Blockchain for Large Language Model Security and Safety: A Holistic Survey

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper provides a comprehensive survey of the use of blockchain technology to enhance the security and safety of large language models (LLMs).
- It explores various blockchain-based approaches to address challenges in LLM security, including model integrity, content moderation, and privacy preservation.
- The survey covers key blockchain concepts, explores blockchain-based solutions for LLM security, and discusses future research directions.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how blockchain technology can be used to improve the security and safety of large language models (LLMs). LLMs are powerful AI systems that can generate human-like text, but they can also be misused for things like spreading misinformation or generating harmful content.
The researchers investigate different ways that blockchain could help address these issues. Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that can be used to verify the integrity of data and transactions. The paper explores how blockchain could be used to ensure the integrity of LLM models, moderate the content they produce, and protect the privacy of the data used to train them.
For example, a blockchain-based system could be used to keep track of changes made to an LLM model over time, making it harder for someone to secretly modify the model for malicious purposes. Blockchain could also be used to create a decentralized content moderation system, where users can collectively decide what content is appropriate.
Overall, the paper provides a comprehensive overview of the potential benefits of using blockchain technology to enhance the security and safety of large language models, which are becoming increasingly important in our digital world.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by introducing the security and safety challenges posed by large language models (LLMs), such as model integrity, content moderation, and privacy preservation. It then provides an overview of key blockchain concepts, including decentralization, immutability, and consensus mechanisms.
The researchers then explore various blockchain-based approaches to address these challenges:
-
Model Integrity: The paper discusses how blockchain could be used to verify the integrity of LLM models by tracking changes and modifications over time in a tamper-evident manner.
-
Content Moderation: The survey examines blockchain-based solutions for decentralized content moderation, where users can collectively decide what content is appropriate.
-
Privacy Preservation: The paper explores how blockchain could be used to protect the privacy of the data used to train LLMs, such as by enabling secure data sharing and access control.
The paper also discusses the potential benefits of integrating blockchain with other technologies, such as decentralized storage and edge computing, to further enhance the security and safety of LLMs.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and well-structured survey of the potential applications of blockchain technology for improving the security and safety of large language models. The authors thoroughly cover the key challenges faced by LLMs and explore various blockchain-based solutions in a systematic manner.
One potential limitation of the research is that it primarily focuses on the theoretical and conceptual aspects of blockchain-based solutions, without delving into the practical implementation details or empirical evaluations. The paper could be strengthened by including case studies or proof-of-concept implementations to demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed approaches.
Additionally, the paper does not address some of the potential challenges and limitations of using blockchain technology, such as scalability, energy consumption, and regulatory considerations. Exploring these aspects could provide a more well-rounded understanding of the suitability and practicality of blockchain-based solutions for LLM security and safety.
Overall, the paper provides a valuable and comprehensive overview of the intersection of blockchain and large language models, and serves as a useful starting point for further research and development in this emerging field.
Conclusion
This survey paper provides a holistic exploration of the use of blockchain technology to enhance the security and safety of large language models (LLMs). By addressing key challenges such as model integrity, content moderation, and privacy preservation, the researchers present a compelling case for the potential benefits of integrating blockchain with LLM systems.
The paper's comprehensive coverage of blockchain concepts and its systematic examination of various blockchain-based solutions make it a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working at the intersection of AI, security, and distributed ledger technologies. As LLMs continue to grow in importance and influence, the insights and future research directions outlined in this survey could pave the way for more secure and trustworthy language AI systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Blockchain for Large Language Model Security and Safety: A Holistic Survey
Caleb Geren, Amanda Board, Gaby G. Dagher, Tim Andersen, Jun Zhuang
With the advent of accessible interfaces for interacting with large language models, there has been an associated explosion in both their commercial and academic interest. Consequently, there has also been an sudden burst of novel attacks associated with large language models, jeopardizing user data on a massive scale. Situated at a comparable crossroads in its development, and equally prolific to LLMs in its rampant growth, blockchain has emerged in recent years as a disruptive technology with the potential to redefine how we approach data handling. In particular, and due to its strong guarantees about data immutability and irrefutability as well as inherent data provenance assurances, blockchain has attracted significant attention as a means to better defend against the array of attacks affecting LLMs and further improve the quality of their responses. In this survey, we holistically evaluate current research on how blockchains are being used to help protect against LLM vulnerabilities, as well as analyze how they may further be used in novel applications. To better serve these ends, we introduce a taxonomy of blockchain for large language models (BC4LLM) and also develop various definitions to precisely capture the nature of different bodies of research in these areas. Moreover, throughout the paper, we present frameworks to contextualize broader research efforts, and in order to motivate the field further, we identify future research goals as well as challenges present in the blockchain for large language model (BC4LLM) space.
Read more7/30/2024
💬

0
Recent Advances in Attack and Defense Approaches of Large Language Models
Jing Cui, Yishi Xu, Zhewei Huang, Shuchang Zhou, Jianbin Jiao, Junge Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized artificial intelligence and machine learning through their advanced text processing and generating capabilities. However, their widespread deployment has raised significant safety and reliability concerns. Established vulnerabilities in deep neural networks, coupled with emerging threat models, may compromise security evaluations and create a false sense of security. Given the extensive research in the field of LLM security, we believe that summarizing the current state of affairs will help the research community better understand the present landscape and inform future developments. This paper reviews current research on LLM vulnerabilities and threats, and evaluates the effectiveness of contemporary defense mechanisms. We analyze recent studies on attack vectors and model weaknesses, providing insights into attack mechanisms and the evolving threat landscape. We also examine current defense strategies, highlighting their strengths and limitations. By contrasting advancements in attack and defense methodologies, we identify research gaps and propose future directions to enhance LLM security. Our goal is to advance the understanding of LLM safety challenges and guide the development of more robust security measures.
Read more9/9/2024

0
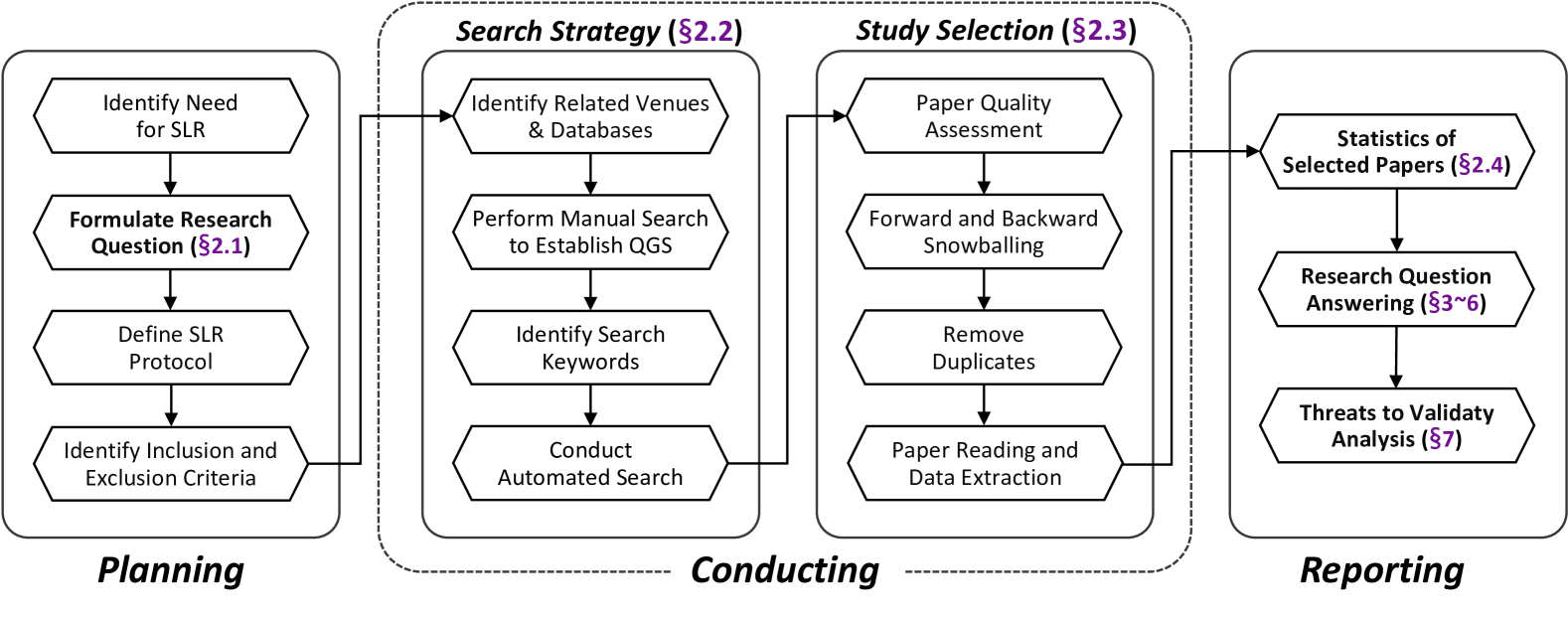
Large Language Models for Cyber Security: A Systematic Literature Review
Hanxiang Xu, Shenao Wang, Ningke Li, Kailong Wang, Yanjie Zhao, Kai Chen, Ting Yu, Yang Liu, Haoyu Wang
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened up new opportunities for leveraging artificial intelligence in various domains, including cybersecurity. As the volume and sophistication of cyber threats continue to grow, there is an increasing need for intelligent systems that can automatically detect vulnerabilities, analyze malware, and respond to attacks. In this survey, we conduct a comprehensive review of the literature on the application of LLMs in cybersecurity (LLM4Security). By comprehensively collecting over 30K relevant papers and systematically analyzing 127 papers from top security and software engineering venues, we aim to provide a holistic view of how LLMs are being used to solve diverse problems across the cybersecurity domain. Through our analysis, we identify several key findings. First, we observe that LLMs are being applied to a wide range of cybersecurity tasks, including vulnerability detection, malware analysis, network intrusion detection, and phishing detection. Second, we find that the datasets used for training and evaluating LLMs in these tasks are often limited in size and diversity, highlighting the need for more comprehensive and representative datasets. Third, we identify several promising techniques for adapting LLMs to specific cybersecurity domains, such as fine-tuning, transfer learning, and domain-specific pre-training. Finally, we discuss the main challenges and opportunities for future research in LLM4Security, including the need for more interpretable and explainable models, the importance of addressing data privacy and security concerns, and the potential for leveraging LLMs for proactive defense and threat hunting. Overall, our survey provides a comprehensive overview of the current state-of-the-art in LLM4Security and identifies several promising directions for future research.
Read more7/30/2024

0
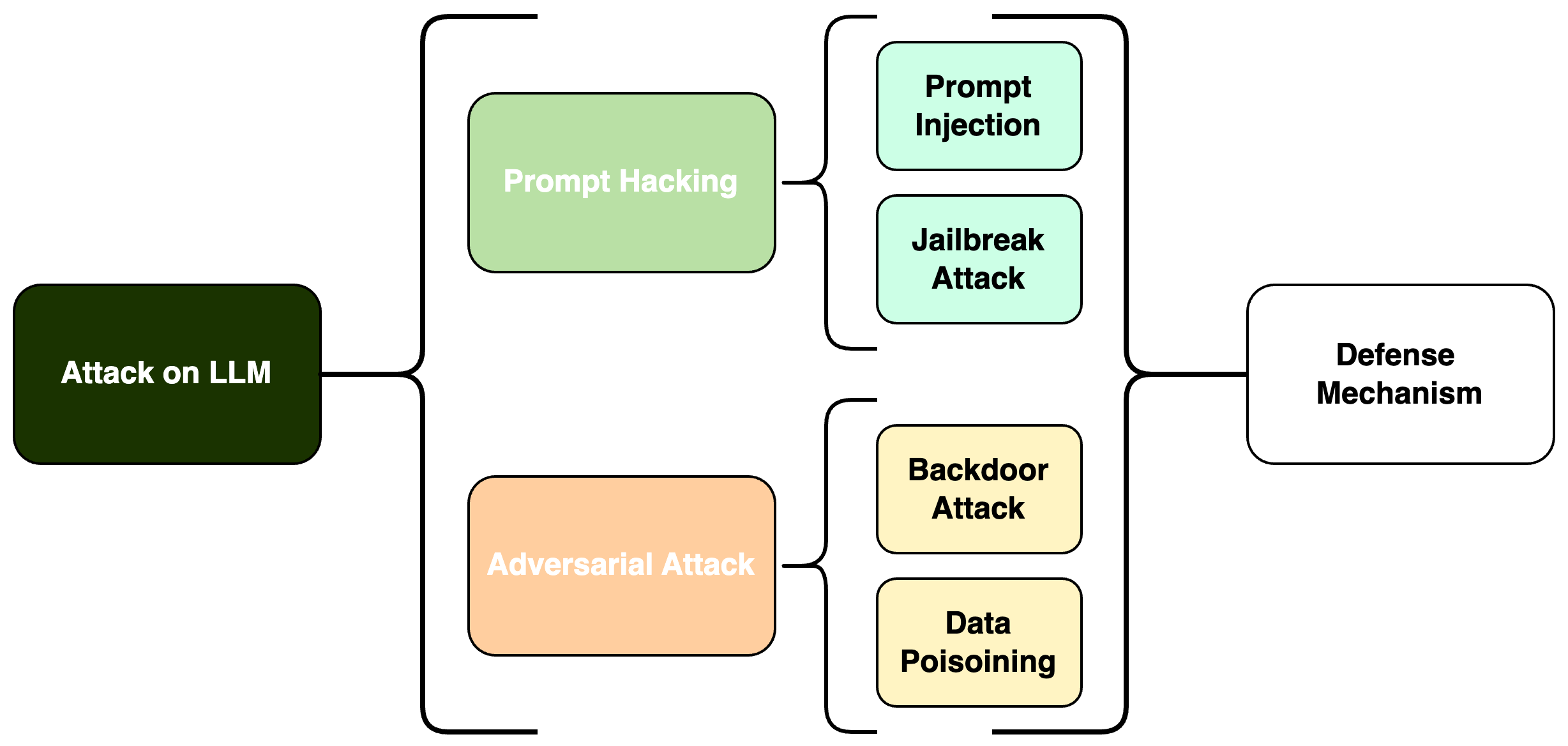
Exploring Vulnerabilities and Protections in Large Language Models: A Survey
Frank Weizhen Liu, Chenhui Hu
As Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly become key components in various AI applications, understanding their security vulnerabilities and the effectiveness of defense mechanisms is crucial. This survey examines the security challenges of LLMs, focusing on two main areas: Prompt Hacking and Adversarial Attacks, each with specific types of threats. Under Prompt Hacking, we explore Prompt Injection and Jailbreaking Attacks, discussing how they work, their potential impacts, and ways to mitigate them. Similarly, we analyze Adversarial Attacks, breaking them down into Data Poisoning Attacks and Backdoor Attacks. This structured examination helps us understand the relationships between these vulnerabilities and the defense strategies that can be implemented. The survey highlights these security challenges and discusses robust defensive frameworks to protect LLMs against these threats. By detailing these security issues, the survey contributes to the broader discussion on creating resilient AI systems that can resist sophisticated attacks.
Read more6/4/2024