Efficacy of Language Model Self-Play in Non-Zero-Sum Games

0

Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Efficacy of Language Model Self-Play in Non-Zero-Sum Games
Austen Liao, Nicholas Tomlin, Dan Klein
Game-playing agents like AlphaGo have achieved superhuman performance through self-play, which is theoretically guaranteed to yield optimal policies in competitive games. However, most language tasks are partially or fully cooperative, so it is an open question whether techniques like self-play can effectively be used to improve language models. We empirically investigate this question in a negotiation game setting known as Deal or No Deal (DoND). Crucially, the objective in DoND can be modified to produce a fully cooperative game, a strictly competitive one, or anything in between. We finetune language models in self-play over multiple rounds of filtered behavior cloning in DoND for each of these objectives. Contrary to expectations, we find that language model self-play leads to significant performance gains in both cooperation and competition with humans, suggesting that self-play and related techniques have promise despite a lack of theoretical guarantees.
Read more6/28/2024

0
Self-Play Preference Optimization for Language Model Alignment
Yue Wu, Zhiqing Sun, Huizhuo Yuan, Kaixuan Ji, Yiming Yang, Quanquan Gu
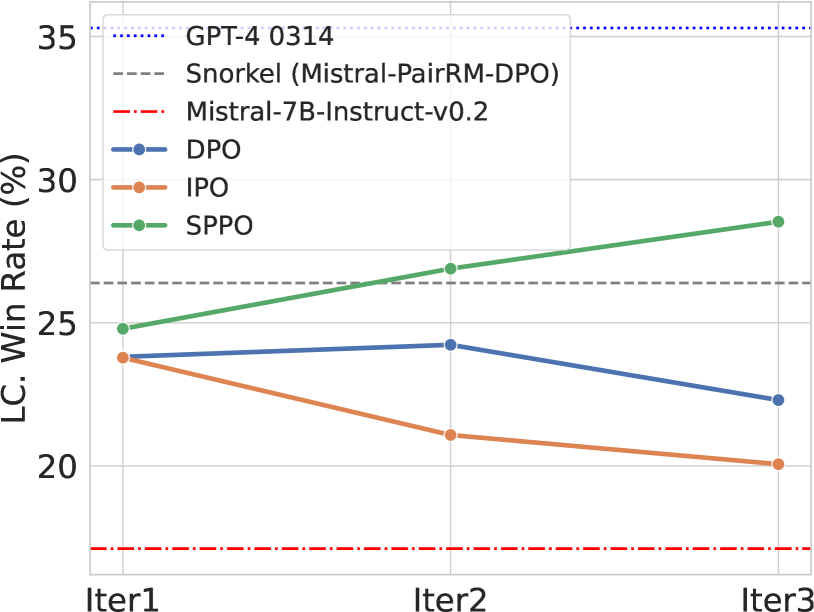
Traditional reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) approaches relying on parametric models like the Bradley-Terry model fall short in capturing the intransitivity and irrationality in human preferences. Recent advancements suggest that directly working with preference probabilities can yield a more accurate reflection of human preferences, enabling more flexible and accurate language model alignment. In this paper, we propose a self-play-based method for language model alignment, which treats the problem as a constant-sum two-player game aimed at identifying the Nash equilibrium policy. Our approach, dubbed Self-Play Preference Optimization (SPPO), approximates the Nash equilibrium through iterative policy updates and enjoys a theoretical convergence guarantee. Our method can effectively increase the log-likelihood of the chosen response and decrease that of the rejected response, which cannot be trivially achieved by symmetric pairwise loss such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Identity Preference Optimization (IPO). In our experiments, using only 60k prompts (without responses) from the UltraFeedback dataset and without any prompt augmentation, by leveraging a pre-trained preference model PairRM with only 0.4B parameters, SPPO can obtain a model from fine-tuning Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 that achieves the state-of-the-art length-controlled win-rate of 28.53% against GPT-4-Turbo on AlpacaEval 2.0. It also outperforms the (iterative) DPO and IPO on MT-Bench and the Open LLM Leaderboard. Starting from a stronger base model Llama-3-8B-Instruct, we are able to achieve a length-controlled win rate of 38.77%. Notably, the strong performance of SPPO is achieved without additional external supervision (e.g., responses, preferences, etc.) from GPT-4 or other stronger language models. Codes are available at https://github.com/uclaml/SPPO.
Read more6/17/2024


2
Self-playing Adversarial Language Game Enhances LLM Reasoning
Pengyu Cheng, Tianhao Hu, Han Xu, Zhisong Zhang, Yong Dai, Lei Han, Nan Du
We explore the self-play training procedure of large language models (LLMs) in a two-player adversarial language game called Adversarial Taboo. In this game, an attacker and a defender communicate around a target word only visible to the attacker. The attacker aims to induce the defender to speak the target word unconsciously, while the defender tries to infer the target word from the attacker's utterances. To win the game, both players should have sufficient knowledge about the target word and high-level reasoning ability to infer and express in this information-reserved conversation. Hence, we are curious about whether LLMs' reasoning ability can be further enhanced by self-play in this adversarial language game (SPAG). With this goal, we select several open-source LLMs and let each act as the attacker and play with a copy of itself as the defender on an extensive range of target words. Through reinforcement learning on the game outcomes, we observe that the LLMs' performances uniformly improve on a broad range of reasoning benchmarks. Furthermore, iteratively adopting this self-play process can continuously promote LLMs' reasoning abilities. The code is at https://github.com/Linear95/SPAG.
Read more5/24/2024

0
Investigating Regularization of Self-Play Language Models
Reda Alami, Abdalgader Abubaker, Mastane Achab, Mohamed El Amine Seddik, Salem Lahlou
This paper explores the effects of various forms of regularization in the context of language model alignment via self-play. While both reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) and direct preference optimization (DPO) require to collect costly human-annotated pairwise preferences, the self-play fine-tuning (SPIN) approach replaces the rejected answers by data generated from the previous iterate. However, the SPIN method presents a performance instability issue in the learning phase, which can be mitigated by playing against a mixture of the two previous iterates. In the same vein, we propose in this work to address this issue from two perspectives: first, by incorporating an additional Kullback-Leibler (KL) regularization to stay at the proximity of the reference policy; second, by using the idea of fictitious play which smoothens the opponent policy across all previous iterations. In particular, we show that the KL-based regularizer boils down to replacing the previous policy by its geometric mixture with the base policy inside of the SPIN loss function. We finally discuss empirical results on MT-Bench as well as on the Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard.
Read more4/9/2024