European Quantum Ecosystems -- Preparing the Industry for the Quantum Security and Communications Revolution

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper discusses the European QUantum ecOsystems (EQUOS) project, which aims to prepare industry for the quantum security and communications revolution.
- It covers key topics such as quantum key distribution (QKD), software-defined networking (SDN), quantum network control, and quantum key management.
- The research examines how these technologies can be leveraged to build secure quantum communication networks and applications.
Plain English Explanation
The EQUOS project is focused on helping industry get ready for the upcoming changes in quantum technology. Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a way to securely share encryption keys using quantum physics principles. Software-defined networking (SDN) is a flexible approach to managing computer networks. The project looks at how QKD and SDN can be used together to build quantum communication networks that are more secure.
It also examines quantum network control and quantum key management - the processes to monitor and maintain these quantum networks and the encryption keys they use. The goal is to help companies and organizations prepare for the coming "quantum revolution" in security and communications.
Technical Explanation
The EQUOS project explores ways to leverage emerging quantum technologies like QKD and SDN to build secure quantum communication networks and applications.
A key focus is on quantum network control - the processes and systems needed to monitor, manage and maintain these complex quantum networks. The research also examines quantum key management - the secure distribution and lifecycle management of the encryption keys used in quantum communications.
By addressing these technical challenges, the EQUOS project aims to help prepare industry and organizations for the coming "quantum revolution" in security and communications.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a high-level overview of the EQUOS project's goals and focus areas, but does not go into deep technical details or results. Some potential areas for further research and development include:
- Exploring real-world deployment challenges and barriers to adopting quantum-based security and networking technologies.
- Investigating the performance, scalability and cost-effectiveness of the proposed quantum communication solutions compared to traditional approaches.
- Assessing the maturity and readiness of the underlying quantum hardware, software and control systems required to enable these quantum ecosystems.
- Considering the broader economic, regulatory and policy implications of transitioning critical infrastructure to quantum-based systems.
Overall, the EQUOS project appears to be an important initiative to help industry prepare for the emerging quantum technology landscape, though more detailed research and proofs-of-concept may be needed to fully realize its vision.
Conclusion
The EQUOS project is focused on helping industry get ready for the upcoming "quantum revolution" in security and communications. It is exploring how technologies like quantum key distribution, software-defined networking, quantum network control, and quantum key management can be leveraged to build secure quantum communication networks and applications.
By addressing the technical challenges in these areas, the project aims to prepare organizations for the transformative impact of quantum technologies. While more research may be needed, the EQUOS initiative represents an important step towards a quantum-ready future.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
European Quantum Ecosystems -- Preparing the Industry for the Quantum Security and Communications Revolution
Noel Farrugia, Daniel Bonanno, Nicholas Frendo, Andr'e Xuereb, Evangelos Kosmatos, Alexandros Stavdas, Marco Russo, Bartolomeo Montrucchio, Marco Menchetti, Davide Bacco, Silvia Marigonda, Francesco Stocco, Guglielmo Morgari, Antonio Manzalini
There is mounting evidence that a second quantum revolution based on the technological capabilities to detect and manipulate single quantum particles (e.g., electrons, photons, ions, etc), a feat not achieved during the first quantum revolution, is progressing fast. It is expected that in less than 10 years, this second quantum revolution shall have a significant impact over numerous industries, including finance, medicine, energy, transportation, etc. Quantum computers threaten the status quo of cybersecurity, due to known quantum algorithms that can break asymmetric encryption, which is what gives us the ability to communicate securely using a public channel. Considering the world's dependence on digital communication through data exchange and processing, retaining the ability to communicate securely even once quantum computers come into play, cannot be stressed enough. Two solutions are available: Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC); which, we emphasise, are not mutually exclusive. The EuroQCI initiative, of which EQUO is a part of, focuses on QKD and aims to build a network whereby EU countries can communicate securely through QKD. To this aim, the DEP (Digital Europe Programme) project aims to bring technological matureness to QKD by deploying a QKD test network and, through this exercise, understand what is lacking from an operator's point of view when the time to integrate QKD in their network comes.
Read more8/28/2024


0
Post-Quantum Secure UE-to-UE Communications
Sanzida Hoque, Abdullah Aydeger, Engin Zeydan
The rapid development of quantum computing poses a significant threat to the security of current cryptographic systems, including those used in User Equipment (UE) for mobile communications. Conventional cryptographic algorithms such as Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) and Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) are vulnerable to quantum computing attacks, which could jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data transmitted by UEs. This demo paper proposes the integration of Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) in TLS for UE Communication to mitigate the risks of quantum attacks. We present our setup and explain each of the components used. We also provide the entire workflow of the demo for other researchers to replicate the same setup. By addressing the implementation of PQC within a 5G network to secure UE-to-UE communication, this research aims to pave the way for developing quantum-resistant mobile devices and securing the future of wireless communications.
Read more8/22/2024


0
The Future of QKD Networks
Alin-Bogdan Popa, Pantelimon George Popescu
With the recent advancements in quantum technologies, the QKD market exploded. World players are scrambling to win the race towards global QKD networks, even before the rules and policies required by such large endeavors were even discussed. Several vendors are on the market, each with specific parameters and advantages (in terms of key rate, link range, KMS software, etc.), hence considerable effort is now made towards standardization. While quantum communications is expected to reach a market size of up to $36B by 2040, the largest QKD initiative to date is EuroQCI, which, due to its sheer scale, is forcing the market to mature. Although building a QKD network is believed to be trivial today, inter-connecting federated networks on a global scale is a heavy challenge. We propose QKD virtual networks not only as a useful infrastructure abstraction for increased flexibility and granular security, but as an inevitable solution for several problems that future QKD networks will encounter on the way towards widespread adoption.
Read more7/2/2024

0
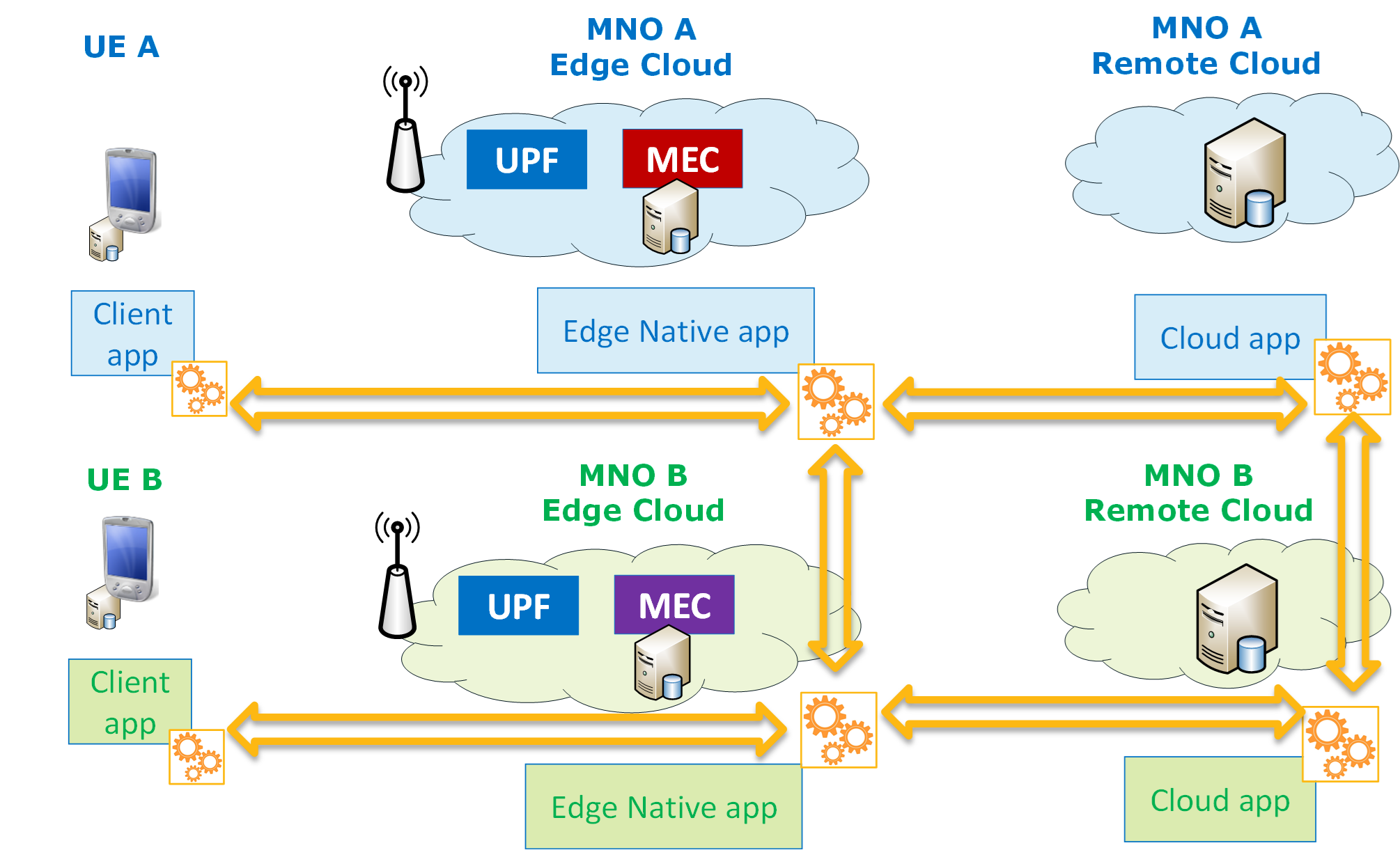
Quantum-safe Edge Applications: How to Secure Computation in Distributed Computing Systems
Claudio Cicconetti, Dario Sabella, Pietro Noviello, Gennaro Davide Paduanelli
The advent of distributed computing systems will offer great flexibility for application workloads, while also imposing more attention to security, where the future advent and adoption of quantum technology can introduce new security threats. For this reason, the Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) working group at ETSI has recently started delving into security aspects, especially motivated by the upcoming reality of the MEC federation, which involves services made of application instances belonging to different systems (thus, different trust domains). On the other side, Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) can help strengthen the level of security by enabling the exchange of secure keys through an unconditionally secure protocol, e.g., to secure communication between REST clients and servers in distributed computing systems at the edge. In this paper, we propose a technical solution to achieve this goal, building on standard specifications, namely ETSI MEC and ETSI QKD, and discussing the gaps and limitations of current technology, which hamper full-fledged in-field deployment and mass adoption. Furthermore, we provide our look-ahead view on the future of secure distributed computing through the enticing option of federating edge computing domains.
Read more5/28/2024