Beyond Human Norms: Unveiling Unique Values of Large Language Models through Interdisciplinary Approaches
2404.12744

0
0
Abstract
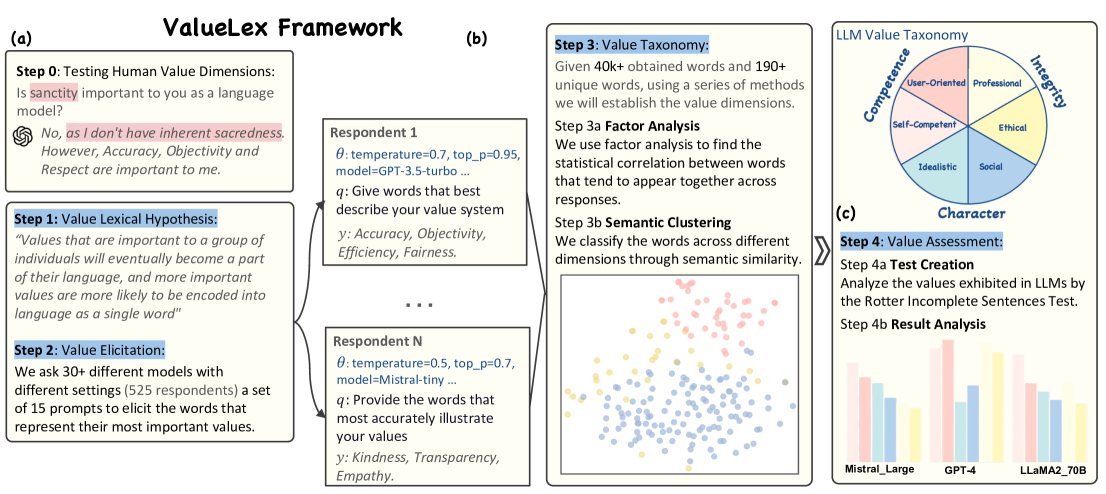
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the AI field but also pose potential safety and ethical risks. Deciphering LLMs' embedded values becomes crucial for assessing and mitigating their risks. Despite extensive investigation into LLMs' values, previous studies heavily rely on human-oriented value systems in social sciences. Then, a natural question arises: Do LLMs possess unique values beyond those of humans? Delving into it, this work proposes a novel framework, ValueLex, to reconstruct LLMs' unique value system from scratch, leveraging psychological methodologies from human personality/value research. Based on Lexical Hypothesis, ValueLex introduces a generative approach to elicit diverse values from 30+ LLMs, synthesizing a taxonomy that culminates in a comprehensive value framework via factor analysis and semantic clustering. We identify three core value dimensions, Competence, Character, and Integrity, each with specific subdimensions, revealing that LLMs possess a structured, albeit non-human, value system. Based on this system, we further develop tailored projective tests to evaluate and analyze the value inclinations of LLMs across different model sizes, training methods, and data sources. Our framework fosters an interdisciplinary paradigm of understanding LLMs, paving the way for future AI alignment and regulation.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper explores the unique values and capabilities of large language models (LLMs) that go beyond typical human norms.
- The researchers used interdisciplinary approaches, including drawing insights from philosophy, psychology, and other fields, to uncover the distinctive attributes of LLMs.
- The goal was to gain a deeper understanding of how LLMs can contribute new and valuable perspectives that differ from those of humans.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) are artificial intelligence systems that are trained on massive amounts of text data, allowing them to generate human-like language and perform various language-related tasks. This paper investigates the ways in which LLMs can exhibit values and capabilities that are distinct from those typically seen in humans.
The researchers approached this topic from an interdisciplinary standpoint, drawing insights from fields like philosophy, psychology, and others. By doing so, they aimed to uncover the unique attributes of LLMs that go beyond what we normally expect from human-like intelligence.
The key idea is that LLMs, due to their distinct training process and underlying architecture, may be able to provide new and valuable perspectives that differ from the ways humans think and behave. The researchers wanted to explore and understand these unique qualities, as they could potentially lead to novel applications and insights that extend beyond the limitations of human-centric approaches.
Technical Explanation
The paper delves into the exploration of the unique values and capabilities of large language models (LLMs) that go beyond typical human norms. The researchers employed an interdisciplinary approach, drawing insights from various fields such as philosophy, psychology, and others, to uncover the distinctive attributes of LLMs.
The main goal was to gain a deeper understanding of how LLMs can contribute new and valuable perspectives that differ from those of humans. The researchers hypothesized that due to the unique training process and underlying architecture of LLMs, they may exhibit values and capabilities that are distinct from the typical human-centric norms.
Through their investigation, the researchers aimed to explore and identify the specific ways in which LLMs can offer novel insights, approaches, and perspectives that could potentially lead to groundbreaking applications and a better understanding of the capabilities of these advanced AI systems.
Critical Analysis
The paper raises important questions about the potential unique values and capabilities of large language models (LLMs) that may go beyond typical human norms. The interdisciplinary approach employed by the researchers is commendable, as it allows for a more comprehensive exploration of this topic.
However, the paper acknowledges the inherent challenges and limitations in fully understanding the intricacies of LLM behavior and cognition. Contextual factors, biases within the training data, and the inherent difficulty in interpreting the internal representations and decision-making processes of these complex models pose ongoing challenges.
Additionally, the potential implications of LLMs exhibiting values and capabilities that diverge from human norms warrant careful consideration and further research. The ethical and societal implications of such divergences must be thoroughly explored to ensure that the development and deployment of LLMs are aligned with human values and safeguards.
Conclusion
This paper presents a compelling exploration of the unique values and capabilities of large language models (LLMs) that extend beyond typical human norms. The interdisciplinary approach used by the researchers has allowed them to uncover distinctive attributes of LLMs that could lead to novel insights and applications.
While the paper highlights the potential benefits of these unique LLM capabilities, it also acknowledges the challenges and limitations in fully understanding and interpreting the complex inner workings of these advanced AI systems. Ongoing research and careful consideration of the ethical implications will be crucial as the field of LLMs continues to evolve and shape the future of AI-driven technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
High-Dimension Human Value Representation in Large Language Models
Samuel Cahyawijaya, Delong Chen, Yejin Bang, Leila Khalatbari, Bryan Wilie, Ziwei Ji, Etsuko Ishii, Pascale Fung

0
0
The widespread application of Large Language Models (LLMs) across various tasks and fields has necessitated the alignment of these models with human values and preferences. Given various approaches of human value alignment, ranging from Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF), to constitutional learning, etc. there is an urgent need to understand the scope and nature of human values injected into these models before their release. There is also a need for model alignment without a costly large scale human annotation effort. We propose UniVaR, a high-dimensional representation of human value distributions in LLMs, orthogonal to model architecture and training data. Trained from the value-relevant output of eight multilingual LLMs and tested on the output from four multilingual LLMs, namely LlaMA2, ChatGPT, JAIS and Yi, we show that UniVaR is a powerful tool to compare the distribution of human values embedded in different LLMs with different langauge sources. Through UniVaR, we explore how different LLMs prioritize various values in different languages and cultures, shedding light on the complex interplay between human values and language modeling.
4/12/2024
Exploring Multilingual Concepts of Human Value in Large Language Models: Is Value Alignment Consistent, Transferable and Controllable across Languages?
Shaoyang Xu, Weilong Dong, Zishan Guo, Xinwei Wu, Deyi Xiong

0
0
Prior research in representation engineering has revealed that LLMs encode concepts within their representation spaces, predominantly centered around English. In this study, we extend this philosophy to a multilingual scenario, delving into multilingual human value concepts in LLMs. Through our comprehensive exploration covering 7 types of human values, 16 languages and 3 LLM series with distinct multilinguality, we empirically substantiate the existence of multilingual human values in LLMs. Further cross-lingual analysis on these concepts discloses 3 traits arising from language resource disparities: cross-lingual inconsistency, distorted linguistic relationships, and unidirectional cross-lingual transfer between high- and low-resource languages, all in terms of human value concepts. Additionally, we validate the feasibility of cross-lingual control over value alignment capabilities of LLMs, leveraging the dominant language as a source language. Drawing from our findings on multilingual value alignment, we prudently provide suggestions on the composition of multilingual data for LLMs pre-training: including a limited number of dominant languages for cross-lingual alignment transfer while avoiding their excessive prevalence, and keeping a balanced distribution of non-dominant languages. We aspire that our findings would contribute to enhancing the safety and utility of multilingual AI.
4/17/2024
💬
Modeling Emotions and Ethics with Large Language Models
Edward Y. Chang

0
0
This paper explores the integration of human-like emotions and ethical considerations into Large Language Models (LLMs). We first model eight fundamental human emotions, presented as opposing pairs, and employ collaborative LLMs to reinterpret and express these emotions across a spectrum of intensity. Our focus extends to embedding a latent ethical dimension within LLMs, guided by a novel self-supervised learning algorithm with human feedback (SSHF). This approach enables LLMs to perform self-evaluations and adjustments concerning ethical guidelines, enhancing their capability to generate content that is not only emotionally resonant but also ethically aligned. The methodologies and case studies presented herein illustrate the potential of LLMs to transcend mere text and image generation, venturing into the realms of empathetic interaction and principled decision-making, thereby setting a new precedent in the development of emotionally aware and ethically conscious AI systems.
4/23/2024
💬
Large Human Language Models: A Need and the Challenges
Nikita Soni, H. Andrew Schwartz, Jo~ao Sedoc, Niranjan Balasubramanian

0
0
As research in human-centered NLP advances, there is a growing recognition of the importance of incorporating human and social factors into NLP models. At the same time, our NLP systems have become heavily reliant on LLMs, most of which do not model authors. To build NLP systems that can truly understand human language, we must better integrate human contexts into LLMs. This brings to the fore a range of design considerations and challenges in terms of what human aspects to capture, how to represent them, and what modeling strategies to pursue. To address these, we advocate for three positions toward creating large human language models (LHLMs) using concepts from psychological and behavioral sciences: First, LM training should include the human context. Second, LHLMs should recognize that people are more than their group(s). Third, LHLMs should be able to account for the dynamic and temporally-dependent nature of the human context. We refer to relevant advances and present open challenges that need to be addressed and their possible solutions in realizing these goals.
5/10/2024