of the anime aesthetic, the researchers have shown how it's possible to "animate" regular photos and give them a more stylized, hand-drawn appearance.
This work highlights the ongoing convergence of realistic and stylized visual mediums, as well as the potential for cross-pollination between different creative domains. While the APISR technique has some limitations and raises important ethical considerations, it also demonstrates the creative possibilities that emerge when we're willing to look beyond the boundaries of our own fields and find inspiration in unexpected places.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Towards Realistic Data Generation for Real-World Super-Resolution
Long Peng, Wenbo Li, Renjing Pei, Jingjing Ren, Xueyang Fu, Yang Wang, Yang Cao, Zheng-Jun Zha

0
0
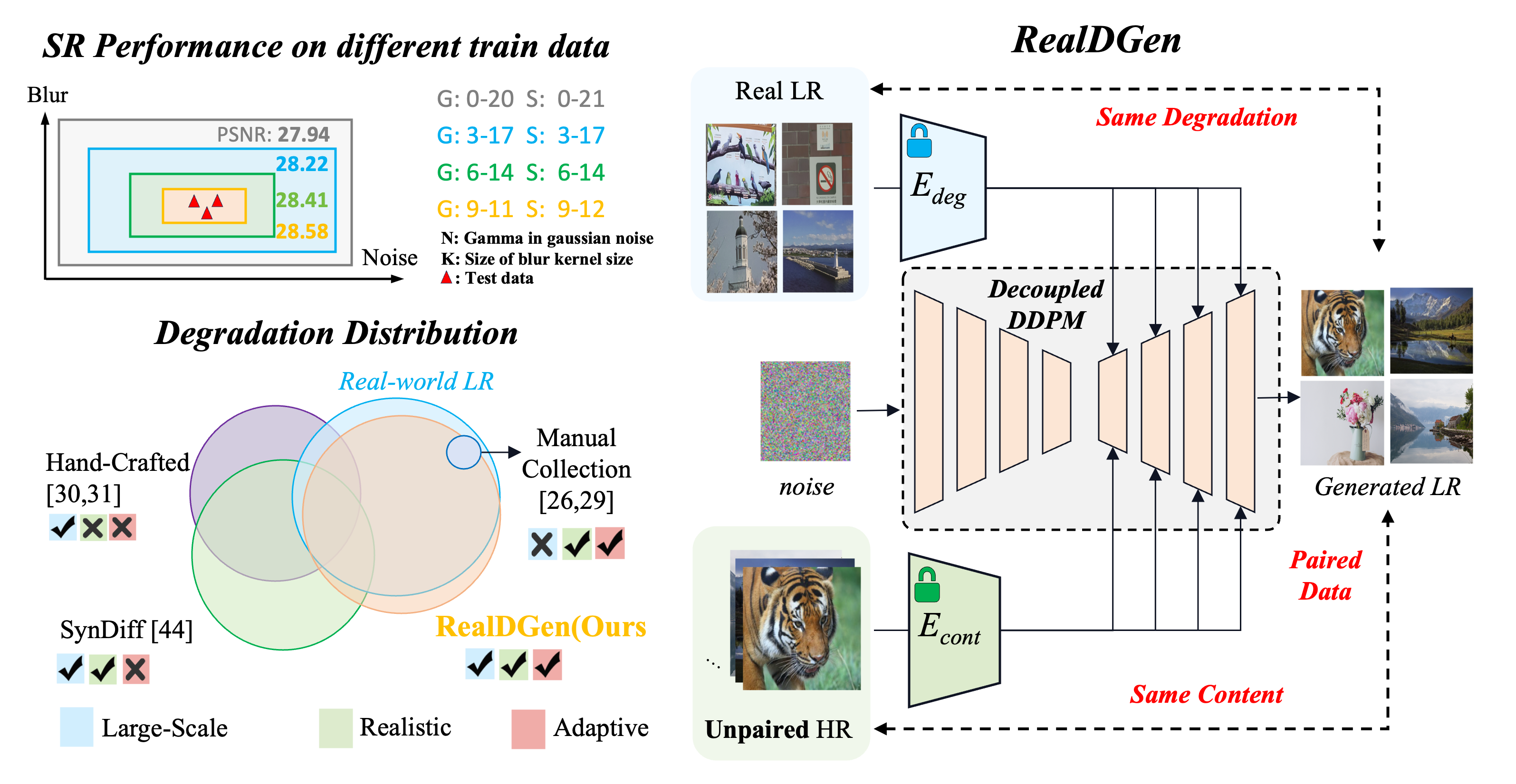
Existing image super-resolution (SR) techniques often fail to generalize effectively in complex real-world settings due to the significant divergence between training data and practical scenarios. To address this challenge, previous efforts have either manually simulated intricate physical-based degradations or utilized learning-based techniques, yet these approaches remain inadequate for producing large-scale, realistic, and diverse data simultaneously. In this paper, we introduce a novel Realistic Decoupled Data Generator (RealDGen), an unsupervised learning data generation framework designed for real-world super-resolution. We meticulously develop content and degradation extraction strategies, which are integrated into a novel content-degradation decoupled diffusion model to create realistic low-resolution images from unpaired real LR and HR images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RealDGen excels in generating large-scale, high-quality paired data that mirrors real-world degradations, significantly advancing the performance of popular SR models on various real-world benchmarks.
6/13/2024

Beyond Image Super-Resolution for Image Recognition with Task-Driven Perceptual Loss
Jaeha Kim, Junghun Oh, Kyoung Mu Lee

0
0
In real-world scenarios, image recognition tasks, such as semantic segmentation and object detection, often pose greater challenges due to the lack of information available within low-resolution (LR) content. Image super-resolution (SR) is one of the promising solutions for addressing the challenges. However, due to the ill-posed property of SR, it is challenging for typical SR methods to restore task-relevant high-frequency contents, which may dilute the advantage of utilizing the SR method. Therefore, in this paper, we propose Super-Resolution for Image Recognition (SR4IR) that effectively guides the generation of SR images beneficial to achieving satisfactory image recognition performance when processing LR images. The critical component of our SR4IR is the task-driven perceptual (TDP) loss that enables the SR network to acquire task-specific knowledge from a network tailored for a specific task. Moreover, we propose a cross-quality patch mix and an alternate training framework that significantly enhances the efficacy of the TDP loss by addressing potential problems when employing the TDP loss. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our SR4IR achieves outstanding task performance by generating SR images useful for a specific image recognition task, including semantic segmentation, object detection, and image classification. The implementation code is available at https://github.com/JaehaKim97/SR4IR.
4/5/2024
🌐
Teacher-Student Network for Real-World Face Super-Resolution with Progressive Embedding of Edge Information
Zhilei Liu, Chenggong Zhang

0
0
Traditional face super-resolution (FSR) methods trained on synthetic datasets usually have poor generalization ability for real-world face images. Recent work has utilized complex degradation models or training networks to simulate the real degradation process, but this limits the performance of these methods due to the domain differences that still exist between the generated low-resolution images and the real low-resolution images. Moreover, because of the existence of a domain gap, the semantic feature information of the target domain may be affected when synthetic data and real data are utilized to train super-resolution models simultaneously. In this study, a real-world face super-resolution teacher-student model is proposed, which considers the domain gap between real and synthetic data and progressively includes diverse edge information by using the recurrent network's intermediate outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach surpasses state-of-the-art methods in obtaining high-quality face images for real-world FSR.
5/9/2024
📉
Real-Time 4K Super-Resolution of Compressed AVIF Images. AIS 2024 Challenge Survey
Marcos V. Conde, Zhijun Lei, Wen Li, Cosmin Stejerean, Ioannis Katsavounidis, Radu Timofte, Kihwan Yoon, Ganzorig Gankhuyag, Jiangtao Lv, Long Sun, Jinshan Pan, Jiangxin Dong, Jinhui Tang, Zhiyuan Li, Hao Wei, Chenyang Ge, Dongyang Zhang, Tianle Liu, Huaian Chen, Yi Jin, Menghan Zhou, Yiqiang Yan, Si Gao, Biao Wu, Shaoli Liu, Chengjian Zheng, Diankai Zhang, Ning Wang, Xintao Qiu, Yuanbo Zhou, Kongxian Wu, Xinwei Dai, Hui Tang, Wei Deng, Qingquan Gao, Tong Tong, Jae-Hyeon Lee, Ui-Jin Choi, Min Yan, Xin Liu, Qian Wang, Xiaoqian Ye, Zhan Du, Tiansen Zhang, Long Peng, Jiaming Guo, Xin Di, Bohao Liao, Zhibo Du, Peize Xia, Renjing Pei, Yang Wang, Yang Cao, Zhengjun Zha, Bingnan Han, Hongyuan Yu, Zhuoyuan Wu, Cheng Wan, Yuqing Liu, Haodong Yu, Jizhe Li, Zhijuan Huang, Yuan Huang, Yajun Zou, Xianyu Guan, Qi Jia, Heng Zhang, Xuanwu Yin, Kunlong Zuo, Hyeon-Cheol Moon, Tae-hyun Jeong, Yoonmo Yang, Jae-Gon Kim, Jinwoo Jeong, Sunjei Kim

0
0
This paper introduces a novel benchmark as part of the AIS 2024 Real-Time Image Super-Resolution (RTSR) Challenge, which aims to upscale compressed images from 540p to 4K resolution (4x factor) in real-time on commercial GPUs. For this, we use a diverse test set containing a variety of 4K images ranging from digital art to gaming and photography. The images are compressed using the modern AVIF codec, instead of JPEG. All the proposed methods improve PSNR fidelity over Lanczos interpolation, and process images under 10ms. Out of the 160 participants, 25 teams submitted their code and models. The solutions present novel designs tailored for memory-efficiency and runtime on edge devices. This survey describes the best solutions for real-time SR of compressed high-resolution images.
4/26/2024