Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Based Networking Problem Optimization

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper proposes a hybrid semantic/bit communication approach for optimizing networking problems.
- It presents a system model and problem formulation for this hybrid communication strategy.
- The research explores the tradeoffs between semantic and bit-based communication in resource-constrained networks.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores a new way of communicating in wireless networks that combines semantic communication and traditional bit-based communication.
In typical wireless networks, information is transmitted as a series of 1s and 0s. This bit-based communication is efficient but doesn't convey much meaning. Semantic communication, on the other hand, tries to transmit the actual meaning or intent behind the information, which can be more efficient but requires more complex algorithms.
The researchers propose a hybrid approach that combines these two strategies. The idea is to leverage the benefits of both to optimize how information is transmitted in resource-constrained wireless networks, like those used for Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
For example, simple status updates could be sent using semantic communication to save bandwidth, while more complex data could still use traditional bit-based methods. The paper explores the tradeoffs involved and how to best optimize this hybrid approach.
Technical Explanation
The paper formulates the hybrid semantic/bit communication networking problem as an optimization problem. The system model includes a base station that communicates with multiple user devices using a combination of semantic and bit-based transmission.
The objective is to minimize the total network power consumption while satisfying quality-of-service constraints for both semantic and bit-based communication. This involves optimizing factors like resource allocation, transmission power, and the mix of semantic versus bit-based communication for each user.
The researchers propose a two-stage optimization approach. First, they solve for the optimal semantic communication parameters. Then, they use those results to optimize the bit-based communication. This hierarchical approach allows them to efficiently navigate the complex tradeoffs involved.
The paper includes numerical simulations to evaluate the performance of the proposed hybrid approach compared to purely semantic or bit-based strategies. The results demonstrate significant improvements in power efficiency and quality-of-service metrics.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-designed exploration of the hybrid semantic/bit communication networking problem. The proposed optimization framework is technically sound and the simulation results seem to support the potential benefits of this hybrid approach.
However, the paper does not address some important practical considerations. For example, it assumes perfect knowledge of channel conditions and user requirements, which may not be realistic in real-world deployments. Additionally, the computational complexity of the optimization process could be a challenge for resource-constrained IoT devices.
Further research is needed to investigate the robustness and scalability of the hybrid approach, as well as ways to reduce the computational burden. Exploring hybrid strategies that dynamically adapt the communication mode based on network conditions could also be a fruitful area of investigation.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel hybrid semantic/bit communication approach for optimizing networking problems in resource-constrained wireless environments. By combining the strengths of semantic and bit-based communication, the proposed framework can achieve significant improvements in power efficiency and quality-of-service metrics.
The technical details of the optimization problem and simulation results demonstrate the potential benefits of this hybrid strategy. While there are some practical considerations that require further research, this work represents an important step towards more intelligent and efficient wireless communication systems, particularly for emerging IoT applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Based Networking Problem Optimization
Le Xia, Yao Sun, Dusit Niyato, Lan Zhang, Lei Zhang, Muhammad Ali Imran
This paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a novel and practical next-generation cellular network where two modes of semantic communication (SemCom) and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist, namely hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we comprehensively develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with several practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by employing a Lagrange primal-dual method and devising a preference list-based heuristic algorithm. Finally, numerical results validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
Read more8/20/2024
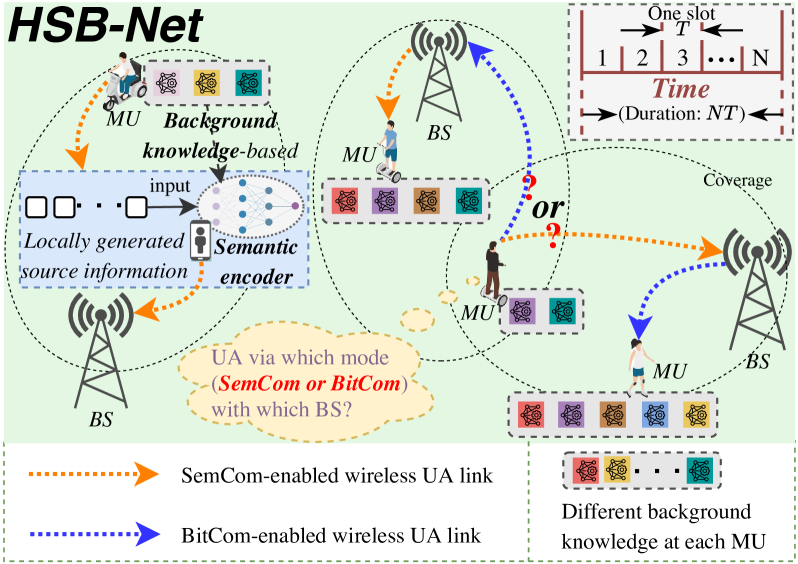

0
Wireless Resource Optimization in Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Networks
Le Xia, Yao Sun, Dusit Niyato, Lan Zhang, Muhammad Ali Imran
Recently, semantic communication (SemCom) has shown great potential in significant resource savings and efficient information exchanges, thus naturally introducing a novel and practical cellular network paradigm where two modes of SemCom and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist. Nevertheless, the involved wireless resource management becomes rather complicated and challenging, given the unique background knowledge matching and time-consuming semantic coding requirements in SemCom. To this end, this paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we specially develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by utilizing a Lagrange primal-dual transformation method and a preference list-based heuristic algorithm with polynomial-time complexity. Numerical results not only demonstrate the accuracy of our analytical queuing model, but also validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
Read more8/21/2024


0
Green Probabilistic Semantic Communication over Wireless Networks
Ruopeng Xu, Zhaohui Yang, Yijie Mao, Chongwen Huang, Qianqian Yang, Lexi Xu, Wei Xu, Zhaoyang Zhang
In this paper, we propose a multi-user green semantic communication system facilitated by a probabilistic knowledge graph (PKG). By integrating probability into the knowledge graph, we enable probabilistic semantic communication (PSC) and represent semantic information accordingly. On this basis, a semantic compression model designed for multi-user downlink task-oriented communication is introduced, utilizing the semantic compression ratio (SCR) as a parameter to connect the computation and communication processes of information transmission. Based on the rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) technology, we derive mathematical expressions for system transmission energy consumption and related formulations. Subsequently, the multi-user green semantic communication system is modeled and the optimal problem with the goal of minimizing system energy consumption comprehensively considering the computation and communication process under given constrains is formulated. In order to address the optimal problem, we propose an alternating optimization algorithm that tackles sub-problems of power allocation and beamforming design, semantic compression ratio, and computation capacity allocation. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating the superiority of our system over methods using Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) instead of RSMA, and highlighting the benefits of our PSC compression model.
Read more8/22/2024
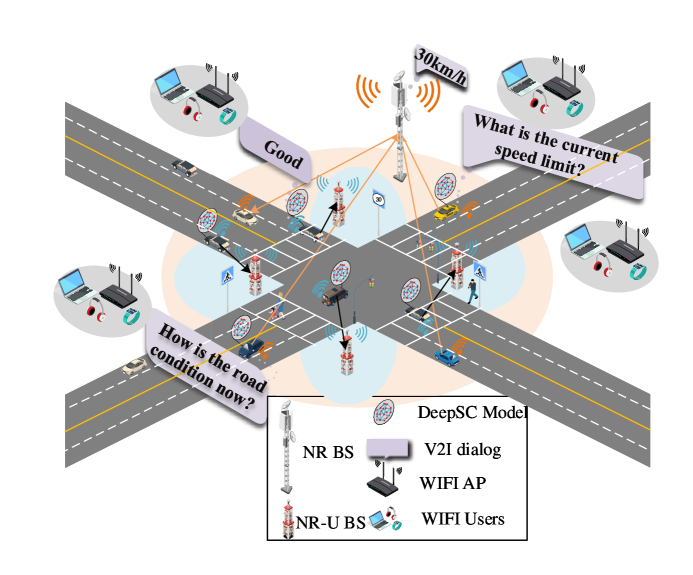

0
Semantic-Aware Resource Allocation Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for 5G-V2X HetNets
Zhiyu Shao, Qiong Wu, Pingyi Fan, Nan Cheng, Qiang Fan, Jiangzhou Wang
This letter proposes a semantic-aware resource allocation (SARA) framework with flexible duty cycle (DC) coexistence mechanism (SARADC) for 5G-V2X Heterogeneous Network (HetNets) based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL) proximal policy optimization (PPO). Specifically, we investigate V2X networks within a two-tiered HetNets structure. In response to the needs of high-speed vehicular networking in urban environments, we design a semantic communication system and introduce two resource allocation metrics: high-speed semantic transmission rate (HSR) and semantic spectrum efficiency (HSSE). Our main goal is to maximize HSSE. Additionally, we address the coexistence of vehicular users and WiFi users in 5G New Radio Unlicensed (NR-U) networks. To tackle this complex challenge, we propose a novel approach that jointly optimizes flexible DC coexistence mechanism and the allocation of resources and base stations (BSs). Unlike traditional bit transmission methods, our approach integrates the semantic communication paradigm into the communication system. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed solution outperforms traditional bit transmission methods with traditional DC coexistence mechanism in terms of HSSE and semantic throughput (ST) for both vehicular and WiFi users.
Read more6/13/2024