Exploratory Preference Optimization: Harnessing Implicit Q*-Approximation for Sample-Efficient RLHF
2405.21046

0
0
🧪
Abstract
Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has emerged as a central tool for language model alignment. We consider online exploration in RLHF, which exploits interactive access to human or AI feedback by deliberately encouraging the model to produce diverse, maximally informative responses. By allowing RLHF to confidently stray from the pre-trained model, online exploration offers the possibility of novel, potentially super-human capabilities, but its full potential as a paradigm for language model training has yet to be realized, owing to computational and statistical bottlenecks in directly adapting existing reinforcement learning techniques. We propose a new algorithm for online exploration in RLHF, Exploratory Preference Optimization (XPO), which is simple and practical -- a one-line change to (online) Direct Preference Optimization (DPO; Rafailov et al., 2023) -- yet enjoys the strongest known provable guarantees and promising empirical performance. XPO augments the DPO objective with a novel and principled exploration bonus, empowering the algorithm to explore outside the support of the initial model and human feedback data. In theory, we show that XPO is provably sample-efficient and converges to a near-optimal language model policy under natural exploration conditions, irrespective of whether the initial model has good coverage. Our analysis, which builds on the observation that DPO implicitly performs a form of $Q^{star}$-approximation (or, Bellman error minimization), combines previously disparate techniques from language modeling and theoretical reinforcement learning in a serendipitous fashion through the perspective of KL-regularized Markov decision processes. Empirically, we find that XPO is more sample-efficient than non-exploratory DPO variants in a preliminary evaluation.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Direct Preference Optimization With Unobserved Preference Heterogeneity
Keertana Chidambaram, Karthik Vinay Seetharaman, Vasilis Syrgkanis

0
0
RLHF has emerged as a pivotal step in aligning language models with human objectives and values. It typically involves learning a reward model from human preference data and then using reinforcement learning to update the generative model accordingly. Conversely, Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) directly optimizes the generative model with preference data, skipping reinforcement learning. However, both RLHF and DPO assume uniform preferences, overlooking the reality of diverse human annotators. This paper presents a new method to align generative models with varied human preferences. We propose an Expectation-Maximization adaptation to DPO, generating a mixture of models based on latent preference types of the annotators. We then introduce a min-max regret ensemble learning model to produce a single generative method to minimize worst-case regret among annotator subgroups with similar latent factors. Our algorithms leverage the simplicity of DPO while accommodating diverse preferences. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach in producing equitable generative policies.
5/27/2024
Iterative Preference Learning from Human Feedback: Bridging Theory and Practice for RLHF under KL-Constraint
Wei Xiong, Hanze Dong, Chenlu Ye, Ziqi Wang, Han Zhong, Heng Ji, Nan Jiang, Tong Zhang

0
0
This paper studies the alignment process of generative models with Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). We first identify the primary challenges of existing popular methods like offline PPO and offline DPO as lacking in strategical exploration of the environment. Then, to understand the mathematical principle of RLHF, we consider a standard mathematical formulation, the reverse-KL regularized contextual bandit for RLHF. Despite its widespread practical application, a rigorous theoretical analysis of this formulation remains open. We investigate its behavior in three distinct settings -- offline, online, and hybrid -- and propose efficient algorithms with finite-sample theoretical guarantees. Moving towards practical applications, our framework, with a robust approximation of the information-theoretical policy improvement oracle, naturally gives rise to several novel RLHF algorithms. This includes an iterative version of the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) algorithm for online settings, and a multi-step rejection sampling strategy for offline scenarios. Our empirical evaluations on real-world alignment experiment of large language model demonstrate that these proposed methods significantly surpass existing strong baselines, such as DPO and Rejection Sampling Optimization (RSO), showcasing the connections between solid theoretical foundations and their potent practical implementations.
5/2/2024
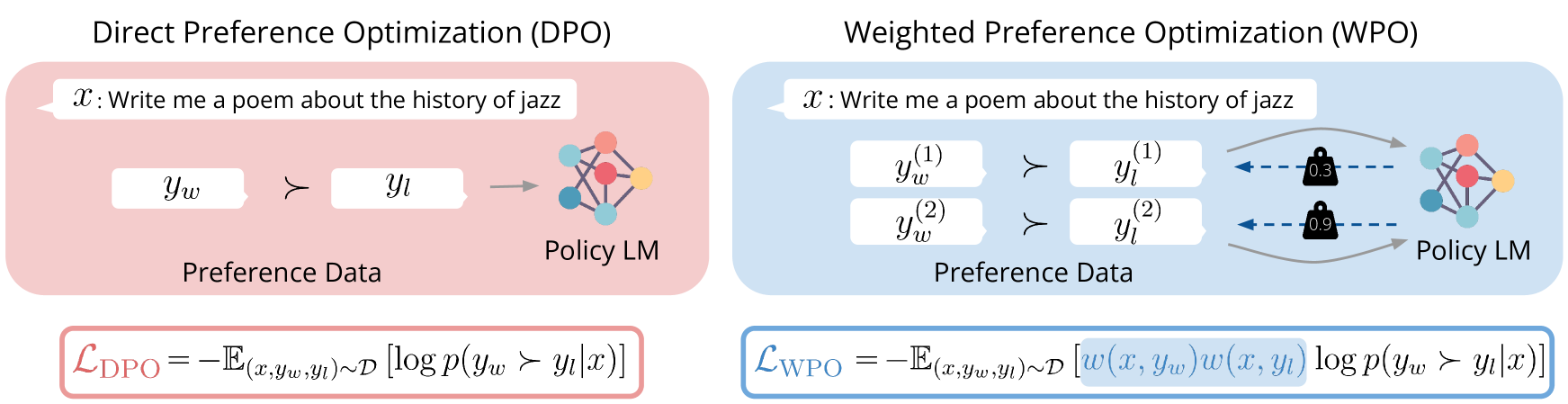
WPO: Enhancing RLHF with Weighted Preference Optimization
Wenxuan Zhou, Ravi Agrawal, Shujian Zhang, Sathish Reddy Indurthi, Sanqiang Zhao, Kaiqiang Song, Silei Xu, Chenguang Zhu

0
0
Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is a promising solution to align large language models (LLMs) more closely with human values. Off-policy preference optimization, where the preference data is obtained from other models, is widely adopted due to its cost efficiency and scalability. However, off-policy preference optimization often suffers from a distributional gap between the policy used for data collection and the target policy, leading to suboptimal optimization. In this paper, we propose a novel strategy to mitigate this problem by simulating on-policy learning with off-policy preference data. Our Weighted Preference Optimization (WPO) method adapts off-policy data to resemble on-policy data more closely by reweighting preference pairs according to their probability under the current policy. This method not only addresses the distributional gap problem but also enhances the optimization process without incurring additional costs. We validate our method on instruction following benchmarks including Alpaca Eval 2 and MT-bench. WPO not only outperforms Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) by up to 5.6% on Alpaca Eval 2 but also establishes a remarkable length-controlled winning rate against GPT-4-turbo of 48.6% based on Llama-3-8B-Instruct, making it the strongest 8B model on the leaderboard. We will release the code and models at https://github.com/wzhouad/WPO.
6/18/2024
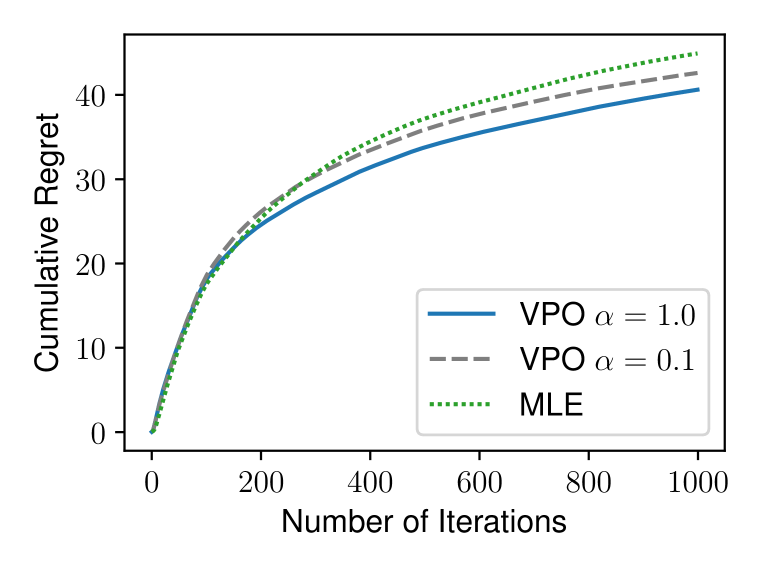
Value-Incentivized Preference Optimization: A Unified Approach to Online and Offline RLHF
Shicong Cen, Jincheng Mei, Katayoon Goshvadi, Hanjun Dai, Tong Yang, Sherry Yang, Dale Schuurmans, Yuejie Chi, Bo Dai

0
0
Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has demonstrated great promise in aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preference. Depending on the availability of preference data, both online and offline RLHF are active areas of investigation. A key bottleneck is understanding how to incorporate uncertainty estimation in the reward function learned from the preference data for RLHF, regardless of how the preference data is collected. While the principles of optimism or pessimism under uncertainty are well-established in standard reinforcement learning (RL), a practically-implementable and theoretically-grounded form amenable to large language models is not yet available, as standard techniques for constructing confidence intervals become intractable under arbitrary policy parameterizations. In this paper, we introduce a unified approach to online and offline RLHF -- value-incentivized preference optimization (VPO) -- which regularizes the maximum-likelihood estimate of the reward function with the corresponding value function, modulated by a $textit{sign}$ to indicate whether the optimism or pessimism is chosen. VPO also directly optimizes the policy with implicit reward modeling, and therefore shares a simpler RLHF pipeline similar to direct preference optimization. Theoretical guarantees of VPO are provided for both online and offline settings, matching the rates of their standard RL counterparts. Moreover, experiments on text summarization and dialog verify the practicality and effectiveness of VPO.
6/6/2024