Planning and Operation of Millimeter-wave Downlink Systems with Hybrid Beamforming
2404.12492

0
0
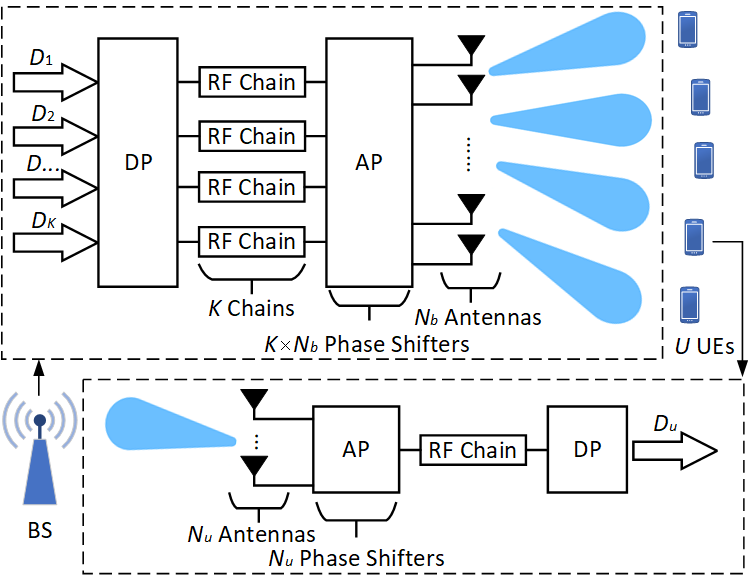
Abstract
This paper investigates downlink radio resource management (RRM) in millimeter-wave systems with codebook-based hybrid beamforming in a single cell. We consider a practical but often overlooked multi-channel scenario where the base station is equipped with fewer radio frequency chains than there are user equipment (UEs) in the cell. In this case, analog beam selection is important because not all beams preferred by UEs can be selected simultaneously, and since the beam selection cannot vary across subchannels in a time slot, this creates a coupling between subchannels within a time slot. None of the solutions proposed in the literature deal with this important constraint. The paper begins with an offline study that analyzes the impact of different RRM procedures and system parameters on performance. An offline joint RRM optimization problem is formulated and solved that includes beam set selection, UE set selection, power distribution, modulation and coding scheme selection, and digital beamforming as a part of hybrid beamforming. The evaluation results of the offline study provide valuable insights that shows the importance of not neglecting the constraint and guide the design of low-complexity and high-performance online downlink RRM schemes in the second part of the paper. The proposed online RRM algorithms perform close to the performance targets obtained from the offline study while offering acceptable runtime.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the planning and operation of millimeter-wave (mmWave) downlink systems using hybrid beamforming techniques.
- The researchers investigate the challenges and trade-offs involved in efficiently managing radio resources in these high-frequency, multi-antenna systems.
- Key topics covered include massive MIMO, 5G and beyond, system planning, and system operation.
Plain English Explanation
Millimeter-wave (mmWave) technology is a promising approach for the next generation of wireless communication networks, like 5G and beyond. These high-frequency signals can transmit large amounts of data but face challenges like signal blockage and interference.
To address these issues, the researchers in this paper looked at using hybrid beamforming, which combines digital and analog signal processing. This allows the system to dynamically focus the mmWave signals towards specific users, improving efficiency and coverage.
The paper explores the planning and operational aspects of these hybrid beamforming mmWave downlink systems. It examines how to best manage the radio resources, such as allocating transmit power and selecting optimal beamforming configurations. This involves balancing factors like user demand, channel conditions, and hardware constraints.
The insights from this research could help designers and operators build more effective mmWave networks that can deliver high-speed wireless connectivity, even in challenging urban environments. By carefully planning and optimizing these complex systems, they can maximize performance and capacity to meet the growing data needs of future wireless applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a framework for planning and operating millimeter-wave (mmWave) downlink systems that employ hybrid beamforming techniques. Hybrid beamforming combines digital precoding in the baseband with analog beamforming in the radio frequency (RF) frontend, enabling efficient utilization of the large antenna arrays typical of mmWave massive MIMO systems.
The authors first formulate an optimization problem to determine the optimal hybrid beamforming configuration that maximizes the system's spectral efficiency, subject to power and hardware constraints. They develop a two-stage algorithm to solve this problem, leveraging techniques like Lagrangian duality and manifold optimization.
Next, the paper addresses the operational aspects of these mmWave downlink systems. It presents a dynamic resource allocation scheme that adapts the hybrid beamforming, power allocation, and user scheduling to changing channel conditions and traffic demands. This is achieved through a Lyapunov optimization framework that minimizes a weighted sum of the queue lengths and transmission power.
The researchers evaluate their proposed planning and operational approaches through extensive simulations, considering various system parameters and user scenarios. The results demonstrate significant performance improvements over conventional digital beamforming and static resource allocation methods, particularly in terms of spectral efficiency and user fairness.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive framework for the planning and operation of mmWave downlink systems using hybrid beamforming. The authors have carefully addressed key challenges such as the trade-off between spectral efficiency and hardware constraints, as well as the dynamic adaptation to time-varying channel and traffic conditions.
One potential limitation is the reliance on perfect channel state information, which may be difficult to achieve in practice due to the highly dynamic and complex mmWave propagation environment. The authors acknowledge this and suggest the need for robust beamforming techniques that can handle imperfect or partial channel knowledge.
Furthermore, the paper focuses primarily on the downlink performance, while the uplink scenario is not considered. Future research could investigate the joint optimization of uplink and downlink resources in these hybrid beamforming mmWave systems, as discussed in related works like Joint Optimization of Uplink OFDMA and MU-MIMO.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into the specific hardware implementation aspects, such as the analog beamforming network design or the impairments introduced by the RF components. Integrating these practical considerations into the system optimization and evaluation could provide further insights for real-world deployments.
Conclusion
This paper presents a comprehensive framework for the planning and operation of millimeter-wave downlink systems employing hybrid beamforming techniques. The authors have developed efficient algorithms to optimize the hybrid beamforming configuration and resource allocation, demonstrating significant performance improvements over conventional approaches.
The insights from this research can inform the design and deployment of future 5G and beyond wireless networks, enabling the delivery of high-speed, low-latency connectivity to a large number of users, even in challenging urban environments. By carefully managing the radio resources and adapting to dynamic channel conditions, these hybrid beamforming mmWave systems can unlock the full potential of emerging wireless applications, such as Codebook-based Beam Tracking for Conformal Array-enabled UAV and Wireless Resource Optimization for Hybrid Semantic-Bit Communication Networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Advancing Ultra-Reliable 6G: Transformer and Semantic Localization Empowered Robust Beamforming in Millimeter-Wave Communications
Avi Deb Raha, Kitae Kim, Apurba Adhikary, Mrityunjoy Gain, Choong Seon Hong

0
0
Advancements in 6G wireless technology have elevated the importance of beamforming, especially for attaining ultra-high data rates via millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequency deployment. Although promising, mmWave bands require substantial beam training to achieve precise beamforming. While initial deep learning models that use RGB camera images demonstrated promise in reducing beam training overhead, their performance suffers due to sensitivity to lighting and environmental variations. Due to this sensitivity, Quality of Service (QoS) fluctuates, eventually affecting the stability and dependability of networks in dynamic environments. This emphasizes a critical need for more robust solutions. This paper proposes a robust beamforming technique to ensure consistent QoS under varying environmental conditions. An optimization problem has been formulated to maximize users' data rates. To solve the formulated NP-hard optimization problem, we decompose it into two subproblems: the semantic localization problem and the optimal beam selection problem. To solve the semantic localization problem, we propose a novel method that leverages the k-means clustering and YOLOv8 model. To solve the beam selection problem, we propose a novel lightweight hybrid architecture that utilizes various data sources and a weighted entropy-based mechanism to predict the optimal beams. Rapid and accurate beam predictions are needed to maintain QoS. A novel metric, Accuracy-Complexity Efficiency (ACE), has been proposed to quantify this. Six testing scenarios have been developed to evaluate the robustness of the proposed model. Finally, the simulation result demonstrates that the proposed model outperforms several state-of-the-art baselines regarding beam prediction accuracy, received power, and ACE in the developed test scenarios.
6/24/2024
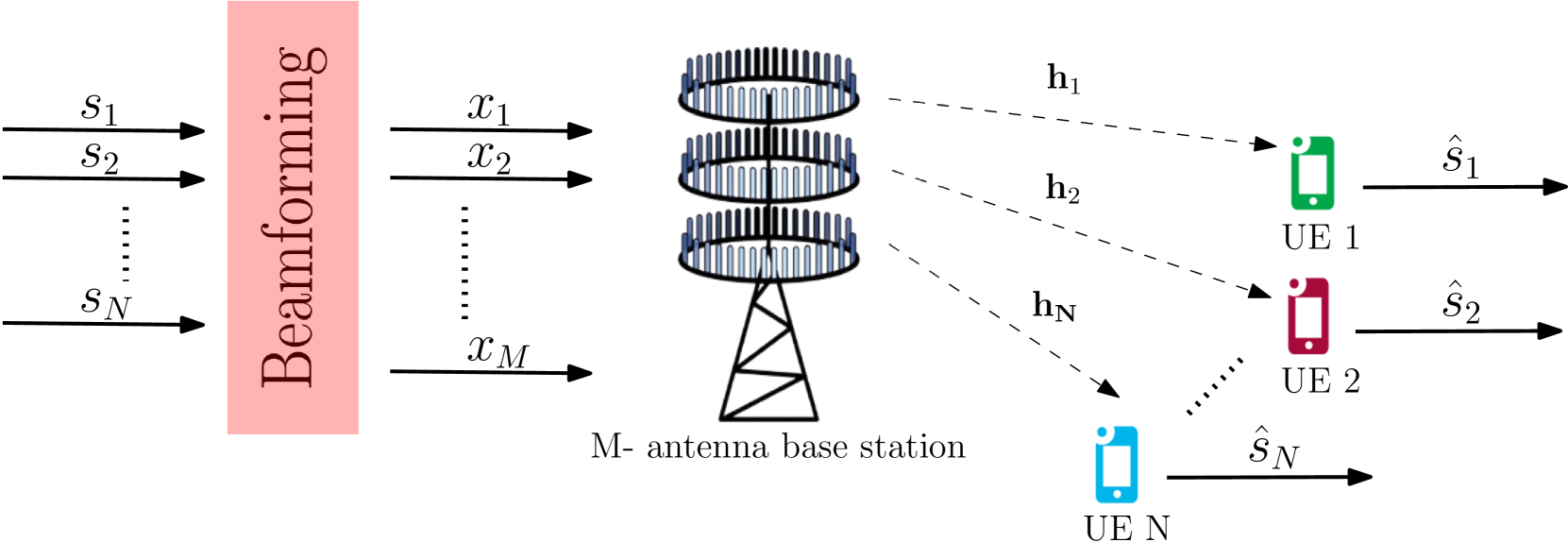
Deep Learning Based Joint Multi-User MISO Power Allocation and Beamforming Design
Cemil Vahapoglu, Timothy J. O'Shea, Tamoghna Roy, Sennur Ulukus

0
0
The evolution of fifth generation (5G) wireless communication networks has led to an increased need for wireless resource management solutions that provide higher data rates, wide coverage, low latency, and power efficiency. Yet, many of existing traditional approaches remain non-practical due to computational limitations, and unrealistic presumptions of static network conditions and algorithm initialization dependencies. This creates an important gap between theoretical analysis and real-time processing of algorithms. To bridge this gap, deep learning based techniques offer promising solutions with their representational capabilities for universal function approximation. We propose a novel unsupervised deep learning based joint power allocation and beamforming design for multi-user multiple-input single-output (MU-MISO) system. The objective is to enhance the spectral efficiency by maximizing the sum-rate with the proposed joint design framework, NNBF-P while also offering computationally efficient solution in contrast to conventional approaches. We conduct experiments for diverse settings to compare the performance of NNBF-P with zero-forcing beamforming (ZFBF), minimum mean square error (MMSE) beamforming, and NNBF, which is also our deep learning based beamforming design without joint power allocation scheme. Experiment results demonstrate the superiority of NNBF-P compared to ZFBF, and MMSE while NNBF can have lower performances than MMSE and ZFBF in some experiment settings. It can also demonstrate the effectiveness of joint design framework with respect to NNBF.
6/13/2024
User Association and Channel Allocation in 5G Mobile Asymmetric Multi-band Heterogeneous Networks
Miao Dai, Gang Sun, Hongfang Yu, Sheng Wang, Dusit Niyato

0
0
With the proliferation of mobile terminals and the continuous upgrading of services, 4G LTE networks are showing signs of weakness. To enhance the capacity of wireless networks, millimeter waves are introduced to drive the evolution of networks towards multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks. The distinct propagation characteristics of mmWaves and microwaves, as well as the vastly different hardware configurations of heterogeneous base stations, make traditional access strategies no longer effective. Therefore, to narrowing the gap between theory and practice, we investigate the access strategy in multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks, taking into account the characteristics of mobile users, asynchronous switching between uplink and downlink of pico base stations, asymmetric service requirements, and user communication continuity. We formulate the problem as integer nonlinear programming and prove its intractability. Thereby, we decouple it into three subproblems: user association, switch point selection, and subchannel allocation, and design an algorithm based on optimal matching and spectral clustering to solve it efficiently. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the comparison methods in terms of overall data rate, effective data rate, and number of satisfied users.
5/30/2024

Hybrid Beamforming Design for RSMA-assisted mmWave Integrated Sensing and Communications
Jun Gong, Wenchi Cheng, Jiangzhou Wang, Jingqing Wang

0
0
Integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) has been considered one of the new paradigms for sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. In the millimeter-wave (mmWave) ISAC system, hybrid beamforming (HBF) is considered an emerging technology to exploit the limited number of radio frequency (RF) chains in order to reduce the system hardware cost and power consumption. However, the HBF structure reduces the spatial degrees of freedom for the ISAC system, which further leads to increased interference between multiple users and between users and radar sensing. To solve the above problem, rate split multiple access (RSMA), which is a flexible and robust interference management strategy, is considered. We investigate the joint common rate allocation and HBF design problem for the HBF-based RSMA-assisted mmWave ISAC scheme. We propose the penalty dual decomposition (PDD) method coupled with the weighted mean squared error (WMMSE) minimization method to solve this high-dimensional non-convex problem, which converges to the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) point of the original problem. Then, we extend the proposed algorithm to the HBF design based on finite-resolution phase shifters (PSs) to further improve the energy efficiency of the system. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm and show that the RSMA-ISAC scheme outperforms other benchmark schemes.
6/10/2024