Augmented Reality and Human-Robot Collaboration Framework for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: System Design, Implementation, and Performance Metrics

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a framework that combines augmented reality (AR) and human-robot collaboration for percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), a surgical procedure to remove kidney stones.
- The proposed framework aims to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of PCNL by leveraging the strengths of both human surgeons and robotic systems.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new way to perform a specific type of surgery called percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL). PCNL is a procedure used to remove kidney stones by making a small incision in the patient's back and using specialized tools to break up and remove the stones.
The researchers have developed a framework that combines augmented reality (AR) technology with human-robot collaboration. AR technology allows the surgeon to see virtual images and information overlaid on the patient's body during the surgery, providing additional guidance and information. The human-robot collaboration aspect means that the surgeon and a robotic system work together to perform the procedure, with each bringing their own strengths and capabilities.
The goal of this framework is to make PCNL surgery more accurate and efficient, ultimately improving patient outcomes. The AR guidance and the collaboration between the human surgeon and the robotic system are designed to enhance the surgeon's precision and decision-making during the delicate procedure.
Technical Explanation
The proposed framework integrates augmented reality and human-robot collaboration to assist surgeons during percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) procedures. The key components of the framework include:
-
3D Kidney and Stone Modeling: Fourier-enhanced multi-modal 3D reconstruction is used to create a detailed 3D model of the patient's kidney and stones based on preoperative imaging data.
-
Augmented Reality Visualization: The 3D kidney and stone model is overlaid on the patient's body using high-precision surgical navigation and semi-automatic infrared calibration techniques, providing the surgeon with enhanced visual information during the procedure.
-
Human-Robot Collaboration: A robotic system is integrated into the workflow to assist the surgeon, with the human and robot collaborating to perform specific surgical tasks, such as stone fragmentation and removal.
The proposed framework aims to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and safety of PCNL procedures by leveraging the complementary strengths of human surgeons and robotic systems.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive framework for integrating augmented reality and human-robot collaboration in PCNL surgery. However, the authors acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research:
-
The framework has only been evaluated in simulated environments and not yet tested in real-world clinical settings. Validating the framework's performance and safety in actual PCNL procedures will be a crucial next step.
-
The integration of the robotic system and the division of tasks between the human surgeon and the robot are not fully detailed. More research is needed to optimize the human-robot collaboration and ensure seamless interactions during the surgical workflow.
-
The paper does not address potential challenges related to the acceptance and adoption of this technology by surgeons and healthcare institutions. Addressing concerns around cost, training, and integration with existing surgical workflows will be important for successful implementation.
Overall, the proposed framework represents a promising approach to enhancing PCNL procedures, but further research and clinical validation are necessary to assess its practical feasibility and long-term impact on patient outcomes.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel framework that combines augmented reality and human-robot collaboration to assist surgeons during percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) procedures. By integrating 3D kidney and stone modeling, AR visualization, and a collaborative robotic system, the framework aims to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and safety of PCNL surgeries.
While the framework shows promise, the authors acknowledge the need for further validation in real-world clinical settings and the exploration of potential challenges related to its adoption and integration into existing surgical practices. Nonetheless, this research represents an important step towards leveraging emerging technologies to enhance the delivery of complex medical procedures and improve patient outcomes.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Augmented Reality and Human-Robot Collaboration Framework for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: System Design, Implementation, and Performance Metrics
Junling Fu, Matteo Pecorella, Elisa Iovene, Maria Chiara Palumbo, Alberto Rota, Alberto Redaelli, Giancarlo Ferrigno, Elena De Momi
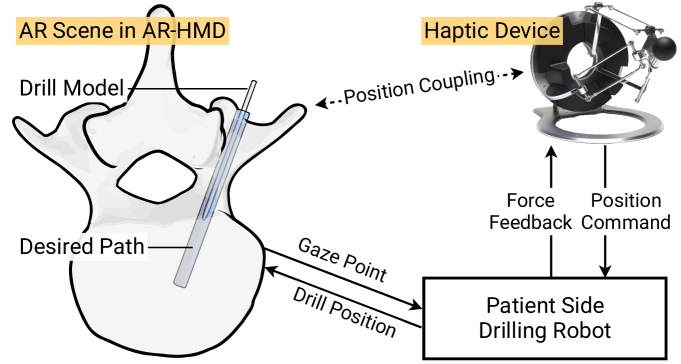
During Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) operations, the surgeon is required to define the incision point on the patient's back, align the needle to a pre-planned path, and perform puncture operations afterward. The procedure is currently performed manually using ultrasound or fluoroscopy imaging for needle orientation, which, however, implies limited accuracy and low reproducibility. This work incorporates Augmented Reality (AR) visualization with an optical see-through head-mounted display (OST-HMD) and Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC) framework to empower the surgeon's task completion performance. In detail, Eye-to-Hand calibration, system registration, and hologram model registration are performed to realize visual guidance. A Cartesian impedance controller is used to guide the operator during the needle puncture task execution. Experiments are conducted to verify the system performance compared with conventional manual puncture procedures and a 2D monitor-based visualisation interface. The results showed that the proposed framework achieves the lowest median and standard deviation error across all the experimental groups, respectively. Furthermore, the NASA-TLX user evaluation results indicate that the proposed framework requires the lowest workload score for task completion compared to other experimental setups. The proposed framework exhibits significant potential for clinical application in the PCNL task, as it enhances the surgeon's perception capability, facilitates collision-free needle insertion path planning, and minimises errors in task completion.
Read more6/26/2024

0
Visual Attention Based Cognitive Human-Robot Collaboration for Pedicle Screw Placement in Robot-Assisted Orthopedic Surgery
Chen Chen, Qikai Zou, Yuhang Song, Shiji Song, Xiang Li
Current orthopedic robotic systems largely focus on navigation, aiding surgeons in positioning a guiding tube but still requiring manual drilling and screw placement. The automation of this task not only demands high precision and safety due to the intricate physical interactions between the surgical tool and bone but also poses significant risks when executed without adequate human oversight. As it involves continuous physical interaction, the robot should collaborate with the surgeon, understand the human intent, and always include the surgeon in the loop. To achieve this, this paper proposes a new cognitive human-robot collaboration framework, including the intuitive AR-haptic human-robot interface, the visual-attention-based surgeon model, and the shared interaction control scheme for the robot. User studies on a robotic platform for orthopedic surgery are presented to illustrate the performance of the proposed method. The results demonstrate that the proposed human-robot collaboration framework outperforms full robot and full human control in terms of safety and ergonomics.
Read more5/16/2024
👁️

0
A Fourier-enhanced multi-modal 3D small object optical mark recognition and positioning method for percutaneous abdominal puncture surgical navigation
Zezhao Guo (College of information and Engineering, Hebei GEO University), Yanzhong Guo (Beijing Yingrui Pioneer Medical Technology Co., Ltd), Zhanfang Zhao (College of information and Engineering, Hebei GEO University)
Navigation for thoracoabdominal puncture surgery is used to locate the needle entry point on the patient's body surface. The traditional reflective ball navigation method is difficult to position the needle entry point on the soft, irregular, smooth chest and abdomen. Due to the lack of clear characteristic points on the body surface using structured light technology, it is difficult to identify and locate arbitrary needle insertion points. Based on the high stability and high accuracy requirements of surgical navigation, this paper proposed a novel method, a muti-modal 3D small object medical marker detection method, which identifies the center of a small single ring as the needle insertion point. Moreover, this novel method leverages Fourier transform enhancement technology to augment the dataset, enrich image details, and enhance the network's capability. The method extracts the Region of Interest (ROI) of the feature image from both enhanced and original images, followed by generating a mask map. Subsequently, the point cloud of the ROI from the depth map is obtained through the registration of ROI point cloud contour fitting. In addition, this method employs Tukey loss for optimal precision. The experimental results show this novel method proposed in this paper not only achieves high-precision and high-stability positioning, but also enables the positioning of any needle insertion point.
Read more4/16/2024
⚙️

0
High-precision surgical navigation using speckle structured light-based thoracoabdominal puncture robot
Zezhao Guo, Yanzhong Guo, Zhanfang Zhao
Abstract Background During percutaneous puncture robotic surgical navigation, the needle insertion point is positioned on the patient's chest and abdomen body surface. By locating any point on the soft skin tissue, it is difficult to apply the traditional reflective ball tracking method. The patient's chest and abdomen body surface has fluctuations in breathing and appears irregular. The chest and abdomen are regular and smooth, lacking obvious features, and it is challenging to locate the needle insertion point on the body surface. Methods This paper designs and experiments a method that is different from previous reflective ball optical markers or magnetic positioning surgical navigation and tracking methods. It is based on a speckle structured light camera to identify the patient's body surface and fit it into a hollow ring with a diameter of 24mm. Results Experimental results show that this method of the system can be small, flexible, and high-precision positioning of any body surface point at multiple angles, achieving a positioning accuracy of 0.033-0.563mm and an image of 7-30 frames/s. Conclusions The positioning recognition ring material used in this method can be well imaged under CT, so the optical positioning of the body surface and the in vivo imaging positioning under CT can be combined to form a unified patient's internal and external positioning world coordinates to achieve internal and external registration. Positioning integration. The system senses motion with six degrees of freedom, up and down, front and back, left and right, and all rotations, with sub-millimeter accuracy, and has broad application prospects in future puncture surgeries.
Read more6/11/2024