BlueTempNet: A Temporal Multi-network Dataset of Social Interactions in Bluesky Social

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper presents a new temporal multi-network dataset called BlueTempNet, which captures social interactions within the Bluesky social media platform.
- The dataset includes various types of interactions, such as posts, replies, likes, and follows, over a one-year period.
- The researchers aim to provide a comprehensive resource for studying social dynamics and modeling temporal social networks.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers have created a new dataset called BlueTempNet that tracks how people interact on the Bluesky social media platform. Bluesky is a decentralized social network that aims to provide a more open and free-speech-friendly alternative to traditional social media.
The dataset contains information about different types of interactions on Bluesky, such as when people post messages, reply to others, like posts, or follow each other. This data is collected over the course of a full year, allowing researchers to see how these social connections and activity patterns change over time.
By making this dataset publicly available, the researchers hope to give other scientists and researchers a valuable resource for studying how social networks and online communities function. Analyzing temporal social networks can provide insights into things like how information spreads, how communities form and evolve, and how individual behaviors influence the overall dynamics of the network.
The Bluesky platform itself is also an interesting case study, as it represents a new model of decentralized social media that aims to address some of the perceived shortcomings of traditional platforms. Datasets like BlueTempNet can help researchers explore the social and technological implications of this shift towards more distributed online communities.
Technical Explanation
The BlueTempNet dataset captures temporal multi-network data from the Bluesky social media platform over a one-year period. The data includes the following types of interactions:
- Posts: When users create new posts or messages on the platform.
- Replies: When users reply to existing posts or messages.
- Likes: When users express approval by liking a post or message.
- Follows: When users choose to follow or subscribe to another user's activity.
This multi-modal interaction data is represented as a series of time-stamped edges between users, forming a temporal network. The researchers leverage this temporal aspect to study the evolution of the social network over time, rather than just analyzing static snapshots.
The dataset covers a wide range of interactions, allowing researchers to model the complex dynamics of social activity on the platform. This could include exploring topics like information diffusion, community formation, and the interplay between different types of social connections.
By making BlueTempNet publicly available, the researchers aim to provide a valuable resource for the research community to study decentralized social networks and their implications for the future of online discourse and social interaction.
Critical Analysis
The BlueTempNet dataset represents a significant contribution to the field of social network analysis, as it provides a comprehensive view of user interactions within a decentralized social media platform. By capturing temporal data across multiple interaction types, the dataset enables researchers to explore the complex dynamics of online social networks in greater depth.
However, the paper does not address several potential limitations or caveats of the dataset. For example, it is unclear how representative the Bluesky user base is of the broader population, or whether there are any biases in the data collection process. Additionally, the researchers do not discuss potential privacy concerns or ethical considerations around the use of this dataset, which could be important when studying social interactions and online behaviors.
Further, the paper lacks a critical analysis of the Bluesky platform itself and the broader implications of decentralized social media. While the dataset provides an opportunity to study these emerging models, the researchers could have engaged in more substantive discussion about the potential benefits, challenges, and societal impact of such platforms.
Despite these limitations, the BlueTempNet dataset represents a valuable contribution to the field, and future research leveraging this resource should aim to address these concerns and explore the dataset's implications more thoroughly.
Conclusion
The BlueTempNet dataset provides a unique and timely opportunity to study the social dynamics of a decentralized social media platform like Bluesky. By capturing a rich set of temporal multi-network data, the researchers have created a valuable resource for the research community to explore the evolving nature of online social interactions.
Analyzing datasets like BlueTempNet can yield important insights into the future of social media and online communities, particularly as new models like Bluesky emerge to challenge the status quo. This research has the potential to inform the design of more ethical, equitable, and empowering social platforms that better serve the needs of users and society.
While the paper could have delved deeper into the broader implications and limitations of the dataset, the BlueTempNet resource still represents a significant step forward in the study of decentralized social networks and their impact on the digital landscape.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
BlueTempNet: A Temporal Multi-network Dataset of Social Interactions in Bluesky Social
Ujun Jeong, Bohan Jiang, Zhen Tan, H. Russell Bernard, Huan Liu
Decentralized social media platforms like Bluesky Social (Bluesky) have made it possible to publicly disclose some user behaviors with millisecond-level precision. Embracing Bluesky's principles of open-source and open-data, we present the first collection of the temporal dynamics of user-driven social interactions. BlueTempNet integrates multiple types of networks into a single multi-network, including user-to-user interactions (following and blocking users) and user-to-community interactions (creating and joining communities). Communities are user-formed groups in custom Feeds, where users subscribe to posts aligned with their interests. Following Bluesky's public data policy, we collect existing Bluesky Feeds, including the users who liked and generated these Feeds, and provide tools to gather users' social interactions within a date range. This data-collection strategy captures past user behaviors and supports the future data collection of user behavior.
Read more7/25/2024

0
I'm in the Bluesky Tonight: Insights from a Year Worth of Social Data
Andrea Failla, Giulio Rossetti
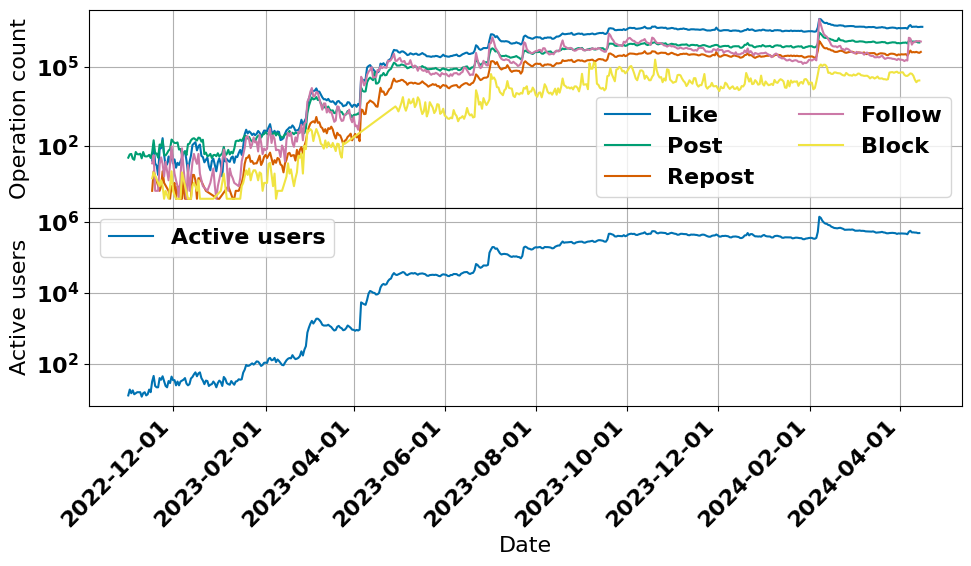
Pollution of online social spaces caused by rampaging d/misinformation is a growing societal concern. However, recent decisions to reduce access to social media APIs are causing a shortage of publicly available, recent, social media data, thus hindering the advancement of computational social science as a whole. We present a large, high-coverage dataset of social interactions and user-generated content from Bluesky Social to address this pressing issue. The dataset contains the complete post history of over 4M users (81% of all registered accounts), totalling 235M posts. We also make available social data covering follow, comment, repost, and quote interactions. Since Bluesky allows users to create and bookmark feed generators (i.e., content recommendation algorithms), we also release the full output of several popular algorithms available on the platform, along with their timestamped ``like'' interactions and time of bookmarking. This dataset allows unprecedented analysis of online behavior and human-machine engagement patterns. Notably, it provides ground-truth data for studying the effects of content exposure and self-selection and performing content virality and diffusion analysis.
Read more5/1/2024

0
Looking AT the Blue Skies of Bluesky
Leonhard Balduf, Saidu Sokoto, Onur Ascigil, Gareth Tyson, Bjorn Scheuermann, Maciej Korczy'nski, Ignacio Castro, Micha{l} Kr'ol
The pitfalls of centralized social networks, such as Facebook and Twitter/X, have led to concerns about control, transparency, and accountability. Decentralized social networks have emerged as a result with the goal of empowering users. These decentralized approaches come with their own tradeoffs, and therefore multiple architectures exist. In this paper, we conduct the first large-scale analysis of Bluesky, a prominent decentralized microblogging platform. In contrast to alternative approaches (e.g. Mastodon), Bluesky decomposes and opens the key functions of the platform into subcomponents that can be provided by third party stakeholders. We collect a comprehensive dataset covering all the key elements of Bluesky, study user activity and assess the diversity of providers for each sub-components.
Read more8/23/2024

0
Modeling social interaction dynamics using temporal graph networks
J. Taery Kim, Archit Naik, Isuru Jayarathne, Sehoon Ha, Jouh Yeong Chew
Integrating intelligent systems, such as robots, into dynamic group settings poses challenges due to the mutual influence of human behaviors and internal states. A robust representation of social interaction dynamics is essential for effective human-robot collaboration. Existing approaches often narrow their focus to facial expressions or speech, overlooking the broader context. We propose employing an adapted Temporal Graph Networks to comprehensively represent social interaction dynamics while enabling its practical implementation. Our method incorporates temporal multi-modal behavioral data including gaze interaction, voice activity and environmental context. This representation of social interaction dynamics is trained as a link prediction problem using annotated gaze interaction data. The F1-score outperformed the baseline model by 37.0%. This improvement is consistent for a secondary task of next speaker prediction which achieves an improvement of 29.0%. Our contributions are two-fold, including a model to representing social interaction dynamics which can be used for many downstream human-robot interaction tasks like human state inference and next speaker prediction. More importantly, this is achieved using a more concise yet efficient message passing method, significantly reducing it from 768 to 14 elements, while outperforming the baseline model.
Read more4/11/2024