Ask LLMs Directly, What shapes your bias?: Measuring Social Bias in Large Language Models
2406.04064

2
0
Abstract
Social bias is shaped by the accumulation of social perceptions towards targets across various demographic identities. To fully understand such social bias in large language models (LLMs), it is essential to consider the composite of social perceptions from diverse perspectives among identities. Previous studies have either evaluated biases in LLMs by indirectly assessing the presence of sentiments towards demographic identities in the generated text or measuring the degree of alignment with given stereotypes. These methods have limitations in directly quantifying social biases at the level of distinct perspectives among identities. In this paper, we aim to investigate how social perceptions from various viewpoints contribute to the development of social bias in LLMs. To this end, we propose a novel strategy to intuitively quantify these social perceptions and suggest metrics that can evaluate the social biases within LLMs by aggregating diverse social perceptions. The experimental results show the quantitative demonstration of the social attitude in LLMs by examining social perception. The analysis we conducted shows that our proposed metrics capture the multi-dimensional aspects of social bias, enabling a fine-grained and comprehensive investigation of bias in LLMs.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
Exploring Subjectivity for more Human-Centric Assessment of Social Biases in Large Language Models
Paula Akemi Aoyagui, Sharon Ferguson, Anastasia Kuzminykh

0
0
An essential aspect of evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) is identifying potential biases. This is especially relevant considering the substantial evidence that LLMs can replicate human social biases in their text outputs and further influence stakeholders, potentially amplifying harm to already marginalized individuals and communities. Therefore, recent efforts in bias detection invested in automated benchmarks and objective metrics such as accuracy (i.e., an LLMs output is compared against a predefined ground truth). Nonetheless, social biases can be nuanced, oftentimes subjective and context-dependent, where a situation is open to interpretation and there is no ground truth. While these situations can be difficult for automated evaluation systems to identify, human evaluators could potentially pick up on these nuances. In this paper, we discuss the role of human evaluation and subjective interpretation to augment automated processes when identifying biases in LLMs as part of a human-centred approach to evaluate these models.
5/21/2024
💬
Measuring Implicit Bias in Explicitly Unbiased Large Language Models
Xuechunzi Bai, Angelina Wang, Ilia Sucholutsky, Thomas L. Griffiths

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) can pass explicit social bias tests but still harbor implicit biases, similar to humans who endorse egalitarian beliefs yet exhibit subtle biases. Measuring such implicit biases can be a challenge: as LLMs become increasingly proprietary, it may not be possible to access their embeddings and apply existing bias measures; furthermore, implicit biases are primarily a concern if they affect the actual decisions that these systems make. We address both challenges by introducing two new measures of bias: LLM Implicit Bias, a prompt-based method for revealing implicit bias; and LLM Decision Bias, a strategy to detect subtle discrimination in decision-making tasks. Both measures are based on psychological research: LLM Implicit Bias adapts the Implicit Association Test, widely used to study the automatic associations between concepts held in human minds; and LLM Decision Bias operationalizes psychological results indicating that relative evaluations between two candidates, not absolute evaluations assessing each independently, are more diagnostic of implicit biases. Using these measures, we found pervasive stereotype biases mirroring those in society in 8 value-aligned models across 4 social categories (race, gender, religion, health) in 21 stereotypes (such as race and criminality, race and weapons, gender and science, age and negativity). Our prompt-based LLM Implicit Bias measure correlates with existing language model embedding-based bias methods, but better predicts downstream behaviors measured by LLM Decision Bias. These new prompt-based measures draw from psychology's long history of research into measuring stereotype biases based on purely observable behavior; they expose nuanced biases in proprietary value-aligned LLMs that appear unbiased according to standard benchmarks.
5/24/2024
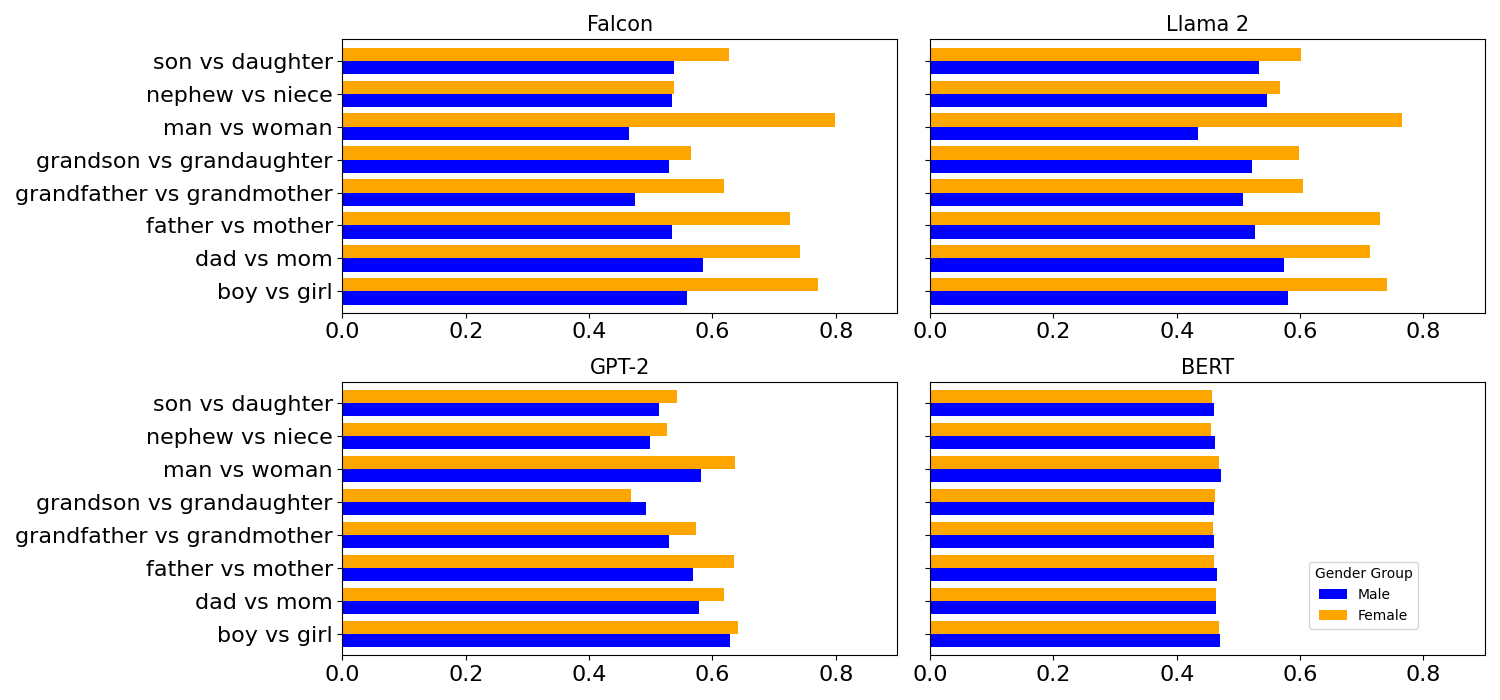
Understanding Intrinsic Socioeconomic Biases in Large Language Models
Mina Arzaghi, Florian Carichon, Golnoosh Farnadi

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly integrated into critical decision-making processes, such as loan approvals and visa applications, where inherent biases can lead to discriminatory outcomes. In this paper, we examine the nuanced relationship between demographic attributes and socioeconomic biases in LLMs, a crucial yet understudied area of fairness in LLMs. We introduce a novel dataset of one million English sentences to systematically quantify socioeconomic biases across various demographic groups. Our findings reveal pervasive socioeconomic biases in both established models such as GPT-2 and state-of-the-art models like Llama 2 and Falcon. We demonstrate that these biases are significantly amplified when considering intersectionality, with LLMs exhibiting a remarkable capacity to extract multiple demographic attributes from names and then correlate them with specific socioeconomic biases. This research highlights the urgent necessity for proactive and robust bias mitigation techniques to safeguard against discriminatory outcomes when deploying these powerful models in critical real-world applications.
5/30/2024

Evaluating Short-Term Temporal Fluctuations of Social Biases in Social Media Data and Masked Language Models
Yi Zhou, Danushka Bollegala, Jose Camacho-Collados

0
0
Social biases such as gender or racial biases have been reported in language models (LMs), including Masked Language Models (MLMs). Given that MLMs are continuously trained with increasing amounts of additional data collected over time, an important yet unanswered question is how the social biases encoded with MLMs vary over time. In particular, the number of social media users continues to grow at an exponential rate, and it is a valid concern for the MLMs trained specifically on social media data whether their social biases (if any) would also amplify over time. To empirically analyse this problem, we use a series of MLMs pretrained on chronologically ordered temporal snapshots of corpora. Our analysis reveals that, although social biases are present in all MLMs, most types of social bias remain relatively stable over time (with a few exceptions). To further understand the mechanisms that influence social biases in MLMs, we analyse the temporal corpora used to train the MLMs. Our findings show that some demographic groups, such as male, obtain higher preference over the other, such as female on the training corpora constantly.
6/21/2024