Can Your Generative Model Detect Out-of-Distribution Covariate Shift?

0

Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Can Your Generative Model Detect Out-of-Distribution Covariate Shift?
Christiaan Viviers, Amaan Valiuddin, Francisco Caetano, Lemar Abdi, Lena Filatova, Peter de With, Fons van der Sommen
Detecting Out-of-Distribution~(OOD) sensory data and covariate distribution shift aims to identify new test examples with different high-level image statistics to the captured, normal and In-Distribution (ID) set. Existing OOD detection literature largely focuses on semantic shift with little-to-no consensus over covariate shift. Generative models capture the ID data in an unsupervised manner, enabling them to effectively identify samples that deviate significantly from this learned distribution, irrespective of the downstream task. In this work, we elucidate the ability of generative models to detect and quantify domain-specific covariate shift through extensive analyses that involves a variety of models. To this end, we conjecture that it is sufficient to detect most occurring sensory faults (anomalies and deviations in global signals statistics) by solely modeling high-frequency signal-dependent and independent details. We propose a novel method, CovariateFlow, for OOD detection, specifically tailored to covariate heteroscedastic high-frequency image-components using conditional Normalizing Flows (cNFs). Our results on CIFAR10 vs. CIFAR10-C and ImageNet200 vs. ImageNet200-C demonstrate the effectiveness of the method by accurately detecting OOD covariate shift. This work contributes to enhancing the fidelity of imaging systems and aiding machine learning models in OOD detection in the presence of covariate shift.
Read more9/6/2024
🌀

0
Unexplored Faces of Robustness and Out-of-Distribution: Covariate Shifts in Environment and Sensor Domains
Eunsu Baek, Keondo Park, Jiyoon Kim, Hyung-Sin Kim
Computer vision applications predict on digital images acquired by a camera from physical scenes through light. However, conventional robustness benchmarks rely on perturbations in digitized images, diverging from distribution shifts occurring in the image acquisition process. To bridge this gap, we introduce a new distribution shift dataset, ImageNet-ES, comprising variations in environmental and camera sensor factors by directly capturing 202k images with a real camera in a controllable testbed. With the new dataset, we evaluate out-of-distribution (OOD) detection and model robustness. We find that existing OOD detection methods do not cope with the covariate shifts in ImageNet-ES, implying that the definition and detection of OOD should be revisited to embrace real-world distribution shifts. We also observe that the model becomes more robust in both ImageNet-C and -ES by learning environment and sensor variations in addition to existing digital augmentations. Lastly, our results suggest that effective shift mitigation via camera sensor control can significantly improve performance without increasing model size. With these findings, our benchmark may aid future research on robustness, OOD, and camera sensor control for computer vision. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/Edw2n/ImageNet-ES.
Read more4/26/2024


0
Rethinking the Evaluation of Out-of-Distribution Detection: A Sorites Paradox
Xingming Long, Jie Zhang, Shiguang Shan, Xilin Chen
Most existing out-of-distribution (OOD) detection benchmarks classify samples with novel labels as the OOD data. However, some marginal OOD samples actually have close semantic contents to the in-distribution (ID) sample, which makes determining the OOD sample a Sorites Paradox. In this paper, we construct a benchmark named Incremental Shift OOD (IS-OOD) to address the issue, in which we divide the test samples into subsets with different semantic and covariate shift degrees relative to the ID dataset. The data division is achieved through a shift measuring method based on our proposed Language Aligned Image feature Decomposition (LAID). Moreover, we construct a Synthetic Incremental Shift (Syn-IS) dataset that contains high-quality generated images with more diverse covariate contents to complement the IS-OOD benchmark. We evaluate current OOD detection methods on our benchmark and find several important insights: (1) The performance of most OOD detection methods significantly improves as the semantic shift increases; (2) Some methods like GradNorm may have different OOD detection mechanisms as they rely less on semantic shifts to make decisions; (3) Excessive covariate shifts in the image are also likely to be considered as OOD for some methods. Our code and data are released in https://github.com/qqwsad5/IS-OOD.
Read more6/17/2024

0
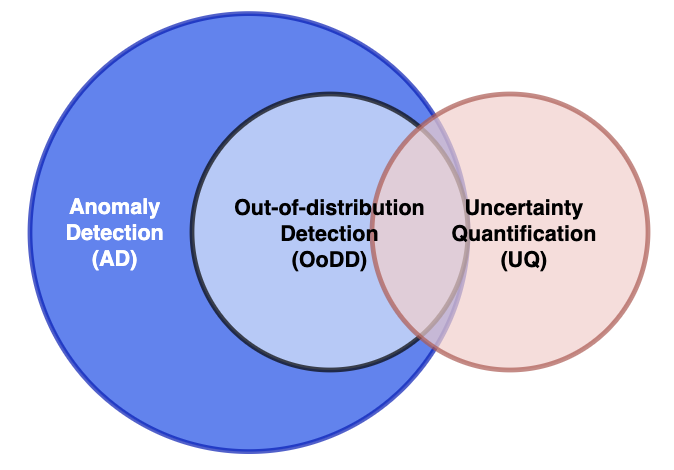
Out-of-distribution Detection in Medical Image Analysis: A survey
Zesheng Hong, Yubiao Yue, Yubin Chen, Lele Cong, Huanjie Lin, Yuanmei Luo, Mini Han Wang, Weidong Wang, Jialong Xu, Xiaoqi Yang, Hechang Chen, Zhenzhang Li, Sihong Xie
Computer-aided diagnostics has benefited from the development of deep learning-based computer vision techniques in these years. Traditional supervised deep learning methods assume that the test sample is drawn from the identical distribution as the training data. However, it is possible to encounter out-of-distribution samples in real-world clinical scenarios, which may cause silent failure in deep learning-based medical image analysis tasks. Recently, research has explored various out-of-distribution (OOD) detection situations and techniques to enable a trustworthy medical AI system. In this survey, we systematically review the recent advances in OOD detection in medical image analysis. We first explore several factors that may cause a distributional shift when using a deep-learning-based model in clinic scenarios, with three different types of distributional shift well defined on top of these factors. Then a framework is suggested to categorize and feature existing solutions, while the previous studies are reviewed based on the methodology taxonomy. Our discussion also includes evaluation protocols and metrics, as well as the challenge and a research direction lack of exploration.
Read more7/4/2024