Hybrid quantum-classical computation for automatic guided vehicles scheduling
2309.03088

0
0
❗
Abstract
Motivated by global efforts to develop quantum computing for practical, industrial-scale challenges, we showcase the effectiveness of state-of-the-art hybrid quantum-classical solvers in addressing the business-centric optimization problem of scheduling Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs). These solvers leverage a noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) device, specifically a D-Wave quantum annealer. In our study, the hybrid solvers exhibit non-zero quantum processing times, indicating a significant contribution of the quantum component to solution efficiency. This hybrid methodology performs comparably to existing classical solvers, thus indicating `quantum readiness' for scheduling tasks. Our analysis focuses on a practical, business-oriented scenario: scheduling AGVs within a factory constrained by limited space, simulating a realistic production setting. Our new approach concerns mapping a realistic AGV problem onto a problem reminiscient of railway scheduling and demonstrating that the AGV problem more suits quantum computing than the railway counterpart and is more dense in terms of an average number of constraints per variable. We demonstrate that a scenario involving 15 AGVs, which holds practical significance due to common bottlenecks like shared main lanes leading to frequent deadlocks, can be efficiently addressed by a hybrid quantum-classical solver within seconds. Consequently, our research paves the way for the near-future business adoption of hybrid quantum-classical solutions for AGV scheduling, anticipating that forthcoming improvements in manufacturing efficiency will increase both the number of AGVs deployed and the premium on factory space.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The paper showcases the effectiveness of hybrid quantum-classical solvers in addressing the optimization problem of scheduling Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs) for practical, industrial-scale challenges.
- The hybrid solvers leverage a noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) device, specifically a D-Wave quantum annealer, and exhibit non-zero quantum processing times, indicating a significant contribution of the quantum component to solution efficiency.
- The research focuses on a practical, business-oriented scenario: scheduling AGVs within a factory constrained by limited space, simulating a realistic production setting.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores the use of hybrid quantum-classical solvers to address a real-world business challenge: scheduling Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in a factory setting. AGVs are autonomous robots used to transport materials within a factory, and their efficient scheduling is crucial for manufacturing productivity.
The researchers used a type of quantum computer called a D-Wave quantum annealer, which is a noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) device. This means the quantum device is not perfect and has some errors, but it can still be used in combination with classical computers to solve complex problems.
The researchers found that the hybrid quantum-classical approach performed comparably to existing classical solvers, suggesting that quantum computing is ready for real-world business applications like AGV scheduling. The quantum component of the hybrid solver contributed significantly to the overall efficiency of the solution.
The paper focuses on a realistic factory scenario, where space is limited, and AGVs need to be scheduled efficiently to avoid bottlenecks and deadlocks. The researchers developed a new approach to map the AGV scheduling problem to a problem similar to railway scheduling, which they found was more suitable for quantum computing than the railway problem itself.
The researchers successfully demonstrated that a scenario involving 15 AGVs, a common challenge in factories, could be efficiently addressed by their hybrid quantum-classical solver within seconds. This paves the way for the adoption of hybrid quantum-classical solutions for AGV scheduling in the near future, as the number of AGVs deployed and the premium on factory space are expected to increase.
Technical Explanation
The paper explores the use of hybrid quantum-classical solvers to address the optimization problem of scheduling Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in a factory setting. The researchers leverage a noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) device, specifically a D-Wave quantum annealer, as the quantum component of the hybrid solver.
The key aspects of the research include:
- Experimental Design: The researchers focus on a practical, business-oriented scenario: scheduling AGVs within a factory constrained by limited space, simulating a realistic production setting.
- Hybrid Quantum-Classical Architecture: The hybrid solvers exhibit non-zero quantum processing times, indicating a significant contribution of the quantum component to solution efficiency.
- Mapping the AGV Scheduling Problem: The researchers develop a new approach to map the AGV scheduling problem to a problem reminiscent of railway scheduling, finding that the AGV problem is more suitable for quantum computing than the railway counterpart and is more dense in terms of an average number of constraints per variable.
- Experiment Insights: The researchers successfully demonstrate that a scenario involving 15 AGVs, which holds practical significance due to common bottlenecks like shared main lanes leading to frequent deadlocks, can be efficiently addressed by their hybrid quantum-classical solver within seconds.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a compelling demonstration of the potential for hybrid quantum-classical solutions in addressing real-world business challenges, such as AGV scheduling in a factory setting. However, some caveats and limitations should be considered:
- Scope of the Study: The paper focuses on a specific scenario with 15 AGVs, which may not be representative of all factory settings. Further research is needed to understand the scalability and performance of the hybrid solver for larger-scale AGV scheduling problems.
- Quantum Hardware Limitations: The use of a NISQ device, while demonstrating the potential of quantum computing, also highlights the current limitations of available quantum hardware. As the technology continues to evolve, the performance and reliability of hybrid solvers may improve.
- Practical Adoption Challenges: While the paper suggests that the hybrid quantum-classical approach is "quantum ready" for AGV scheduling, the practical adoption of such solutions in real-world manufacturing settings may face additional challenges, such as integration with existing systems, training of personnel, and regulatory or safety considerations.
Overall, the paper presents a promising step towards the practical application of hybrid quantum-classical solutions for business optimization problems, but further research and development will be necessary to fully realize the potential of this approach.
Conclusion
The research showcased in this paper demonstrates the effectiveness of hybrid quantum-classical solvers in addressing the optimization problem of scheduling Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in a factory setting. The hybrid approach, leveraging a noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) device, exhibits non-zero quantum processing times, indicating a significant contribution of the quantum component to solution efficiency.
The paper's focus on a practical, business-oriented scenario highlights the potential for quantum computing to solve real-world problems and paves the way for the near-future adoption of hybrid quantum-classical solutions for AGV scheduling. The researchers' successful demonstration of efficiently addressing a scenario with 15 AGVs, a common challenge in factories, suggests that quantum computing is ready for business applications and that forthcoming improvements in manufacturing efficiency will further increase the relevance of this approach.
As the field of hybrid quantum-classical solutions continues to evolve, this research serves as a valuable contribution to the ongoing efforts to harness the power of quantum computing for practical, industrial-scale challenges.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Hybrid Quantum Tabu Search for Solving the Vehicle Routing Problem
James Holliday, Braeden Morgan, Hugh Churchill, Khoa Luu

0
0
There has never been a more exciting time for the future of quantum computing than now. Near-term quantum computing usage is now the next XPRIZE. With that challenge in mind we have explored a new approach as a hybrid quantum-classical algorithm for solving NP-Hard optimization problems. We have focused on the classic problem of the Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP) because of its real-world industry applications. Heuristics are often employed to solve this problem because it is difficult. In addition, meta-heuristic algorithms have proven to be capable of finding reasonable solutions to optimization problems like the CVRP. Recent research has shown that quantum-only and hybrid quantum/classical approaches to solving the CVRP are possible. Where quantum approaches are usually limited to minimal optimization problems, hybrid approaches have been able to solve more significant problems. Still, the hybrid approaches often need help finding solutions as good as their classical counterparts. In our proposed approach, we created a hybrid quantum/classical metaheuristic algorithm capable of finding the best-known solution to a classic CVRP problem. Our experimental results show that our proposed algorithm often outperforms other hybrid approaches.
4/23/2024
Utilising a Quantum Hybrid Solver for Bi-objective Quadratic Assignment Problems
Mayowa Ayodele

0
0
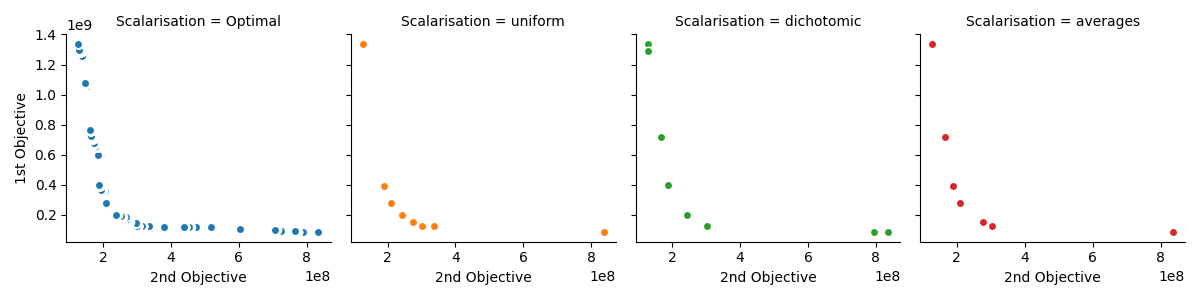
The intersection between quantum computing and optimisation has been an area of interest in recent years. There have been numerous studies exploring the application of quantum and quantum-hybrid solvers to various optimisation problems. This work explores scalarisation methods within the context of solving the bi-objective quadratic assignment problem using a quantum-hybrid solver. We show results that are consistent with previous research on a different Ising machine.
5/29/2024
New!Solving a Real-World Package Delivery Routing Problem Using Quantum Annealers
Eneko Osaba, Esther Villar-Rodriguez, Ant'on Asla

0
0
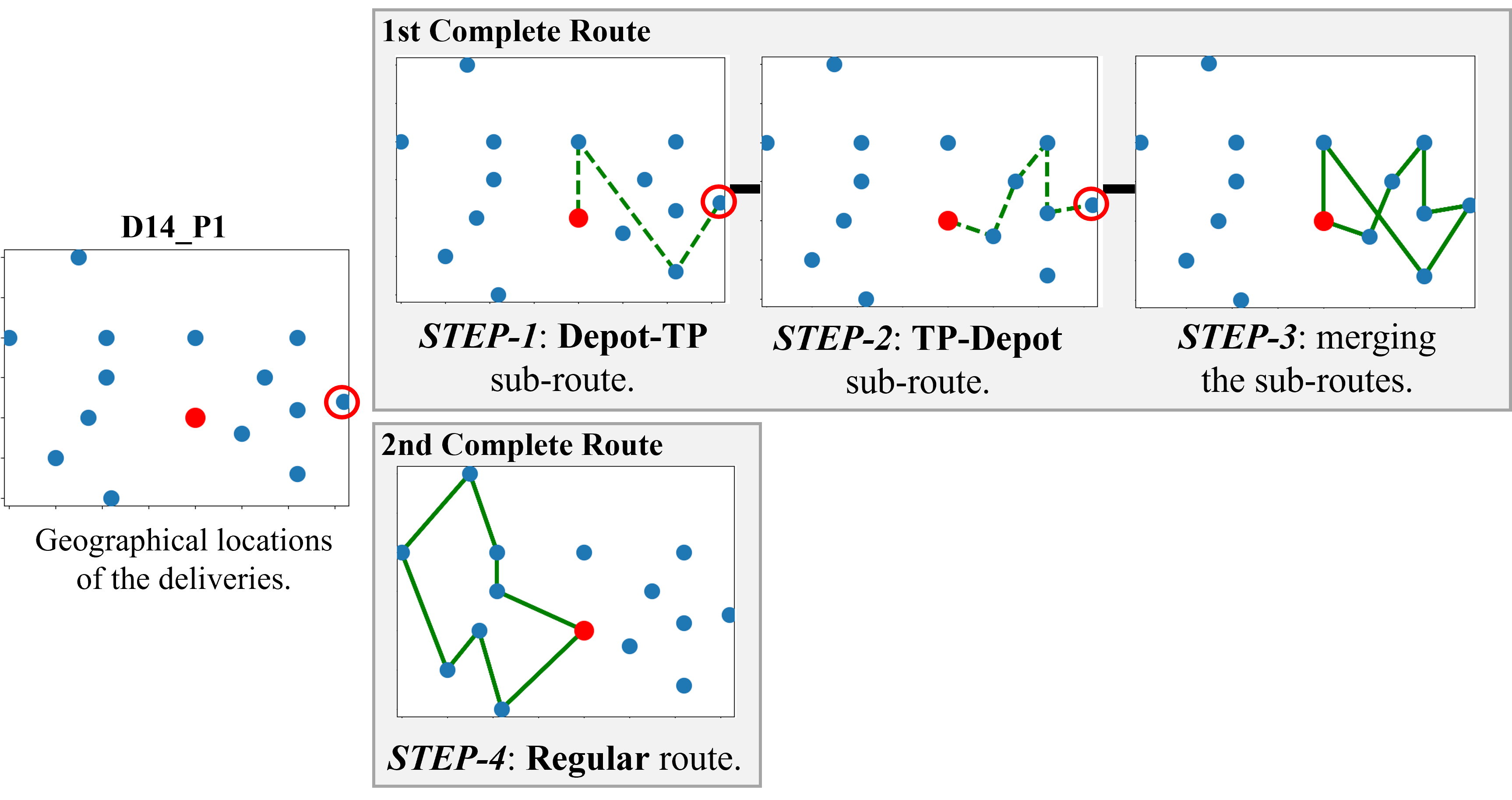
Research focused on the conjunction between quantum computing and routing problems has been very prolific in recent years. Most of the works revolve around classical problems such as the Traveling Salesman Problem or the Vehicle Routing Problem. The real-world applicability of these problems is dependent on the objectives and constraints considered. Anyway, it is undeniable that it is often difficult to translate complex requirements into these classical formulations.The main objective of this research is to present a solving scheme for dealing with realistic instances while maintaining all the characteristics and restrictions of the original real-world problem. Thus, a quantum-classical strategy has been developed, coined Q4RPD, that considers a set of real constraints such as a heterogeneous fleet of vehicles, priority deliveries, and capacities characterized by two values: weight and dimensions of the packages. Q4RPD resorts to the Leap Constrained Quadratic Model Hybrid Solver of D-Wave. To demonstrate the application of Q4RPD, an experimentation composed of six different instances has been conducted, aiming to serve as illustrative examples.
7/1/2024
Quantum Computing in Intelligent Transportation Systems: A Survey
Yifan Zhuang, Talha Azfar, Yinhai Wang, Wei Sun, Xiaokun Cara Wang, Qianwen Vivian Guo, Ruimin Ke

0
0
Quantum computing, a field utilizing the principles of quantum mechanics, promises great advancements across various industries. This survey paper is focused on the burgeoning intersection of quantum computing and intelligent transportation systems, exploring its potential to transform areas such as traffic optimization, logistics, routing, and autonomous vehicles. By examining current research efforts, challenges, and future directions, this survey aims to provide a comprehensive overview of how quantum computing could affect the future of transportation.
6/5/2024