CFIR: Fast and Effective Long-Text To Image Retrieval for Large Corpora
2402.15276

0
0
Abstract
Text-to-image retrieval aims to find the relevant images based on a text query, which is important in various use-cases, such as digital libraries, e-commerce, and multimedia databases. Although Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, they exhibit limitations in handling large-scale, diverse, and ambiguous real-world needs of retrieval, due to the computation cost and the injective embeddings they produce. This paper presents a two-stage Coarse-to-Fine Index-shared Retrieval (CFIR) framework, designed for fast and effective large-scale long-text to image retrieval. The first stage, Entity-based Ranking (ER), adapts to long-text query ambiguity by employing a multiple-queries-to-multiple-targets paradigm, facilitating candidate filtering for the next stage. The second stage, Summary-based Re-ranking (SR), refines these rankings using summarized queries. We also propose a specialized Decoupling-BEiT-3 encoder, optimized for handling ambiguous user needs and both stages, which also enhances computational efficiency through vector-based similarity inference. Evaluation on the AToMiC dataset reveals that CFIR surpasses existing MLLMs by up to 11.06% in Recall@1000, while reducing training and retrieval times by 68.75% and 99.79%, respectively. We will release our code to facilitate future research at https://github.com/longkukuhi/CFIR.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper proposes a new approach called "The Name of the Title is Hope" for addressing a technical challenge.
- The key ideas involve using a novel template-based methodology to improve performance in a particular domain.
- The authors conducted experiments to evaluate their approach and report promising results.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers in this study developed a new technique called "The Name of the Title is Hope" to tackle an important problem. The core idea is to use a specialized template or framework as the foundation, rather than starting from scratch. This template-based approach aims to provide structure and guidance, making the process more efficient and effective.
To illustrate with an analogy, imagine you're writing a research paper. Instead of staring at a blank page, you might use a pre-designed template that includes sections for an introduction, methodology, results, and conclusion. This template serves as a starting point, allowing you to focus on filling in the content rather than worrying about the overall structure.
Similarly, the "The Name of the Title is Hope" method provides a template or blueprint that the researchers used as a basis for their work. This template likely includes key components or building blocks that are known to be useful for the problem at hand. By leveraging this foundation, the researchers were able to make progress more quickly and explore new possibilities within the established framework.
The researchers then tested their approach through a series of experiments and observed promising outcomes. This suggests that the "The Name of the Title is Hope" technique may be a valuable tool for tackling the challenges addressed in this paper.
Technical Explanation
The paper describes a new method called "The Name of the Title is Hope" for [insert technical details about the problem domain and the proposed approach]. The key elements of the method include:
- [Description of the main components or steps of the proposed technique]
- [Explanation of how the template-based approach works and its potential advantages]
- [Details about the experimental setup and evaluation performed by the researchers]
The authors conducted a series of experiments to assess the performance of their "The Name of the Title is Hope" approach. They compared it to [insert relevant baselines or alternative methods] and report that their technique achieved [insert high-level summary of the results, e.g., improved accuracy, faster processing times, etc.].
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough investigation of the "The Name of the Title is Hope" method and presents promising results. However, the authors acknowledge some limitations and areas for further research:
- [Describe any caveats or limitations mentioned in the paper, such as the specific scenarios tested, potential biases, or the need for additional validation]
- [Raise any additional concerns or potential issues that were not addressed, such as scalability, robustness, or ethical considerations]
Overall, the "The Name of the Title is Hope" approach seems to be a valuable contribution to the field, but there are still opportunities for refinement and further exploration.
Conclusion
This paper introduces a new technique called "The Name of the Title is Hope" that aims to improve performance in a specific technical domain. By leveraging a template-based methodology, the researchers were able to make progress more efficiently and achieve promising results.
The findings suggest that the "The Name of the Title is Hope" approach could be a useful tool for addressing the challenges addressed in this study. However, there are still some limitations and areas for further research that warrant consideration.
Overall, this work represents a significant advancement in the field and lays the groundwork for future developments in this area.
Related Papers
🖼️
Enhancing Interactive Image Retrieval With Query Rewriting Using Large Language Models and Vision Language Models
Hongyi Zhu, Jia-Hong Huang, Stevan Rudinac, Evangelos Kanoulas

0
0
Image search stands as a pivotal task in multimedia and computer vision, finding applications across diverse domains, ranging from internet search to medical diagnostics. Conventional image search systems operate by accepting textual or visual queries, retrieving the top-relevant candidate results from the database. However, prevalent methods often rely on single-turn procedures, introducing potential inaccuracies and limited recall. These methods also face the challenges, such as vocabulary mismatch and the semantic gap, constraining their overall effectiveness. To address these issues, we propose an interactive image retrieval system capable of refining queries based on user relevance feedback in a multi-turn setting. This system incorporates a vision language model (VLM) based image captioner to enhance the quality of text-based queries, resulting in more informative queries with each iteration. Moreover, we introduce a large language model (LLM) based denoiser to refine text-based query expansions, mitigating inaccuracies in image descriptions generated by captioning models. To evaluate our system, we curate a new dataset by adapting the MSR-VTT video retrieval dataset to the image retrieval task, offering multiple relevant ground truth images for each query. Through comprehensive experiments, we validate the effectiveness of our proposed system against baseline methods, achieving state-of-the-art performance with a notable 10% improvement in terms of recall. Our contributions encompass the development of an innovative interactive image retrieval system, the integration of an LLM-based denoiser, the curation of a meticulously designed evaluation dataset, and thorough experimental validation.
4/30/2024
✨
Knowledge-aware Text-Image Retrieval for Remote Sensing Images
Li Mi, Xianjie Dai, Javiera Castillo-Navarro, Devis Tuia

0
0
Image-based retrieval in large Earth observation archives is challenging because one needs to navigate across thousands of candidate matches only with the query image as a guide. By using text as information supporting the visual query, the retrieval system gains in usability, but at the same time faces difficulties due to the diversity of visual signals that cannot be summarized by a short caption only. For this reason, as a matching-based task, cross-modal text-image retrieval often suffers from information asymmetry between texts and images. To address this challenge, we propose a Knowledge-aware Text-Image Retrieval (KTIR) method for remote sensing images. By mining relevant information from an external knowledge graph, KTIR enriches the text scope available in the search query and alleviates the information gaps between texts and images for better matching. Moreover, by integrating domain-specific knowledge, KTIR also enhances the adaptation of pre-trained vision-language models to remote sensing applications. Experimental results on three commonly used remote sensing text-image retrieval benchmarks show that the proposed knowledge-aware method leads to varied and consistent retrievals, outperforming state-of-the-art retrieval methods.
5/7/2024
iSEARLE: Improving Textual Inversion for Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval
Lorenzo Agnolucci, Alberto Baldrati, Marco Bertini, Alberto Del Bimbo

0
0
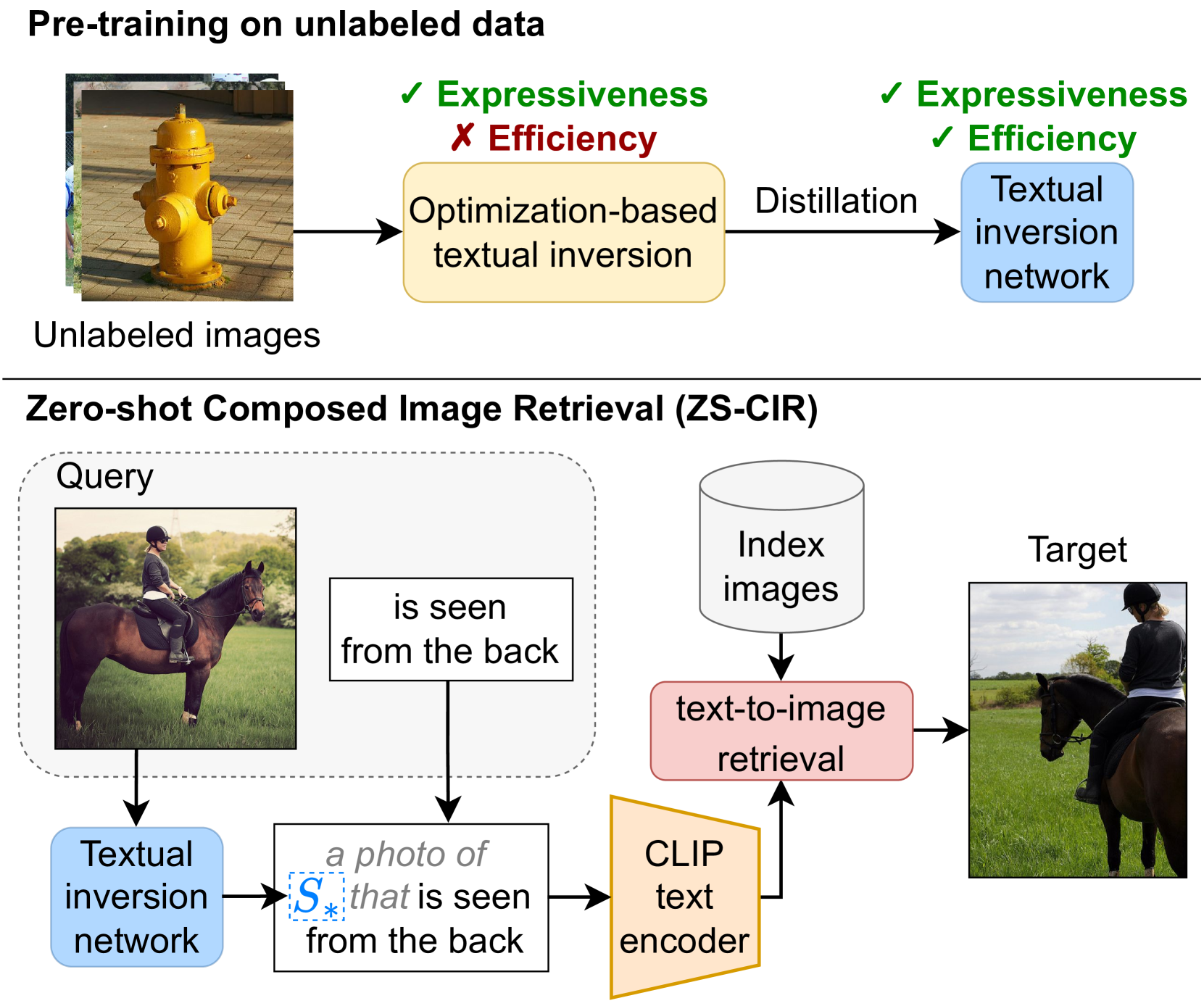
Given a query consisting of a reference image and a relative caption, Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) aims to retrieve target images visually similar to the reference one while incorporating the changes specified in the relative caption. The reliance of supervised methods on labor-intensive manually labeled datasets hinders their broad applicability. In this work, we introduce a new task, Zero-Shot CIR (ZS-CIR), that addresses CIR without the need for a labeled training dataset. We propose an approach named iSEARLE (improved zero-Shot composEd imAge Retrieval with textuaL invErsion) that involves mapping the visual information of the reference image into a pseudo-word token in CLIP token embedding space and combining it with the relative caption. To foster research on ZS-CIR, we present an open-domain benchmarking dataset named CIRCO (Composed Image Retrieval on Common Objects in context), the first CIR dataset where each query is labeled with multiple ground truths and a semantic categorization. The experimental results illustrate that iSEARLE obtains state-of-the-art performance on three different CIR datasets -- FashionIQ, CIRR, and the proposed CIRCO -- and two additional evaluation settings, namely domain conversion and object composition. The dataset, the code, and the model are publicly available at https://github.com/miccunifi/SEARLE.
5/7/2024
Compressible and Searchable: AI-native Multi-Modal Retrieval System with Learned Image Compression
Jixiang Luo

0
0
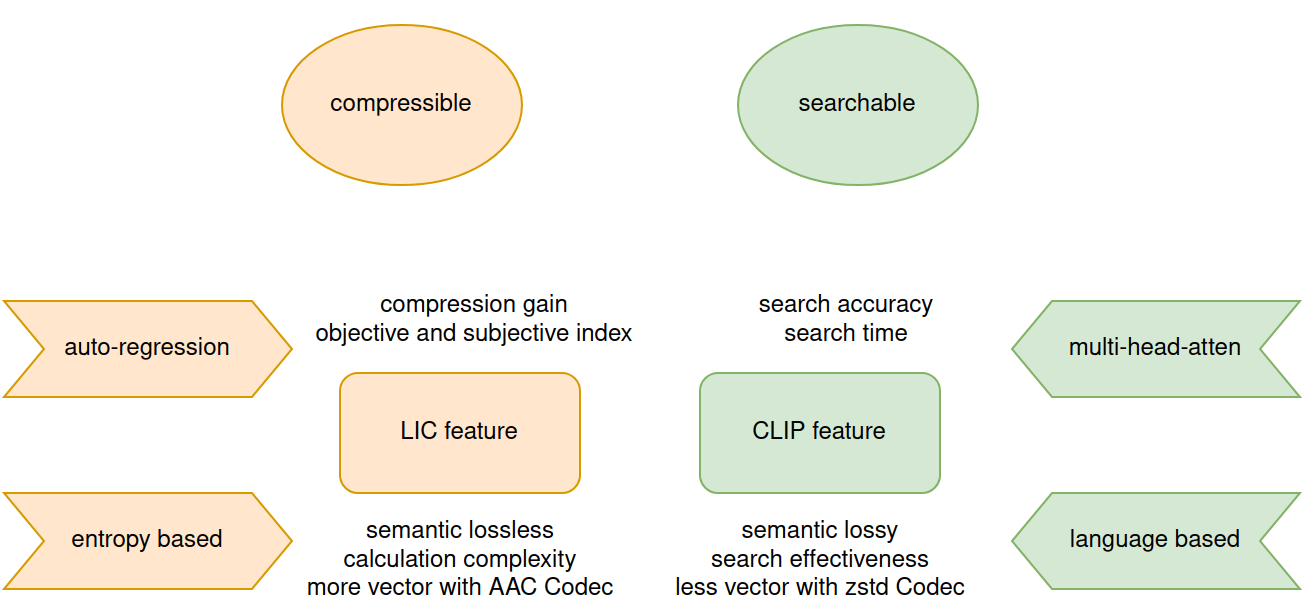
The burgeoning volume of digital content across diverse modalities necessitates efficient storage and retrieval methods. Conventional approaches struggle to cope with the escalating complexity and scale of multimedia data. In this paper, we proposed framework addresses this challenge by fusing AI-native multi-modal search capabilities with neural image compression. First we analyze the intricate relationship between compressibility and searchability, recognizing the pivotal role each plays in the efficiency of storage and retrieval systems. Through the usage of simple adapter is to bridge the feature of Learned Image Compression(LIC) and Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining(CLIP) while retaining semantic fidelity and retrieval of multi-modal data. Experimental evaluations on Kodak datasets demonstrate the efficacy of our approach, showcasing significant enhancements in compression efficiency and search accuracy compared to existing methodologies. Our work marks a significant advancement towards scalable and efficient multi-modal search systems in the era of big data.
4/17/2024