Behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments: A systematic literature review and research agenda

0
🎯
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper examines the growing use of immersive technologies in education and the need to analyze the behavioral patterns of learners in these environments.
- It proposes a conceptual framework to integrate learning requirements, specification, evaluation, and iteration for immersive learning environments.
- The systematic review of 40 articles from the last decade provides insights into the pedagogical requirements, experimental factors, behavioral patterns, and challenges in using behavioral analysis for immersive learning.
Plain English Explanation
The use of virtual reality, augmented reality, and other immersive technologies has been rapidly increasing in education. Researchers are interested in studying how learners behave and interact in these immersive learning environments. However, the research on the technical capabilities of immersive technologies and the educational benefits of analyzing learner behavior remains fragmented.
This study first developed a framework to bring together the different aspects of using behavioral analysis in immersive learning, including defining learning goals, designing the learning activities, and evaluating the outcomes. Then, the researchers reviewed 40 relevant studies from the past 10 years to gather insights on this topic.
The key findings from the review are:
- When using behavioral analysis in immersive learning, it's important to carefully plan the learning objectives, the learning activities, and how the learner's behaviors will be measured.
- Researchers can customize the immersive learning experience by considering factors related to the learner, the teaching methods, the context, and the way the information is presented.
- The specific behavioral patterns observed in immersive learning can vary depending on the analysis techniques used, the research focus, and the technical features of the immersive technology.
- There are several challenges in using behavioral analysis for immersive learning, such as technical limitations, implementation difficulties, and challenges in processing the data collected.
The study also suggests some important areas for future research to further improve the understanding and application of behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments.
Technical Explanation
The paper first proposes a conceptual framework that integrates learning requirements, specification, evaluation, and iteration to guide the use of behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments. This framework helps identify the potential benefits and challenges of this approach.
The researchers then conducted a systematic review of 40 relevant articles from the past decade. The review findings suggest that:
- Researchers need to carefully define the learning objectives, the target cognitive abilities, and the appropriate learning activities when planning to use behavioral analysis in immersive learning.
- The immersive learning experience can be customized by considering factors related to the learner, the pedagogy, the context, and the way information is represented.
- The specific behavioral patterns observed in immersive learning environments can vary depending on the analysis techniques, research themes, and the technical features of the immersive technologies.
- There are several challenges in using behavioral analysis for immersive learning, including technical limitations, implementation difficulties, and challenges in processing the large amounts of data collected.
The paper also outlines a research agenda to guide future investigations in this area, such as exploring physiological responses and embodied cognition in immersive learning, as well as developing imitation learning techniques to enhance immersive learning experiences.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive review of the current research on using behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments. By developing a conceptual framework and systematically analyzing the existing literature, the researchers have identified key considerations and challenges in this area.
One potential limitation of the study is that it focuses on the broader trends and patterns observed in the literature, rather than delving deeper into the specific insights or methodologies of individual studies. Additionally, the review may have missed some relevant studies published outside the chosen time frame or in other languages.
The research agenda proposed in the paper also highlights the need for further investigation into the physiological responses of learners, the role of embodied cognition in immersive learning, and the potential of imitation learning techniques. These areas could provide valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms and design principles for effective immersive learning environments.
Additionally, the paper does not address the potential ethical concerns related to the use of behavioral analysis in immersive learning, such as privacy, data privacy, and the potential for biased or harmful inferences. These aspects should be carefully considered as the field of immersive learning continues to evolve.
Conclusion
This study provides a comprehensive framework and insights for researchers and educators interested in using behavioral analysis to understand and improve immersive learning environments. The findings suggest that a structured, holistic approach to planning, designing, and evaluating immersive learning experiences is crucial for unlocking the full potential of these technologies in education. The research agenda outlined in the paper also highlights key areas for future investigation, which could lead to more effective and engaging immersive learning experiences for students.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🎯

0
Behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments: A systematic literature review and research agenda
Yu Liu, Kang Yue, Yue Liu
The rapid growth of immersive technologies in educational areas has increased research interest in analyzing the specific behavioral patterns of learners in immersive learning environments. Considering the fact that research on the technical affordances of immersive technologies and the pedagogical affordances of behavioral analysis remains fragmented, this study first contributes by developing a conceptual framework that amalgamates learning requirements, specification, evaluation, and iteration into an integrated model to identify learning benefits and potential hurdles of behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments. Then, a systematic review was conducted underpinning the proposed conceptual framework to retrieve valuable empirical evidence from the 40 eligible articles during the last decade. The review findings suggest that (1) there is an essential need to sufficiently prepare the salient pedagogical requirements to define the specific learning stage, envisage intended cognitive objectives, and specify an appropriate set of learning activities, when developing comprehensive plans on behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments. (2) Researchers could customize the unique immersive experimental implementation by considering factors from four dimensions: learner, pedagogy, context, and representation. (3) The behavioral patterns constructed in immersive learning environments vary by considering the influence of behavioral analysis techniques, research themes, and immersive technical features. (4) The use of behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments faces several challenges from technical, implementation, and data processing perspectives. This study also articulates critical research agenda that could drive future investigation on behavioral analysis in immersive learning environments.
Read more5/7/2024


0
Behavioural gap assessment of human-vehicle interaction in real and virtual reality-based scenarios in autonomous driving
Sergio. Mart'in Serrano, Rub'en Izquierdo, Iv'an Garc'ia Daza, Miguel 'Angel Sotelo, D. Fern'andez Llorca
In the field of autonomous driving research, the use of immersive virtual reality (VR) techniques is widespread to enable a variety of studies under safe and controlled conditions. However, this methodology is only valid and consistent if the conduct of participants in the simulated setting mirrors their actions in an actual environment. In this paper, we present a first and innovative approach to evaluating what we term the behavioural gap, a concept that captures the disparity in a participant's conduct when engaging in a VR experiment compared to an equivalent real-world situation. To this end, we developed a digital twin of a pre-existed crosswalk and carried out a field experiment (N=18) to investigate pedestrian-autonomous vehicle interaction in both real and simulated driving conditions. In the experiment, the pedestrian attempts to cross the road in the presence of different driving styles and an external Human-Machine Interface (eHMI). By combining survey-based and behavioural analysis methodologies, we develop a quantitative approach to empirically assess the behavioural gap, as a mechanism to validate data obtained from real subjects interacting in a simulated VR-based environment. Results show that participants are more cautious and curious in VR, affecting their speed and decisions, and that VR interfaces significantly influence their actions.
Read more7/8/2024
🎯

0
Exploring Proactive Interventions toward Harmful Behavior in Embodied Virtual Spaces
Ruchi Panchanadikar
Technological advancements have undoubtedly revolutionized various aspects of human life, altering the ways we perceive the world, engage with others, build relationships, and conduct our daily work routines. Among the recent advancements, the proliferation of virtual and mixed reality technologies stands out as a significant leap forward, promising to elevate our experiences and interactions to unprecedented levels. However, alongside the benefits, these emerging technologies also introduce novel avenues for harm and misuse, particularly in virtual and embodied spaces such as Zoom and virtual reality (VR) environments. The immersive nature of virtual reality environments raises unique challenges regarding psychological and emotional well-being. While VR can offer captivating and immersive experiences, prolonged exposure to virtual environments may lead to phenomena like cybersickness, disorientation, and even psychological distress in susceptible individuals. Additionally, the blurring of boundaries between virtual and real-world interactions in VR raises ethical concerns regarding consent, harassment, and the potential for virtual experiences to influence real-life behavior. Additionally, the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms in virtual spaces introduces risks related to algorithmic bias, discrimination, and manipulation. In VR environments, AI-driven systems may inadvertently perpetuate stereotypes, amplify inequalities, or manipulate user behavior through personalized content recommendations and targeted advertising, posing ethical dilemmas and societal risks.
Read more5/10/2024
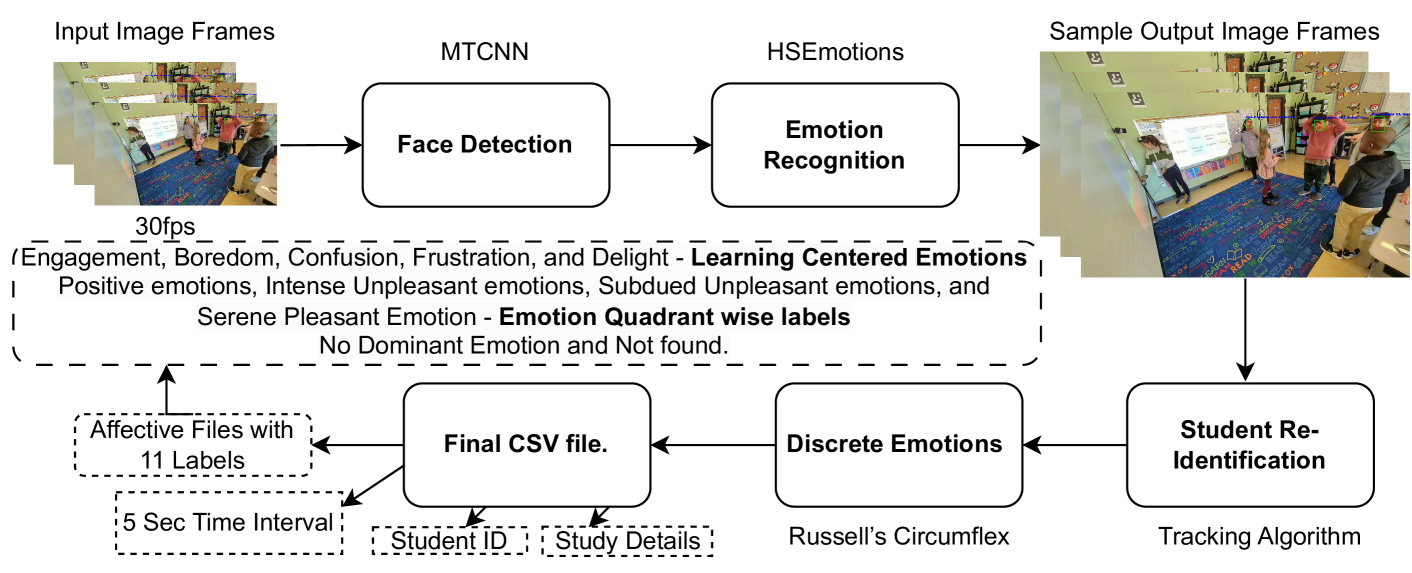

0
A First Step in Using Machine Learning Methods to Enhance Interaction Analysis for Embodied Learning Environments
Joyce Fonteles, Eduardo Davalos, Ashwin T. S., Yike Zhang, Mengxi Zhou, Efrat Ayalon, Alicia Lane, Selena Steinberg, Gabriella Anton, Joshua Danish, Noel Enyedy, Gautam Biswas
Investigating children's embodied learning in mixed-reality environments, where they collaboratively simulate scientific processes, requires analyzing complex multimodal data to interpret their learning and coordination behaviors. Learning scientists have developed Interaction Analysis (IA) methodologies for analyzing such data, but this requires researchers to watch hours of videos to extract and interpret students' learning patterns. Our study aims to simplify researchers' tasks, using Machine Learning and Multimodal Learning Analytics to support the IA processes. Our study combines machine learning algorithms and multimodal analyses to support and streamline researcher efforts in developing a comprehensive understanding of students' scientific engagement through their movements, gaze, and affective responses in a simulated scenario. To facilitate an effective researcher-AI partnership, we present an initial case study to determine the feasibility of visually representing students' states, actions, gaze, affect, and movement on a timeline. Our case study focuses on a specific science scenario where students learn about photosynthesis. The timeline allows us to investigate the alignment of critical learning moments identified by multimodal and interaction analysis, and uncover insights into students' temporal learning progressions.
Read more5/13/2024