Exploding AI Power Use: an Opportunity to Rethink Grid Planning and Management
2311.11645

0
0
🤖
Abstract
The unprecedented rapid growth of computing demand for AI is projected to increase global annual datacenter (DC) growth from 7.2% to 11.3%. We project the 5-year AI DC demand for several power grids and assess whether they will allow desired AI growth (resource adequacy). If not, several desperate measures -- grid policies that enable more load growth and maintain grid reliability by sacrificing new DC reliability are considered. We find that two DC hotspots -- EirGrid (Ireland) and Dominion (US) -- will have difficulty accommodating new DCs needed by the AI growth. In EirGrid, relaxing new DC reliability guarantees increases the power available to 1.6x--4.1x while maintaining 99.6% actual power availability for the new DCs, sufficient for the 5-year AI demand. In Dominion, relaxing reliability guarantees increases available DC capacity similarly (1.5x--4.6x) but not enough for the 5-year AI demand. New DCs only receive 89% power availability. Study of other US power grids -- SPP, CAISO, ERCOT -- shows that sufficient capacity exists for the projected AI load growth. Our results suggest the need to rethink adequacy assessment and also grid planning and management. New research opportunities include coordinated planning, reliability models that incorporate load flexibility, and adaptive load abstractions.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper examines the projected growth in computing demand for AI and its impact on global datacenter (DC) infrastructure.
- The researchers analyze whether major power grids can accommodate the expected surge in AI-driven DC demand over the next 5 years.
- They find that some power grids, like EirGrid (Ireland) and Dominion (US), will struggle to meet the new DC requirements without making compromises to reliability.
- The paper suggests the need to rethink grid planning and management, as well as explore new research areas like coordinated planning and adaptive load models.
Plain English Explanation
The rapid growth of AI is driving a massive increase in computing power demand globally. The researchers project that annual datacenter growth will rise from 7.2% to 11.3% to meet this AI-related computing need.
They looked at several major power grids to see if they would be able to handle the expected surge in new datacenters required to support AI over the next 5 years. Unfortunately, they found that two regions - EirGrid in Ireland and Dominion in the US - were likely to have trouble accommodating all the new datacenters.
To address this problem, the researchers considered some desperate measures. They found that by relaxing the reliability guarantees for new datacenters in these regions, the power grids could actually free up 1.6x to 4.6x more capacity. This would be enough for the EirGrid region to meet the 5-year AI demand, but still not quite sufficient for Dominion.
The overall takeaway is that existing power grid planning and management approaches may need to be rethought to keep up with the insatiable computing needs of AI. New research is needed on topics like coordinated grid planning, more flexible reliability models, and better ways to adapt to fluctuating datacenter loads.
Technical Explanation
The researchers used a data-driven approach to project the dramatic growth in computing demand driven by the rise of AI. They estimate that global annual datacenter growth will increase from 7.2% to 11.3% to meet this AI-related load.
To understand the impact on power grid infrastructure, the team analyzed several major grid regions, including EirGrid in Ireland, Dominion in the US, SPP, CAISO, and ERCOT. They assessed whether these grids would have sufficient capacity to accommodate the projected 5-year growth in AI-driven datacenters.
The analysis revealed that two regions - EirGrid and Dominion - were likely to face challenges in meeting the new datacenter demand. To address this, the researchers explored "desperate measures" - grid policies that could enable more load growth while maintaining overall grid reliability, but at the expense of new datacenter reliability.
For EirGrid, the team found that relaxing reliability guarantees for new datacenters could increase the available power by 1.6x to 4.1x, which would be sufficient to meet the 5-year AI demand while still maintaining 99.6% actual power availability. In Dominion, a similar approach increased available capacity, but not enough to fully support the projected AI load growth - new datacenters would only receive 89% power availability.
The study of the other US grids, however, showed that they had sufficient capacity to handle the forecasted AI-driven load increases.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a valuable analysis of the potential strain that the growth of AI computing could place on power grid infrastructure in certain regions. The researchers' consideration of "desperate measures" to increase available capacity, even at the expense of datacenter reliability, highlights the challenging trade-offs that grid operators may face.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into the potential consequences of reduced reliability for new datacenters. While the EirGrid scenario maintains 99.6% actual power availability, the Dominion case drops to only 89% - which could have significant implications for the performance and resilience of AI systems running in those facilities.
Additionally, the paper acknowledges the need for "new research opportunities" in areas like coordinated planning and adaptive load models, but does not provide much detail on what those new approaches might entail. Further exploration of these research directions and their potential benefits would strengthen the paper's contribution.
Finally, the analysis is limited to a few specific grid regions. While the researchers note that other grids seem to have sufficient capacity, a more comprehensive global assessment could yield additional insights and help inform broader grid planning and policy decisions.
Conclusion
This paper sheds light on a critical, yet often overlooked, challenge facing the rapid growth of AI computing - the ability of power grids to keep up with the surging demand. The researchers' projections and analysis of several major grid regions reveal that some areas, like EirGrid and Dominion, may struggle to accommodate the new datacenter capacity needed to support AI unless they are willing to compromise on reliability.
The paper suggests the need to rethink traditional approaches to grid planning and management, and explore new research areas that could help address the unique requirements of AI workloads. As AI continues to transform industries and our daily lives, ensuring the underlying power infrastructure can support the computing demands will be crucial. This work highlights an important challenge that deserves further attention from both the research community and grid operators.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
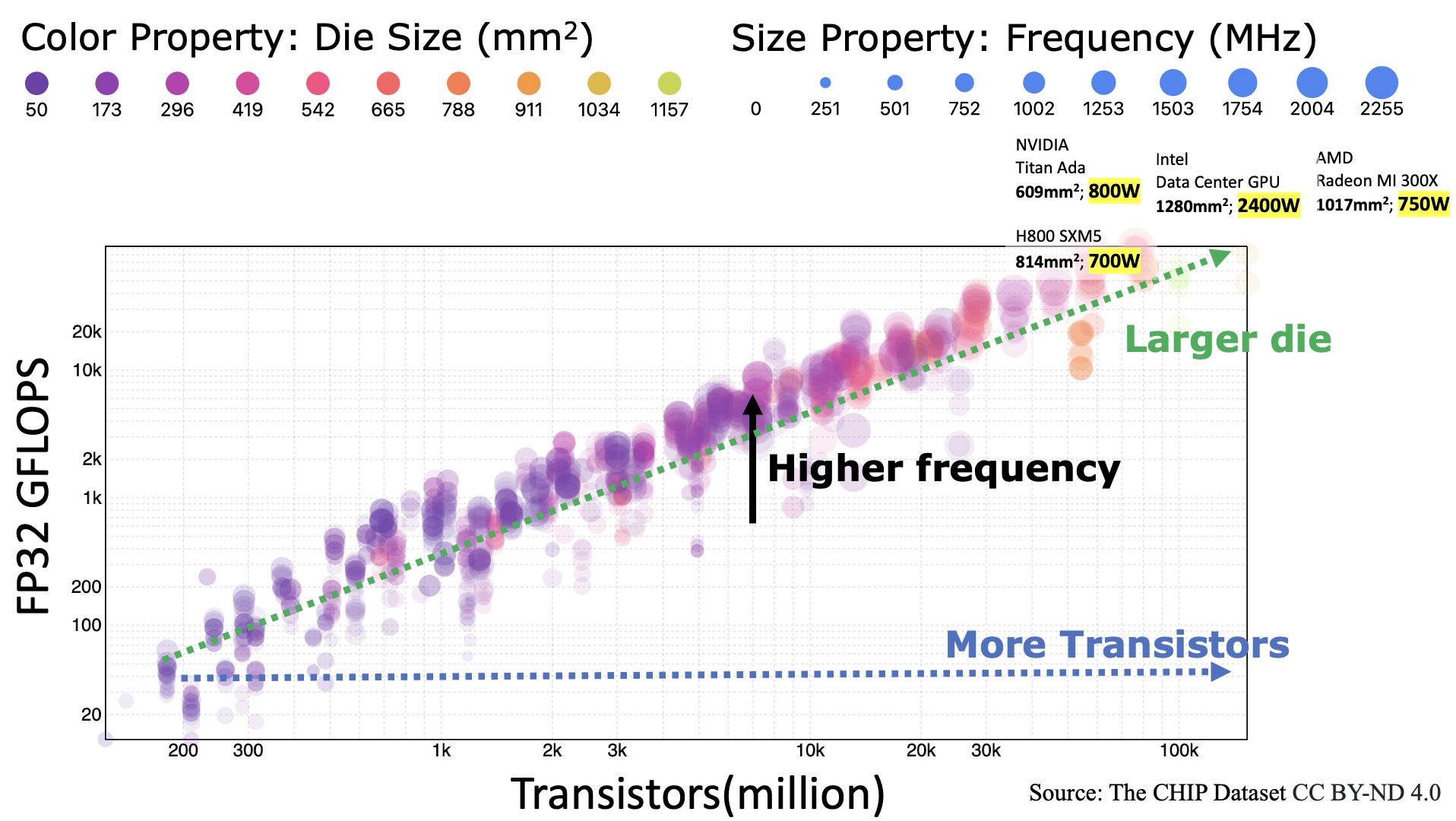
Beyond Efficiency: Scaling AI Sustainably
Carole-Jean Wu, Bilge Acun, Ramya Raghavendra, Kim Hazelwood

0
0
Barroso's seminal contributions in energy-proportional warehouse-scale computing launched an era where modern datacenters have become more energy efficient and cost effective than ever before. At the same time, modern AI applications have driven ever-increasing demands in computing, highlighting the importance of optimizing efficiency across the entire deep learning model development cycle. This paper characterizes the carbon impact of AI, including both operational carbon emissions from training and inference as well as embodied carbon emissions from datacenter construction and hardware manufacturing. We highlight key efficiency optimization opportunities for cutting-edge AI technologies, from deep learning recommendation models to multi-modal generative AI tasks. To scale AI sustainably, we must also go beyond efficiency and optimize across the life cycle of computing infrastructures, from hardware manufacturing to datacenter operations and end-of-life processing for the hardware.
6/26/2024

Robustness Analysis of AI Models in Critical Energy Systems
Pantelis Dogoulis, Matthieu Jimenez, Salah Ghamizi, Maxime Cordy, Yves Le Traon

0
0
This paper analyzes the robustness of state-of-the-art AI-based models for power grid operations under the $N-1$ security criterion. While these models perform well in regular grid settings, our results highlight a significant loss in accuracy following the disconnection of a line.%under this security criterion. Using graph theory-based analysis, we demonstrate the impact of node connectivity on this loss. Our findings emphasize the need for practical scenario considerations in developing AI methodologies for critical infrastructure.
6/21/2024
AI-Driven Approaches for Optimizing Power Consumption: A Comprehensive Survey
Parag Biswas, Abdur Rashid, Angona Biswas, Md Abdullah Al Nasim, Kishor Datta Gupta, Roy George

0
0
Reduced environmental effect, lower operating costs, and a stable and sustainable energy supply for current and future generations are the main reasons why power optimization is important. Power optimization makes ensuring that energy is used more effectively, cutting down on waste and optimizing the utilization of resources.In today's world, power optimization and artificial intelligence (AI) integration are essential to changing the way energy is produced, used, and distributed. Real-time monitoring and analysis of power usage trends is made possible by AI-driven algorithms and predictive analytics, which enable dynamic modifications to effectively satisfy demand. Efficiency and sustainability are increased when power consumption is optimized in different sectors thanks to the use of intelligent systems. This survey paper comprises an extensive review of the several AI techniques used for power optimization as well as a methodical analysis of the literature for the study of various intelligent system application domains across different disciplines of power consumption.This literature review identifies the performance and outcomes of 17 different research methods by assessing them, and it aims to distill valuable insights into their strengths and limitations. Furthermore, this article outlines future directions in the integration of AI for power consumption optimization.
6/26/2024
🤿
Resilience of the Electric Grid through Trustable IoT-Coordinated Assets
Vineet J. Nair, Venkatesh Venkataramanan, Priyank Srivastava, Partha S. Sarker, Anurag Srivastava, Laurentiu D. Marinovici, Jun Zha, Christopher Irwin, Prateek Mittal, John Williams, H. Vincent Poor, Anuradha M. Annaswamy

0
0
The electricity grid has evolved from a physical system to a cyber-physical system with digital devices that perform measurement, control, communication, computation, and actuation. The increased penetration of distributed energy resources (DERs) that include renewable generation, flexible loads, and storage provides extraordinary opportunities for improvements in efficiency and sustainability. However, they can introduce new vulnerabilities in the form of cyberattacks, which can cause significant challenges in ensuring grid resilience. %, i.e. the ability to rapidly restore grid services in the face of severe disruptions. We propose a framework in this paper for achieving grid resilience through suitably coordinated assets including a network of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. A local electricity market is proposed to identify trustable assets and carry out this coordination. Situational Awareness (SA) of locally available DERs with the ability to inject power or reduce consumption is enabled by the market, together with a monitoring procedure for their trustability and commitment. With this SA, we show that a variety of cyberattacks can be mitigated using local trustable resources without stressing the bulk grid. The demonstrations are carried out using a variety of platforms with a high-fidelity co-simulation platform, real-time hardware-in-the-loop validation, and a utility-friendly simulator.
6/24/2024