Green Probabilistic Semantic Communication over Wireless Networks

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explores a "green" approach to semantic communication over wireless networks
- Utilizes a probabilistic knowledge graph (PKG) and rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) techniques
- Aims to improve energy efficiency and semantic information transmission
Plain English Explanation
This research paper presents a new approach to semantic communication over wireless networks. The key idea is to use a probabilistic knowledge graph (PKG) to represent the semantic information being transmitted, and rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) techniques to efficiently share the wireless channel.
The goal is to improve the energy efficiency of the communication system while still effectively transmitting the semantic information. This "green" approach could have important implications for the design of future wireless networks.
Technical Explanation
The paper first presents the system model, which includes a base station communicating with multiple user devices over a wireless channel. The semantic information to be transmitted is represented using a PKG, which encodes the relationships between different concepts.
The researchers then develop a rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) scheme to efficiently share the wireless resources among the users. RSMA allows for simultaneous transmission of both semantic and traditional bit-level information, improving the overall efficiency.
Key aspects of the system design include optimizing the power allocation, rate splitting, and PKG encoding to minimize energy consumption while maximizing the successful transmission of semantic information.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to green semantic communication, but there are some potential limitations and areas for further research:
- The performance of the system may be dependent on the accuracy and completeness of the PKG, which could be challenging to build and maintain in real-world scenarios.
- The optimization problem formulated in the paper may be computationally complex, especially for large-scale wireless networks with many users.
- The paper does not address potential issues with semantic information security or robustness to channel impairments, which are important considerations for practical deployment.
Further research could explore these areas and investigate the scalability and real-world applicability of the proposed approach.
Conclusion
This research paper presents an innovative "green" approach to semantic communication over wireless networks. By leveraging a probabilistic knowledge graph and rate-splitting multiple access techniques, the system aims to improve energy efficiency and the transmission of semantic information.
The proposed solution offers a promising direction for the design of future wireless networks that prioritize both energy sustainability and the effective communication of high-level semantic information.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Green Probabilistic Semantic Communication over Wireless Networks
Ruopeng Xu, Zhaohui Yang, Yijie Mao, Chongwen Huang, Qianqian Yang, Lexi Xu, Wei Xu, Zhaoyang Zhang
In this paper, we propose a multi-user green semantic communication system facilitated by a probabilistic knowledge graph (PKG). By integrating probability into the knowledge graph, we enable probabilistic semantic communication (PSC) and represent semantic information accordingly. On this basis, a semantic compression model designed for multi-user downlink task-oriented communication is introduced, utilizing the semantic compression ratio (SCR) as a parameter to connect the computation and communication processes of information transmission. Based on the rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) technology, we derive mathematical expressions for system transmission energy consumption and related formulations. Subsequently, the multi-user green semantic communication system is modeled and the optimal problem with the goal of minimizing system energy consumption comprehensively considering the computation and communication process under given constrains is formulated. In order to address the optimal problem, we propose an alternating optimization algorithm that tackles sub-problems of power allocation and beamforming design, semantic compression ratio, and computation capacity allocation. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating the superiority of our system over methods using Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) instead of RSMA, and highlighting the benefits of our PSC compression model.
Read more8/22/2024


0
On the Computing and Communication Tradeoff in Reasoning-Based Multi-User Semantic Communications
Nitisha Singh, Christo Kurisummoottil Thomas, Walid Saad, Emilio Calvanese Strinati
Semantic communication (SC) is recognized as a promising approach for enabling reliable communication with minimal data transfer while maintaining seamless connectivity for a group of wireless users. Unlocking the advantages of SC for multi-user cases requires revisiting how communication and computing resources are allocated. This reassessment should consider the reasoning abilities of end-users, enabling receiving nodes to fill in missing information or anticipate future events more effectively. Yet, state-of-the-art SC systems primarily focus on resource allocation through compression based on semantic relevance, while overlooking the underlying data generation mechanisms and the tradeoff between communications and computing. Thus, they cannot help prevent a disruption in connectivity. In contrast, in this paper, a novel framework for computing and communication resource allocation is proposed that seeks to demonstrate how SC systems with reasoning capabilities at the end nodes can improve reliability in an end-to-end multi-user wireless system with intermittent communication links. Towards this end, a novel reasoning-aware SC system is proposed for enabling users to utilize their local computing resources to reason the representations when the communication links are unavailable. To optimize communication and computing resource allocation in this system, a noncooperative game is formulated among multiple users whose objective is to maximize the effective semantic information (computed as a product of reliability and semantic information) while controlling the number of semantically relevant links that are disrupted. Simulation results show that the proposed reasoning-aware SC system results in at least a $16.6%$ enhancement in throughput and a significant improvement in reliability compared to classical communications systems that do not incorporate reasoning.
Read more6/24/2024

0
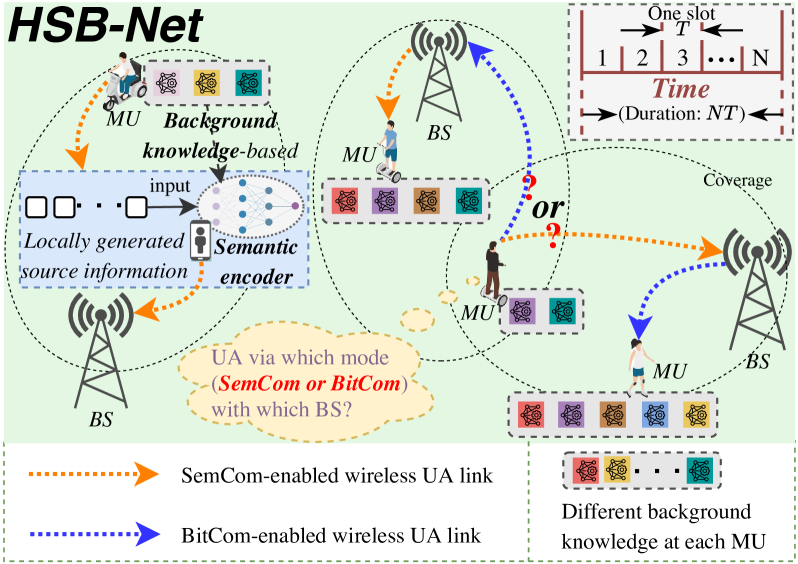
Wireless Resource Optimization in Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Networks
Le Xia, Yao Sun, Dusit Niyato, Lan Zhang, Muhammad Ali Imran
Recently, semantic communication (SemCom) has shown great potential in significant resource savings and efficient information exchanges, thus naturally introducing a novel and practical cellular network paradigm where two modes of SemCom and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist. Nevertheless, the involved wireless resource management becomes rather complicated and challenging, given the unique background knowledge matching and time-consuming semantic coding requirements in SemCom. To this end, this paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we specially develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by utilizing a Lagrange primal-dual transformation method and a preference list-based heuristic algorithm with polynomial-time complexity. Numerical results not only demonstrate the accuracy of our analytical queuing model, but also validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
Read more8/21/2024


0
Rethinking Generative Semantic Communication for Multi-User Systems with Multi-Modal LLM
Wanting Yang, Zehui Xiong, Shiwen Mao, Tony Q. S. Quek, Ping Zhang, Merouane Debbah, Rahim Tafazolli
The surge in connected devices in 6G with typical massive access scenarios, such as smart agriculture, and smart cities, poses significant challenges to unsustainable traditional communication with limited radio resources and already high system complexity. Fortunately, the booming artificial intelligence technology and the growing computational power of devices offer a promising 6G enabler: semantic communication (SemCom). However, existing deep learning-based SemCom paradigms struggle to extend to multi-user scenarios due to their rigid end-to-end training approach. Consequently, to truly empower 6G networks with this critical technology, this article rethinks generative SemCom for multi-user system with multi-modal large language model (MLLM), and propose a novel framework called M2GSC. In this framework, the MLLM, which serves as shared knowledge base (SKB), plays three critical roles for complex tasks, spawning a series of benefits such as semantic encoding standardization and semantic decoding personalization. Meanwhile, to enhance the performance of M2GSC framework and to advance its implementation in 6G, we highlight three research directions on M2GSC framework, namely, upgrading SKB to closed loop agent, adaptive semantic encoding offloading, and streamlined semantic decoding offloading. Finally, a case study is conducted to demonstrate the preliminary validation on the effectiveness of the M2GSC framework in terms of streamlined decoding offloading.
Read more8/19/2024