Generating Synthetic Time Series Data for Cyber-Physical Systems
2404.08601

0
0
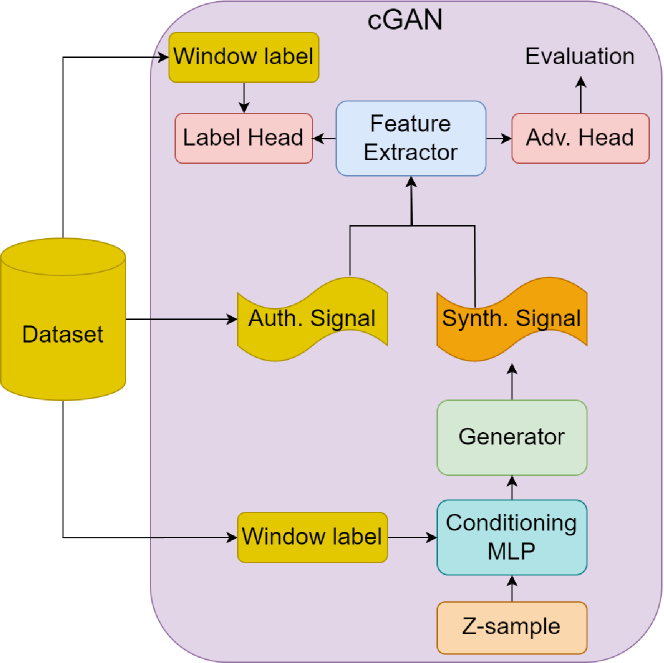
Abstract
Data augmentation is an important facilitator of deep learning applications in the time series domain. A gap is identified in the literature, demonstrating sparse exploration of the transformer, the dominant sequence model, for data augmentation in time series. A architecture hybridizing several successful priors is put forth and tested using a powerful time domain similarity metric. Results suggest the challenge of this domain, and several valuable directions for future work.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Time Series Data Augmentation as an Imbalanced Learning Problem
Vitor Cerqueira, Nuno Moniz, Ricardo In'acio, Carlos Soares

0
0
Recent state-of-the-art forecasting methods are trained on collections of time series. These methods, often referred to as global models, can capture common patterns in different time series to improve their generalization performance. However, they require large amounts of data that might not be readily available. Besides this, global models sometimes fail to capture relevant patterns unique to a particular time series. In these cases, data augmentation can be useful to increase the sample size of time series datasets. The main contribution of this work is a novel method for generating univariate time series synthetic samples. Our approach stems from the insight that the observations concerning a particular time series of interest represent only a small fraction of all observations. In this context, we frame the problem of training a forecasting model as an imbalanced learning task. Oversampling strategies are popular approaches used to deal with the imbalance problem in machine learning. We use these techniques to create synthetic time series observations and improve the accuracy of forecasting models. We carried out experiments using 7 different databases that contain a total of 5502 univariate time series. We found that the proposed solution outperforms both a global and a local model, thus providing a better trade-off between these two approaches.
4/30/2024
📊
Data Augmentation Policy Search for Long-Term Forecasting
Liran Nochumsohn, Omri Azencot

0
0
Data augmentation serves as a popular regularization technique to combat overfitting challenges in neural networks. While automatic augmentation has demonstrated success in image classification tasks, its application to time-series problems, particularly in long-term forecasting, has received comparatively less attention. To address this gap, we introduce a time-series automatic augmentation approach named TSAA, which is both efficient and easy to implement. The solution involves tackling the associated bilevel optimization problem through a two-step process: initially training a non-augmented model for a limited number of epochs, followed by an iterative split procedure. During this iterative process, we alternate between identifying a robust augmentation policy through Bayesian optimization and refining the model while discarding suboptimal runs. Extensive evaluations on challenging univariate and multivariate forecasting benchmark problems demonstrate that TSAA consistently outperforms several robust baselines, suggesting its potential integration into prediction pipelines.
5/2/2024
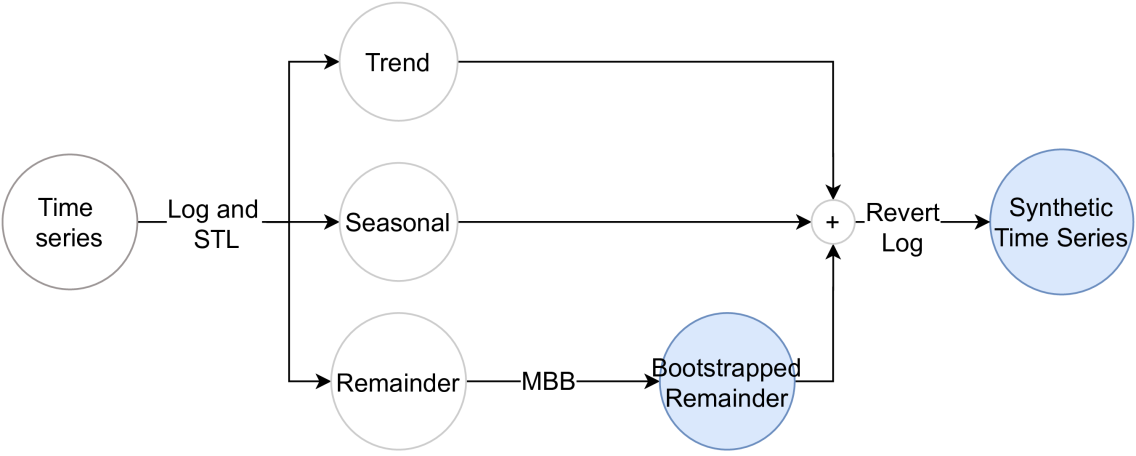
On-the-fly Data Augmentation for Forecasting with Deep Learning
Vitor Cerqueira, Mois'es Santos, Yassine Baghoussi, Carlos Soares

0
0
Deep learning approaches are increasingly used to tackle forecasting tasks. A key factor in the successful application of these methods is a large enough training sample size, which is not always available. In these scenarios, synthetic data generation techniques are usually applied to augment the dataset. Data augmentation is typically applied before fitting a model. However, these approaches create a single augmented dataset, potentially limiting their effectiveness. This work introduces OnDAT (On-the-fly Data Augmentation for Time series) to address this issue by applying data augmentation during training and validation. Contrary to traditional methods that create a single, static augmented dataset beforehand, OnDAT performs augmentation on-the-fly. By generating a new augmented dataset on each iteration, the model is exposed to a constantly changing augmented data variations. We hypothesize this process enables a better exploration of the data space, which reduces the potential for overfitting and improves forecasting performance. We validated the proposed approach using a state-of-the-art deep learning forecasting method and 8 benchmark datasets containing a total of 75797 time series. The experiments suggest that OnDAT leads to better forecasting performance than a strategy that applies data augmentation before training as well as a strategy that does not involve data augmentation. The method and experiments are publicly available.
4/29/2024
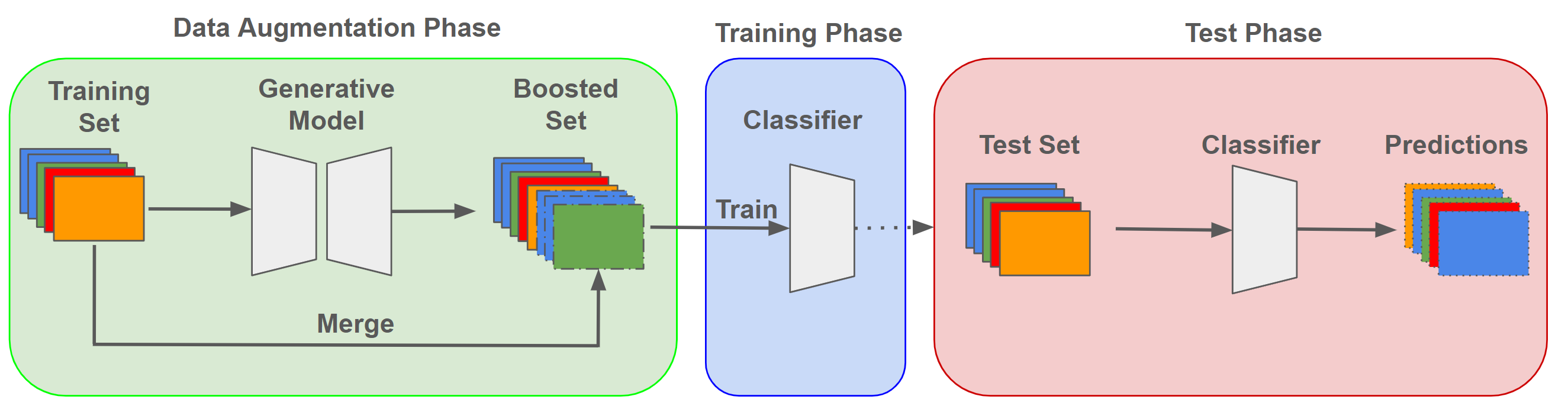
A Comparative Study on Enhancing Prediction in Social Network Advertisement through Data Augmentation
Qikai Yang, Panfeng Li, Xinhe Xu, Zhicheng Ding, Wenjing Zhou, Yi Nian

0
0
In the ever-evolving landscape of social network advertising, the volume and accuracy of data play a critical role in the performance of predictive models. However, the development of robust predictive algorithms is often hampered by the limited size and potential bias present in real-world datasets. This study presents and explores a generative augmentation framework of social network advertising data. Our framework explores three generative models for data augmentation - Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) - to enrich data availability and diversity in the context of social network advertising analytics effectiveness. By performing synthetic extensions of the feature space, we find that through data augmentation, the performance of various classifiers has been quantitatively improved. Furthermore, we compare the relative performance gains brought by each data augmentation technique, providing insights for practitioners to select appropriate techniques to enhance model performance. This paper contributes to the literature by showing that synthetic data augmentation alleviates the limitations imposed by small or imbalanced datasets in the field of social network advertising. At the same time, this article also provides a comparative perspective on the practicality of different data augmentation methods, thereby guiding practitioners to choose appropriate techniques to enhance model performance.
4/30/2024