BIM-SLAM: Integrating BIM Models in Multi-session SLAM for Lifelong Mapping using 3D LiDAR

0
👁️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- 3D LiDAR sensor technology is becoming more advanced and cheaper
- Digitalization in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry has led to the availability of 3D building information models (BIM models) for a large part of the built environment
- This paper explores how 3D BIM models can support 3D LiDAR simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) in indoor, GPS-denied environments
Plain English Explanation
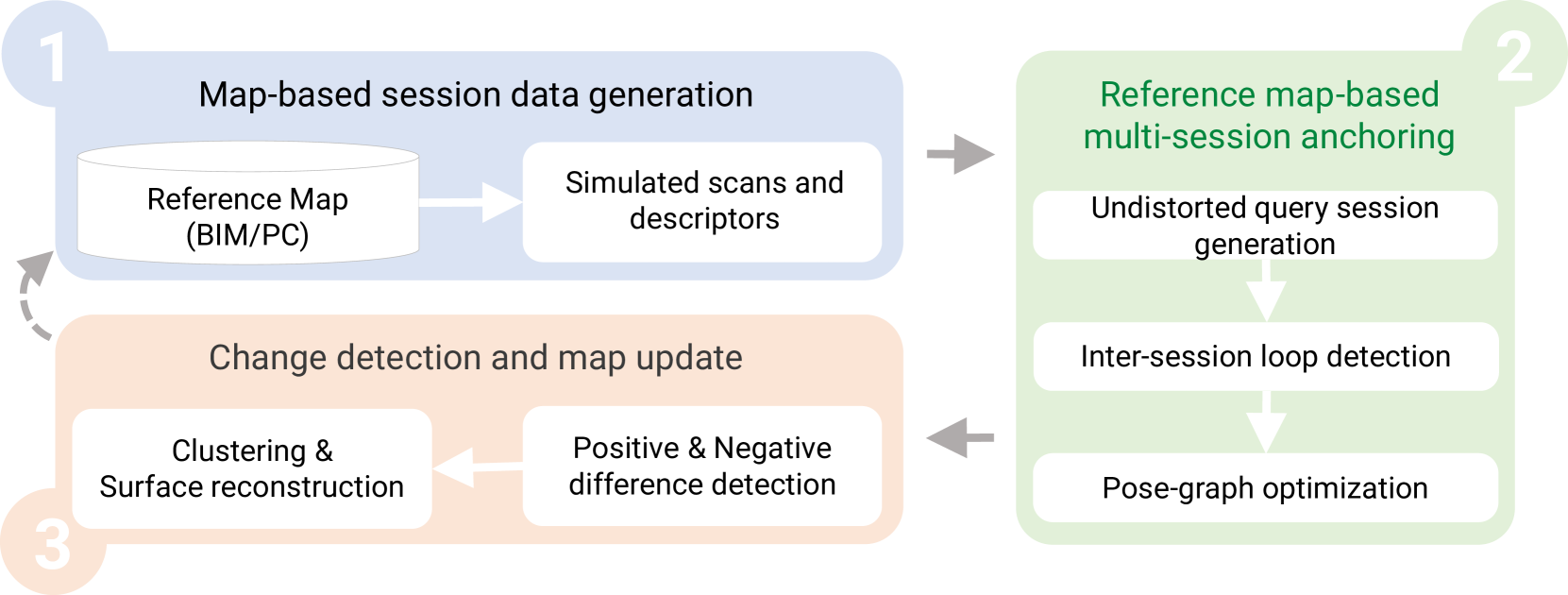
The paper proposes a methodology that leverages 3D BIM models to create an updated map of indoor environments using sequential 3D LiDAR measurements. The process involves:
- Generating initial session data (pose graph-based map and descriptors) from the BIM models
- Aligning real-world data with the session data from the model using multi-session anchoring to minimize drift
- Identifying, grouping, and reconstructing new elements not present in the BIM model in a surface representation for better visualization
This framework enables the creation of a coherent map aligned with the BIM model without requiring prior knowledge of the initial pose of the robot or the robot being inside the map.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a methodology that combines the benefits of 3D BIM models and 3D LiDAR SLAM to create an updated map of indoor environments.
The process starts by generating initial session data (pose graph-based map and descriptors) from the BIM models. This provides a reference frame for the environment. Then, real-world 3D LiDAR data is aligned with the session data from the model using multi-session anchoring. This helps minimize the drift on the real-world data by leveraging the accuracy of the BIM model.
Finally, the new elements not present in the BIM model are identified, grouped, and reconstructed in a surface representation. This allows for a better visualization of the updated map alongside the original BIM model.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to leveraging BIM models and 3D LiDAR technology to create coherent, up-to-date maps of indoor environments. However, the authors do not address potential limitations, such as the accuracy of the BIM models, the ability to handle dynamic changes in the environment, or the computational requirements of the proposed methodology.
Additionally, the paper does not provide a comprehensive evaluation of the framework's performance compared to other SLAM approaches or the impact of different BIM model quality and coverage on the final map accuracy.
Further research could explore the robustness of the methodology in handling various types of indoor environments, the scalability to larger-scale buildings, and the integration with other sensor modalities to enhance the mapping capabilities.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach to leveraging 3D BIM models and 3D LiDAR technology to create updated maps of indoor environments. The proposed framework enables the creation of a coherent map aligned with the BIM model without requiring prior knowledge of the robot's initial pose or the robot being inside the map.
The ability to combine the benefits of BIM models and 3D LiDAR SLAM has the potential to improve the efficiency and accuracy of indoor mapping, which is crucial for applications such as building maintenance, facility management, and indoor navigation. Further research and development of this methodology could lead to advancements in the digitalization of the built environment and the integration of various sensor technologies for comprehensive indoor mapping solutions.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👁️

0
BIM-SLAM: Integrating BIM Models in Multi-session SLAM for Lifelong Mapping using 3D LiDAR
Miguel Arturo Vega Torres, Alexander Braun, Andr'e Borrmann
While 3D LiDAR sensor technology is becoming more advanced and cheaper every day, the growth of digitalization in the AEC industry contributes to the fact that 3D building information models (BIM models) are now available for a large part of the built environment. These two facts open the question of how 3D models can support 3D LiDAR long-term SLAM in indoor, GPS-denied environments. This paper proposes a methodology that leverages BIM models to create an updated map of indoor environments with sequential LiDAR measurements. Session data (pose graph-based map and descriptors) are initially generated from BIM models. Then, real-world data is aligned with the session data from the model using multi-session anchoring while minimizing the drift on the real-world data. Finally, the new elements not present in the BIM model are identified, grouped, and reconstructed in a surface representation, allowing a better visualization next to the BIM model. The framework enables the creation of a coherent map aligned with the BIM model that does not require prior knowledge of the initial pose of the robot, and it does not need to be inside the map.
Read more8/29/2024

0
SLAM2REF: Advancing Long-Term Mapping with 3D LiDAR and Reference Map Integration for Precise 6-DoF Trajectory Estimation and Map Extension
Miguel Arturo Vega Torres, Alexander Braun, Andr'e Borrmann
This paper presents a pioneering solution to the task of integrating mobile 3D LiDAR and inertial measurement unit (IMU) data with existing building information models or point clouds, which is crucial for achieving precise long-term localization and mapping in indoor, GPS-denied environments. Our proposed framework, SLAM2REF, introduces a novel approach for automatic alignment and map extension utilizing reference 3D maps. The methodology is supported by a sophisticated multi-session anchoring technique, which integrates novel descriptors and registration methodologies. Real-world experiments reveal the framework's remarkable robustness and accuracy, surpassing current state-of-the-art methods. Our open-source framework's significance lies in its contribution to resilient map data management, enhancing processes across diverse sectors such as construction site monitoring, emergency response, disaster management, and others, where fast-updated digital 3D maps contribute to better decision-making and productivity. Moreover, it offers advancements in localization and mapping research. Link to the repository: https://github.com/MigVega/SLAM2REF, Data: https://doi.org/10.14459/2024mp1743877.
Read more8/29/2024
🛠️

0
SLAM for Indoor Mapping of Wide Area Construction Environments
Vincent Ress, Wei Zhang, David Skuddis, Norbert Haala, Uwe Soergel
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), i.e., the reconstruction of the environment represented by a (3D) map and the concurrent pose estimation, has made astonishing progress. Meanwhile, large scale applications aiming at the data collection in complex environments like factory halls or construction sites are becoming feasible. However, in contrast to small scale scenarios with building interiors separated to single rooms, shop floors or construction areas require measures at larger distances in potentially texture less areas under difficult illumination. Pose estimation is further aggravated since no GNSS measures are available as it is usual for such indoor applications. In our work, we realize data collection in a large factory hall by a robot system equipped with four stereo cameras as well as a 3D laser scanner. We apply our state-of-the-art LiDAR and visual SLAM approaches and discuss the respective pros and cons of the different sensor types for trajectory estimation and dense map generation in such an environment. Additionally, dense and accurate depth maps are generated by 3D Gaussian splatting, which we plan to use in the context of our project aiming on the automatic construction and site monitoring.
Read more4/29/2024


0
2DLIW-SLAM:2D LiDAR-Inertial-Wheel Odometry with Real-Time Loop Closure
Bin Zhang, Zexin Peng, Bi Zeng, Junjie Lu
Due to budgetary constraints, indoor navigation typically employs 2D LiDAR rather than 3D LiDAR. However, the utilization of 2D LiDAR in Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) frequently encounters challenges related to motion degeneracy, particularly in geometrically similar environments. To address this problem, this paper proposes a robust, accurate, and multi-sensor-fused 2D LiDAR SLAM system specifically designed for indoor mobile robots. To commence, the original LiDAR data undergoes meticulous processing through point and line extraction. Leveraging the distinctive characteristics of indoor environments, line-line constraints are established to complement other sensor data effectively, thereby augmenting the overall robustness and precision of the system. Concurrently, a tightly-coupled front-end is created, integrating data from the 2D LiDAR, IMU, and wheel odometry, thus enabling real-time state estimation. Building upon this solid foundation, a novel global feature point matching-based loop closure detection algorithm is proposed. This algorithm proves highly effective in mitigating front-end accumulated errors and ultimately constructs a globally consistent map. The experimental results indicate that our system fully meets real-time requirements. When compared to Cartographer, our system not only exhibits lower trajectory errors but also demonstrates stronger robustness, particularly in degeneracy problem.
Read more4/24/2024