Generative AI and Teachers -- For Us or Against Us? A Case Study
2404.03486

0
0

Abstract
We present insightful results of a survey on the adoption of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) by university teachers in their teaching activities. The transformation of education by GenAI, particularly large language models (LLMs), has been presenting both opportunities and challenges, including cheating by students. We prepared the online survey according to best practices and the questions were created by the authors, who have pedagogy experience. The survey contained 12 questions and a pilot study was first conducted. The survey was then sent to all teachers in multiple departments across different campuses of the university of interest in Sweden: Lule{aa} University of Technology. The survey was available in both Swedish and English. The results show that 35 teachers (more than half) use GenAI out of 67 respondents. Preparation is the teaching activity with the most frequency that GenAI is used for and ChatGPT is the most commonly used GenAI. 59% say it has impacted their teaching, however, 55% say there should be legislation around the use of GenAI, especially as inaccuracies and cheating are the biggest concerns.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper explores the relationship between generative AI models and human teachers in education.
- The authors conduct a case study to examine the potential benefits and drawbacks of integrating generative AI into teaching and learning.
- The research aims to provide insights into how generative AI can be leveraged to support or complement human teachers, rather than replace them.
Plain English Explanation
The paper examines the role of generative AI models in educational settings, exploring whether they can be a helpful tool for teachers or a potential threat. The authors investigate this through a case study, looking at how generative AI could be integrated into teaching and learning in a way that supports human teachers rather than replaces them.
The key idea is to understand the balance between the capabilities of generative AI and the unique strengths of human teachers. Generative AI models have the ability to create original content, generate personalized learning materials, and provide targeted feedback to students. However, teachers bring essential human qualities like empathy, emotional support, and the ability to adapt to individual student needs. The paper explores how these different strengths can be combined to enhance the educational experience.
For example, generative AI could be used to generate initial lesson plans or customize content for specific students, allowing teachers to focus more on facilitating discussions, providing one-on-one attention, and nurturing the social-emotional aspects of learning. The goal is to find ways for generative AI and human teachers to work together in a complementary fashion, rather than seeing them as inherently in competition.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a case study that examines the potential integration of generative AI models into teaching and learning environments. The authors use a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative data on student outcomes with qualitative insights from interviews with teachers and students.
The study involved two classrooms: one that used generative AI-powered tools to support instruction, and a control group that relied on traditional teaching methods. The generative AI tools were used for tasks like generating personalized learning content, providing real-time feedback on student work, and automating certain administrative tasks.
The researchers collected data on student engagement, learning outcomes, and teacher workload. They also conducted interviews to understand the perceptions and experiences of both teachers and students in the AI-assisted classroom.
The findings suggest that generative AI can be a valuable complement to human teachers, but its implementation requires careful planning and collaboration. While the AI-powered tools showed promise in areas like content personalization and workload reduction, teachers emphasized the importance of maintaining their own instructional agency and nurturing the social-emotional aspects of learning.
The paper also highlights the need for ongoing monitoring and adjustment as generative AI is integrated into educational settings, to ensure that it enhances rather than replaces the unique strengths of human teachers.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thoughtful and balanced perspective on the role of generative AI in education. The case study approach allows the authors to delve into the nuanced interplay between the capabilities of AI and the essential human qualities of teachers.
One potential limitation of the study is the relatively small sample size, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the study was conducted over a relatively short time frame, and it would be valuable to explore the long-term impacts of integrating generative AI into teaching and learning.
The paper also acknowledges the need for ongoing research and experimentation to fully understand the best practices for leveraging generative AI in educational contexts. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be crucial to monitor its effects, address potential biases or unintended consequences, and ensure that it enhances rather than undermines the role of human teachers.
Conclusion
This paper provides a valuable case study on the integration of generative AI models into teaching and learning. The findings suggest that, when implemented thoughtfully, generative AI can be a powerful tool to support and complement human teachers, rather than replace them.
The key is to find ways for generative AI and human teachers to work together in a symbiotic relationship, where the strengths of each are leveraged to create a more engaging and effective educational experience for students. As AI-powered tools continue to evolve, this will be an important area of ongoing research and experimentation to ensure that the technology serves to enhance, rather than diminish, the essential role of human teachers in the educational process.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
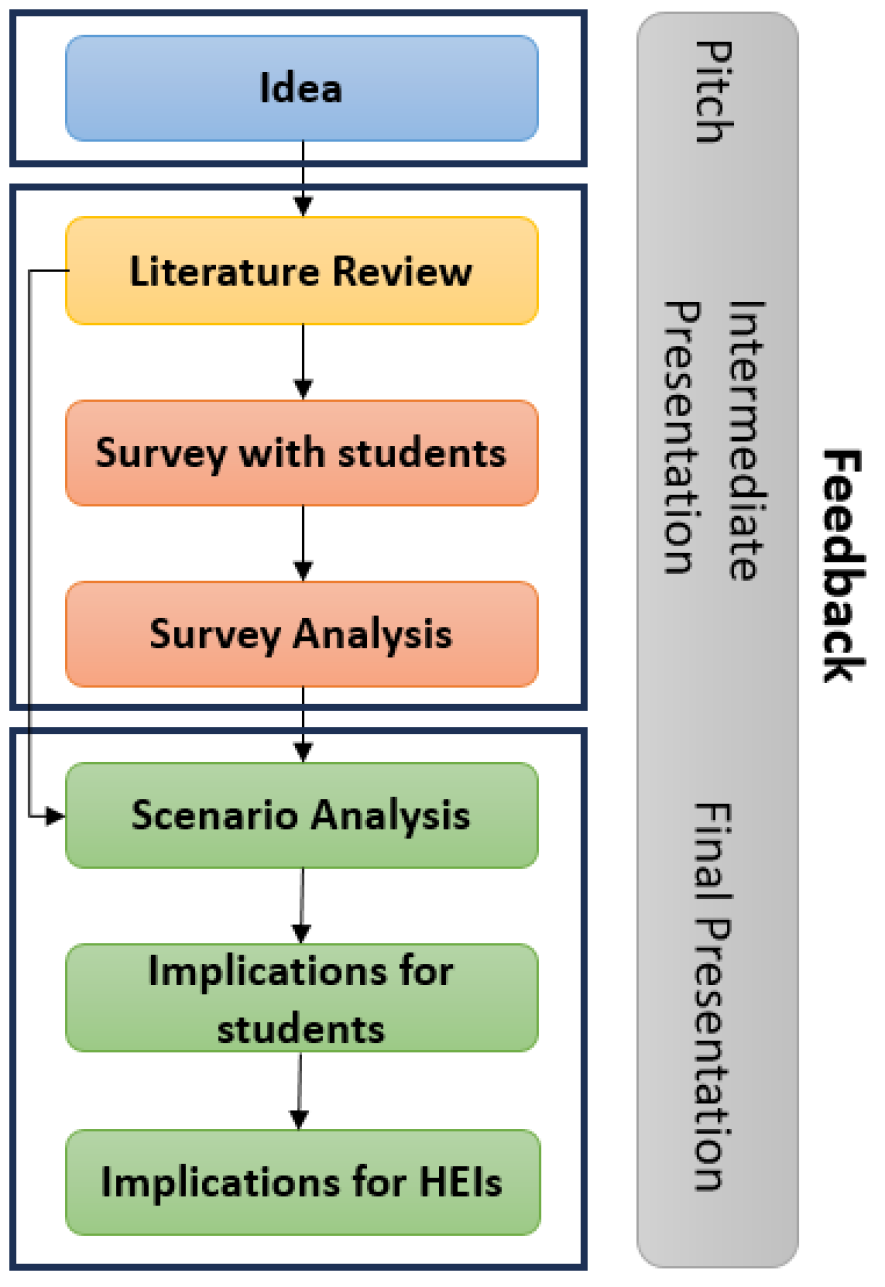
The Evolution of Learning: Assessing the Transformative Impact of Generative AI on Higher Education
Stefanie Krause, Bhumi Hitesh Panchal, Nikhil Ubhe

0
0
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) models such as ChatGPT have experienced a surge in popularity, attracting 100 million active users in 2 months and generating an estimated 10 million daily queries. Despite this remarkable adoption, there remains a limited understanding to which extent this innovative technology influences higher education. This research paper investigates the impact of GAI on university students and Higher Education Institutions (HEIs). The study adopts a mixed-methods approach, combining a comprehensive survey with scenario analysis to explore potential benefits, drawbacks, and transformative changes the new technology brings. Using an online survey with 130 participants we assessed students' perspectives and attitudes concerning present ChatGPT usage in academics. Results show that students use the current technology for tasks like assignment writing and exam preparation and believe it to be a effective help in achieving academic goals. The scenario analysis afterwards projected potential future scenarios, providing valuable insights into the possibilities and challenges associated with incorporating GAI into higher education. The main motivation is to gain a tangible and precise understanding of the potential consequences for HEIs and to provide guidance responding to the evolving learning environment. The findings indicate that irresponsible and excessive use of the technology could result in significant challenges. Hence, HEIs must develop stringent policies, reevaluate learning objectives, upskill their lecturers, adjust the curriculum and reconsider examination approaches.
4/17/2024
👀
Student Reflections on Self-Initiated GenAI Use in HCI Education
Hauke Sandhaus, Maria Teresa Parreira, Wendy Ju

0
0
This study explores students' self-initiated use of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) tools in an interactive systems design class. Through 12 group interviews, students revealed the dual nature of GenAI in (1) stimulating creativity and (2) speeding up design iterations, alongside concerns over its potential to cause shallow learning and reliance. GenAI's benefits were pronounced in the execution phase of design, aiding rapid prototyping and ideation, while its use in initial insight generation posed risks to depth and reflective practice. This reflection highlights the complex role of GenAI in Human-Computer Interaction education, emphasizing the need for balanced integration to leverage its advantages without compromising fundamental learning outcomes.
5/3/2024
🤖
The collective use and evaluation of generative AI tools in digital humanities research: Survey-based results
Meredith Dedema, Rongqian Ma

0
0
The advent of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) technologies has revolutionized research, with significant implications for Digital Humanities (DH), a field inherently intertwined with technological progress. This article investigates how digital humanities scholars adopt, practice, as well as critically evaluate, GenAI technologies such as ChatGPT in the research process. Drawing on 76 responses collected from an international survey study, we explored digital humanities scholars' rationale for GenAI adoption in research, identified specific use cases and practices of using GenAI to support various DH research tasks, and analyzed scholars' collective perceptions of GenAI's benefits, risks, and impact on DH research. The survey results suggest that DH research communities hold divisive sentiments towards the value of GenAI in DH scholarship, whereas the actual usage diversifies among individuals and across research tasks. Our survey-based analysis has the potential to serve as a basis for further empirical research on the impact of GenAI on the evolution of DH scholarship.
4/22/2024
⛏️
Not a Swiss Army Knife: Academics' Perceptions of Trade-Offs Around Generative Artificial Intelligence Use
Afsaneh Razi, Layla Bouzoubaa, Aria Pessianzadeh, John S. Seberger, Rezvaneh Rezapour

0
0
In the rapidly evolving landscape of computing disciplines, substantial efforts are being dedicated to unraveling the sociotechnical implications of generative AI (Gen AI). While existing research has manifested in various forms, there remains a notable gap concerning the direct engagement of knowledge workers in academia with Gen AI. We interviewed 18 knowledge workers, including faculty and students, to investigate the social and technical dimensions of Gen AI from their perspective. Our participants raised concerns about the opacity of the data used to train Gen AI. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to identify and address inaccurate, biased, and potentially harmful, information generated by these models. Knowledge workers also expressed worries about Gen AI undermining trust in the relationship between instructor and student and discussed potential solutions, such as pedagogy readiness, to mitigate them. Additionally, participants recognized Gen AI's potential to democratize knowledge by accelerating the learning process and act as an accessible research assistant. However, there were also concerns about potential social and power imbalances stemming from unequal access to such technologies. Our study offers insights into the concerns and hopes of knowledge workers about the ethical use of Gen AI in educational settings and beyond, with implications for navigating this new landscape.
5/3/2024