Post-Quantum Secure UE-to-UE Communications

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Examines post-quantum secure user equipment (UE) to UE communications in 5G networks
- Presents a 5G-based testbed for analyzing post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms
- Evaluates the performance and security of PQC algorithms in a real-world 5G environment
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores how to securely connect user devices (UEs) in 5G cellular networks, even in a future where quantum computers can break current encryption. It describes a test system built using 5G technology to evaluate different post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms.
Post-quantum cryptography refers to encryption techniques that can resist attacks from quantum computers. This is important as quantum computers, when they become feasible, could potentially crack the encryption methods used today.
The researchers set up a 5G network testbed to measure the performance and security of different PQC algorithms when used for communications between 5G user devices. This allows them to see how well these quantum-resistant encryption methods would work in a real 5G system.
Technical Explanation
The paper describes a 5G-based testbed developed to evaluate the use of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms for secure user equipment (UE) to UE communications in 5G networks.
The testbed architecture includes 5G core network elements like the access and mobility management function (AMF), session management function (SMF), and user plane function (UPF). It also incorporates PQC algorithms as alternatives to the standard 5G encryption protocols.
Experiments were conducted to measure the performance impact and security of PQC algorithms within this 5G environment. Parameters like throughput, latency, and key exchange times were analyzed to understand how the quantum-resistant encryption would affect the 5G network's operation.
The results indicate that certain PQC algorithms can be effectively integrated into 5G systems to provide post-quantum security for UE-to-UE communications, without significantly degrading network performance.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive evaluation of PQC algorithms in a realistic 5G testbed. However, it does not address some potential limitations:
- The testbed is relatively small-scale and may not fully capture the complexities of a large commercial 5G network.
- Only a subset of PQC algorithms were tested, and there are many other candidates that warrant investigation.
- The security analysis is focused on the cryptographic aspects, but does not consider broader 5G network security implications.
Further research could expand the testbed scale, explore a wider range of PQC schemes, and investigate system-level security and resilience in depth. Nonetheless, this work represents an important step towards ensuring 5G networks can defend against future quantum computing threats.
Conclusion
This paper demonstrates a practical approach for evaluating post-quantum cryptography within a 5G network environment. The results indicate that PQC algorithms can be effectively integrated into 5G to provide quantum-resistant security for UE-to-UE communications, without significantly impacting network performance.
This research is an important contribution towards ensuring the long-term security of 5G and future cellular networks in the face of the quantum computing threat. Continued development and testing of PQC solutions within realistic 5G contexts will be crucial as the industry prepares for the post-quantum era.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Post-Quantum Secure UE-to-UE Communications
Sanzida Hoque, Abdullah Aydeger, Engin Zeydan
The rapid development of quantum computing poses a significant threat to the security of current cryptographic systems, including those used in User Equipment (UE) for mobile communications. Conventional cryptographic algorithms such as Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) and Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) are vulnerable to quantum computing attacks, which could jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data transmitted by UEs. This demo paper proposes the integration of Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) in TLS for UE Communication to mitigate the risks of quantum attacks. We present our setup and explain each of the components used. We also provide the entire workflow of the demo for other researchers to replicate the same setup. By addressing the implementation of PQC within a 5G network to secure UE-to-UE communication, this research aims to pave the way for developing quantum-resistant mobile devices and securing the future of wireless communications.
Read more8/22/2024

0
Exploring Post Quantum Cryptography with Quantum Key Distribution for Sustainable Mobile Network Architecture Design
Sanzida Hoque, Abdullah Aydeger, Engin Zeydan
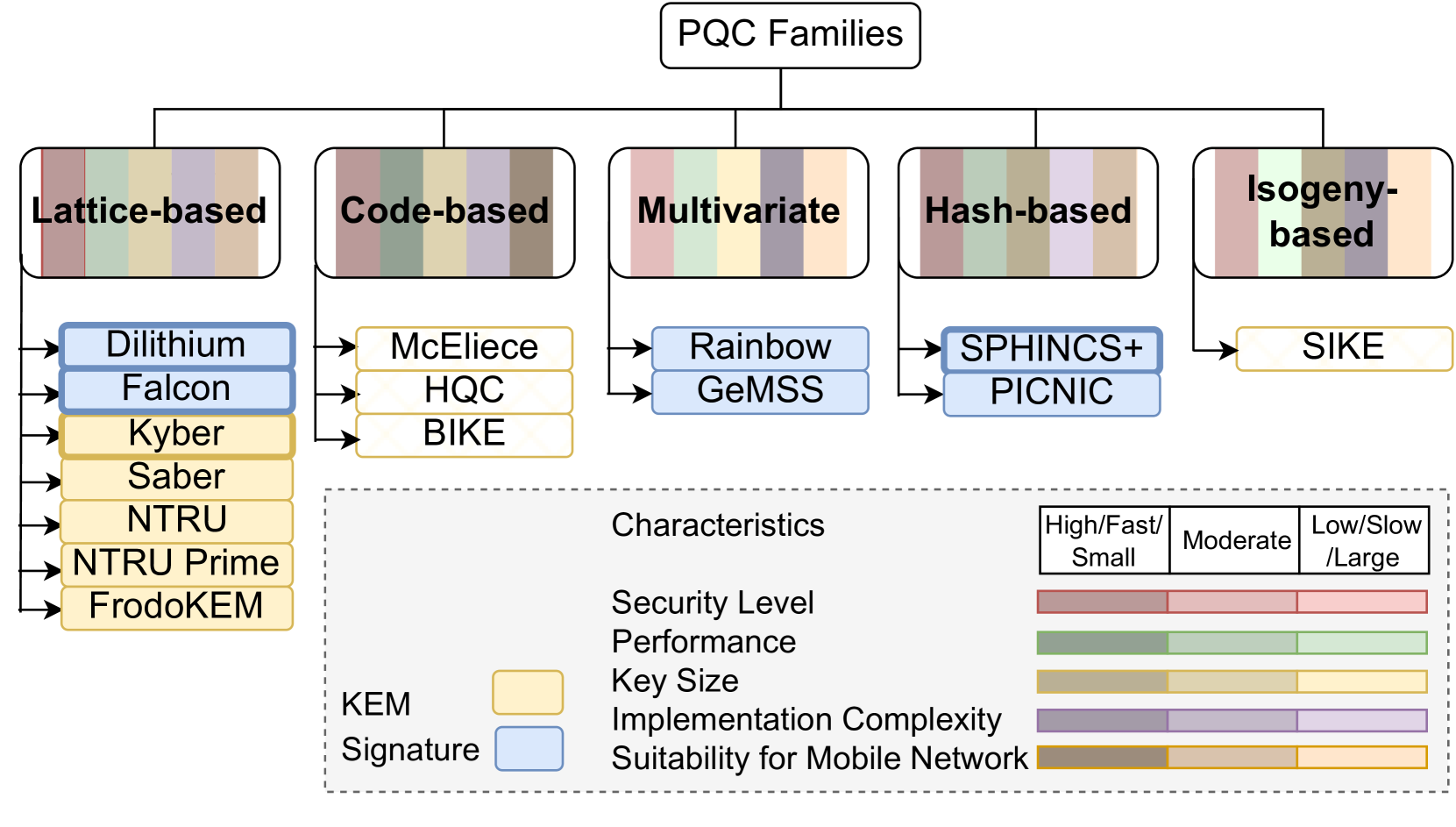
The proliferation of mobile networks and their increasing importance to modern life, combined with the emerging threat of quantum computing, present new challenges and opportunities for cybersecurity. This paper addresses the complexity of protecting these critical infrastructures against future quantum attacks while considering operational sustainability. We begin with an overview of the current landscape, identify the main vulnerabilities in mobile networks, and evaluate existing security solutions with new post-quantum cryptography (PQC) methods. We then present a quantum-secure architecture with PQC and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) tailored explicitly for sustainable mobile networks and illustrate its applicability with several use cases that emphasize the need for advanced protection measures in this new era. In addition, a comprehensive analysis of PQC algorithm families is presented, focusing on their suitability for integration in mobile environments, with particular attention to the trade-offs between energy consumption and security improvements. Finally, recommendations for strengthening mobile networks against quantum threats are provided through a detailed examination of current challenges and opportunities.
Read more4/17/2024
🔮

0
Applications of Post-quantum Cryptography
Emils Bagirovs, Grigory Provodin, Tuomo Sipola, Jari Hautamaki
With the constantly advancing capabilities of quantum computers, conventional cryptographic systems relying on complex math problems may encounter unforeseen vulnerabilities. Unlike regular computers, which are often deemed cost-ineffective in cryptographic attacks, quantum computers have a significant advantage in calculation speed. This distinction potentially makes currently used algorithms less secure or even completely vulnerable, compelling the exploration of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) as the most reasonable solution to quantum threats. This review aims to provide current information on applications, benefits, and challenges associated with the PQC. The review employs a systematic scoping review with the scope restricted to the years 2022 and 2023; only articles that were published in scientific journals were used in this paper. The review examined the articles on the applications of quantum computing in various spheres. However, the scope of this paper was restricted to the domain of the PQC because most of the analyzed articles featured this field. Subsequently, the paper is analyzing various PQC algorithms, including lattice-based, hash-based, code-based, multivariate polynomial, and isogeny-based cryptography. Each algorithm is being judged based on its potential applications, robustness, and challenges. All the analyzed algorithms are promising for the post-quantum era in such applications as digital signatures, communication channels, and IoT. Moreover, some of the algorithms are already implemented in the spheres of banking transactions, communication, and intellectual property. Meanwhile, despite their potential, these algorithms face serious challenges since they lack standardization, require vast amounts of storage and computation power, and might have unknown vulnerabilities that can be discovered only with years of cryptanalysis.
Read more6/26/2024


0
European Quantum Ecosystems -- Preparing the Industry for the Quantum Security and Communications Revolution
Noel Farrugia, Daniel Bonanno, Nicholas Frendo, Andr'e Xuereb, Evangelos Kosmatos, Alexandros Stavdas, Marco Russo, Bartolomeo Montrucchio, Marco Menchetti, Davide Bacco, Silvia Marigonda, Francesco Stocco, Guglielmo Morgari, Antonio Manzalini
There is mounting evidence that a second quantum revolution based on the technological capabilities to detect and manipulate single quantum particles (e.g., electrons, photons, ions, etc), a feat not achieved during the first quantum revolution, is progressing fast. It is expected that in less than 10 years, this second quantum revolution shall have a significant impact over numerous industries, including finance, medicine, energy, transportation, etc. Quantum computers threaten the status quo of cybersecurity, due to known quantum algorithms that can break asymmetric encryption, which is what gives us the ability to communicate securely using a public channel. Considering the world's dependence on digital communication through data exchange and processing, retaining the ability to communicate securely even once quantum computers come into play, cannot be stressed enough. Two solutions are available: Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC); which, we emphasise, are not mutually exclusive. The EuroQCI initiative, of which EQUO is a part of, focuses on QKD and aims to build a network whereby EU countries can communicate securely through QKD. To this aim, the DEP (Digital Europe Programme) project aims to bring technological matureness to QKD by deploying a QKD test network and, through this exercise, understand what is lacking from an operator's point of view when the time to integrate QKD in their network comes.
Read more8/28/2024