Blockchain-Enabled Accountability in Data Supply Chain: A Data Bill of Materials Approach

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Blockchain technology can enable greater accountability and transparency in data supply chains.
- The paper proposes a "data bill of materials" approach to track the origin and transformations of data assets.
- This allows for better provenance, lineage, and auditability of data throughout its lifecycle.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores how blockchain technology can be used to improve accountability and transparency in data supply chains. The key idea is a "data bill of materials" - a way to track the origins, transformations, and history of data assets as they flow through a supply chain.
Just like a physical product has a bill of materials showing its components, the data bill of materials records the various data sources, processing steps, and modifications that a digital dataset undergoes. This provides a detailed provenance and lineage for the data, allowing it to be audited and its quality to be assessed.
By using a decentralized, tamper-resistant blockchain to maintain this bill of materials, the researchers aim to create a trusted record of data provenance that multiple parties can access and verify. This could have important applications in sensitive domains like healthcare, finance, or supply chain management, where data integrity and traceability are critical.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a framework for a "data bill of materials" that leverages blockchain technology to provide accountability and transparency in data supply chains. Key elements include:
- Data Provenance Tracking: Each transformation or transaction performed on a data asset is recorded on the blockchain, creating a verifiable lineage of how the data was sourced, processed, and used.
- Tamper-Resistant Ledger: The decentralized, cryptographically-secured nature of the blockchain ensures the data bill of materials cannot be unilaterally altered, providing auditability.
- Multi-Stakeholder Participation: All parties involved in the data supply chain can access and validate the information stored on the blockchain, promoting shared accountability.
- Metadata Management: The framework captures detailed metadata about data assets, including their lineage, quality attributes, and usage constraints.
The researchers demonstrate the feasibility of this approach through a prototype implementation and use case scenarios in domains like healthcare and financial services. They show how the data bill of materials can enable better data governance, risk management, and compliance for organizations dealing with sensitive or mission-critical data.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling vision for how blockchain technology can enhance accountability and transparency in data supply chains. The data bill of materials concept is a novel and potentially impactful approach to data provenance tracking.
However, the researchers acknowledge several practical challenges and limitations that would need to be addressed:
- Scalability: Storing comprehensive metadata and transaction histories for large-scale data assets on a blockchain may pose scalability issues that require careful architecture and optimization.
- Adoption Barriers: Transitioning existing data supply chain practices to a blockchain-based system would likely face organizational and technical hurdles that the paper does not fully address.
- Regulatory Considerations: The use of blockchain for sensitive data domains may raise legal and compliance questions that require further exploration.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into potential privacy and security risks that could arise from maintaining a detailed, accessible record of data provenance. Careful design and access controls would be needed to mitigate these concerns.
Overall, the research presents an interesting and promising direction, but further work is needed to fully validate the feasibility and practical implications of the data bill of materials approach.
Conclusion
This paper introduces an innovative blockchain-based framework for enhancing accountability and transparency in data supply chains. The "data bill of materials" concept provides a way to track the origin, transformations, and usage of data assets, enabling better provenance, lineage, and auditability.
If successfully implemented, this approach could have significant benefits for organizations dealing with sensitive or mission-critical data, such as improved data governance, risk management, and compliance. The blockchain-enabled tamper-resistance and multi-stakeholder participation aspects are particularly compelling features.
However, the researchers acknowledge several practical challenges that would need to be addressed, including scalability, adoption barriers, and regulatory considerations. Careful design and further validation would be required to fully realize the potential of this data accountability framework.
Overall, this paper presents an innovative and promising direction for enhancing transparency and trust in data supply chains using blockchain technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Blockchain-Enabled Accountability in Data Supply Chain: A Data Bill of Materials Approach
Yue Liu, Dawen Zhang, Boming Xia, Julia Anticev, Tunde Adebayo, Zhenchang Xing, Moses Machao
In the era of advanced artificial intelligence, highlighted by large-scale generative models like GPT-4, ensuring the traceability, verifiability, and reproducibility of datasets throughout their lifecycle is paramount for research institutions and technology companies. These organisations increasingly rely on vast corpora to train and fine-tune advanced AI models, resulting in intricate data supply chains that demand effective data governance mechanisms. In addition, the challenge intensifies as diverse stakeholders may use assorted tools, often without adequate measures to ensure the accountability of data and the reliability of outcomes. In this study, we adapt the concept of ``Software Bill of Materials into the field of data governance and management to address the above challenges, and introduce ``Data Bill of Materials (DataBOM) to capture the dependency relationship between different datasets and stakeholders by storing specific metadata. We demonstrate a platform architecture for providing blockchain-based DataBOM services, present the interaction protocol for stakeholders, and discuss the minimal requirements for DataBOM metadata. The proposed solution is evaluated in terms of feasibility and performance via case study and quantitative analysis respectively.
Read more8/19/2024


0
Sustainable business decision modelling with blockchain and digital twins: A survey
Gyan Wickremasinghe, Siofra Frost, Karen Rafferty, Vishal Sharma
Industry 4.0 and beyond will rely heavily on sustainable Business Decision Modelling (BDM) that can be accelerated by blockchain and Digital Twin (DT) solutions. BDM is built on models and frameworks refined by key identification factors, data analysis, and mathematical or computational aspects applicable to complex business scenarios. Gaining actionable intelligence from collected data for BDM requires a carefully considered infrastructure to ensure data transparency, security, accessibility and sustainability. Organisations should consider social, economic and environmental factors (based on the triple bottom line approach) to ensure sustainability when integrating such an infrastructure. These sustainability features directly impact BDM concerning resource optimisation, stakeholder engagement, regulatory compliance and environmental impacts. To further understand these segments, taxonomies are defined to evaluate blockchain and DT sustainability features based on an in-depth review of the current state-of-the-art research. Detailed comparative evaluations provide insight into the reachability of the sustainable solution in terms of ideologies, access control and performance overheads. Several research questions are put forward to motivate further research that significantly impacts BDM. Finally, a case study based on an exemplary supply chain management system is presented to show the interoperability of blockchain and DT with BDM.
Read more5/21/2024
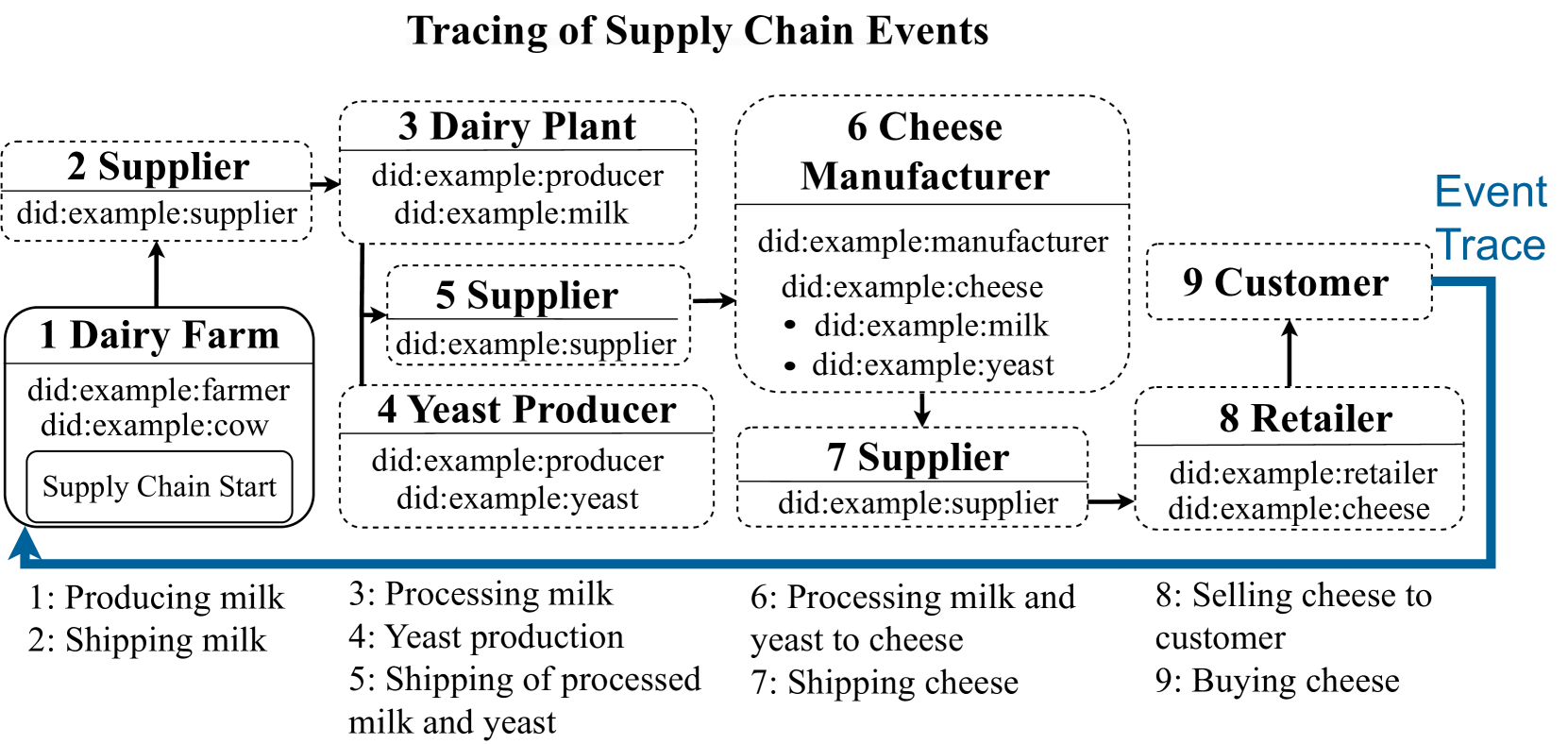

0
DIDChain: Advancing Supply Chain Data Management with Decentralized Identifiers and Blockchain
Patrick Herbke, Sid Lamichhane, Kaustabh Barman, Sanjeet Raj Pandey, Axel Kupper, Andreas Abraham, Markus Sabadello
Supply chain data management faces challenges in traceability, transparency, and trust. These issues stem from data silos and communication barriers. This research introduces DIDChain, a framework leveraging blockchain technology, Decentralized Identifiers, and the InterPlanetary File System. DIDChain improves supply chain data management. To address privacy concerns, DIDChain employs a hybrid blockchain architecture that combines public blockchain transparency with the control of private systems. Our hybrid approach preserves the authenticity and reliability of supply chain events. It also respects the data privacy requirements of the participants in the supply chain. Central to DIDChain is the cheqd infrastructure. The cheqd infrastructure enables digital tracing of asset events, such as an asset moving from the milk-producing dairy farm to the cheese manufacturer. In this research, assets are raw materials and products. The cheqd infrastructure ensures the traceability and reliability of assets in the management of supply chain data. Our contribution to blockchain-enabled supply chain systems demonstrates the robustness of DIDChain. Integrating blockchain technology through DIDChain offers a solution to data silos and communication barriers. With DIDChain, we propose a framework to transform the supply chain infrastructure across industries.
Read more9/4/2024


0
A Survey on Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance with Progress and Future directions
Zhengdong Luo
Supply Chain Finance is very important for supply chain competition, which is an important tool to activate the capital flow in the supply chain. Supply Chain Finance-related research can support multiple applications and services, such as providing accounts receivable financing, enhancing risk management, and optimizing supply chain management. For more than a decade, the development of Blockchain has attracted widely attention in various fields, especially in finance. With the characteristics of data tamper-proof, forgery-proof, cryptography, consensus verification, and decentralization, Blockchain fits well with the realistic needs of Supply Chain Finance, which requires data integrity, authenticity, privacy, and information sharing. Therefore, it is time to summarize the applications of Blockchain technology in the field of Supply Chain Finance. What Blockchain technology brings to Supply Chain Finance is not only to alleviate the problems of information asymmetry, credit disassembly, and financing cost, but also to improve Supply Chain Finance operations through smart contracts to intelligent Supply Chain Finance and in combination with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and data mining, jointly. So there has been some work in Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance research for different Supply Chain Finance oriented applications, but most of these work are at the management level to propose conceptual frameworks or simply use Blockchain without exploiting its deep applications. Moreover, there are few systematic reviews providing a comprehensive summary of current work in the area of Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance. In this paper, we ...
Read more8/20/2024