Solving a Real-World Package Delivery Routing Problem Using Quantum Annealers
2403.15114

0
0
Abstract
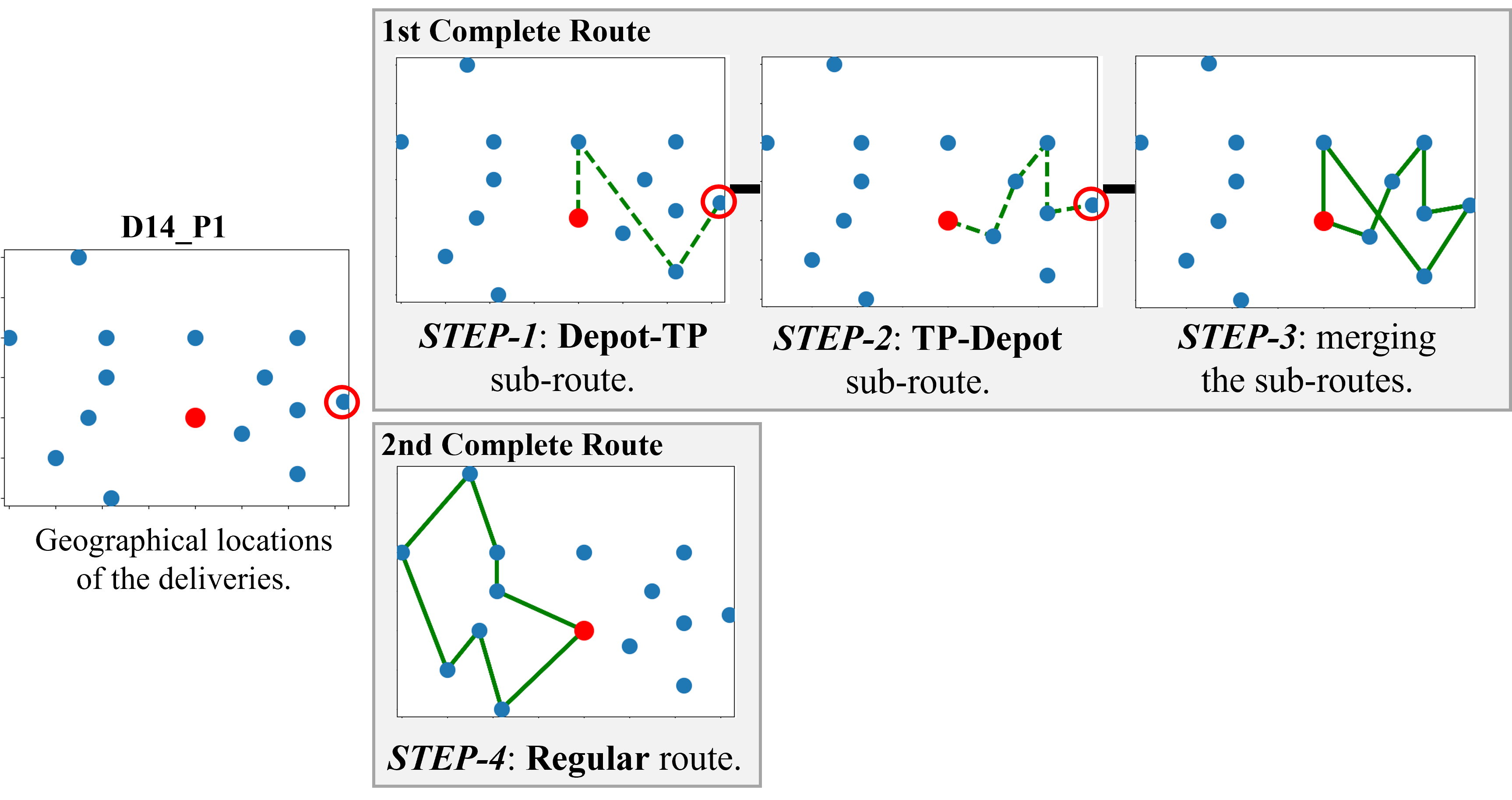
Research focused on the conjunction between quantum computing and routing problems has been very prolific in recent years. Most of the works revolve around classical problems such as the Traveling Salesman Problem or the Vehicle Routing Problem. The real-world applicability of these problems is dependent on the objectives and constraints considered. Anyway, it is undeniable that it is often difficult to translate complex requirements into these classical formulations.The main objective of this research is to present a solving scheme for dealing with realistic instances while maintaining all the characteristics and restrictions of the original real-world problem. Thus, a quantum-classical strategy has been developed, coined Q4RPD, that considers a set of real constraints such as a heterogeneous fleet of vehicles, priority deliveries, and capacities characterized by two values: weight and dimensions of the packages. Q4RPD resorts to the Leap Constrained Quadratic Model Hybrid Solver of D-Wave. To demonstrate the application of Q4RPD, an experimentation composed of six different instances has been conducted, aiming to serve as illustrative examples.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper examines the use of quantum annealers, a type of quantum computing hardware, to solve a real-world package delivery routing problem.
- The researchers develop a hybrid approach that combines quantum annealing with a classical Tabu search algorithm to optimize delivery routes.
- The proposed method is tested on a case study involving a logistics company, demonstrating its effectiveness in finding efficient delivery routes.
Plain English Explanation
In this paper, the researchers explore using quantum annealers to solve a practical problem faced by package delivery companies. Specifically, they are looking at how to optimize the routes taken by delivery trucks to ensure packages are delivered in the most efficient way possible.
The researchers developed a new approach that combines the power of quantum computing with a classical optimization technique called Tabu search. Quantum annealers are a type of quantum hardware that can be used to solve complex optimization problems, like finding the most efficient delivery routes. By integrating quantum annealing with Tabu search, the researchers were able to create a hybrid system that performs better than using either approach alone.
To test their method, the researchers worked with a real-world logistics company and applied their hybrid approach to a case study. The results showed that the new system was able to find delivery routes that were more efficient than the ones the company was using previously. This could help delivery companies save time and money, while also reducing their environmental impact by driving fewer miles.
Technical Explanation
The researchers in this paper propose a hybrid approach that combines quantum annealing with a classical Tabu search algorithm to solve a real-world package delivery routing problem.
The core idea is to leverage the optimization capabilities of quantum annealers to find efficient delivery routes, while using Tabu search to refine and improve the solutions. The quantum annealer is used to generate an initial set of candidate routes, which are then further optimized by the Tabu search algorithm.
To evaluate their approach, the researchers conducted a case study with a logistics company, using real-world data on package pickups and deliveries. They compared the performance of their hybrid quantum-classical method against a traditional Tabu search approach, as well as other benchmark algorithms.
The results showed that the hybrid approach outperformed the other methods, finding delivery routes that were more efficient in terms of total distance traveled and delivery times. The researchers attribute this improved performance to the synergistic integration of quantum annealing and Tabu search, which allows the system to explore a wider range of solution spaces and converge on high-quality results.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach for solving real-world package delivery routing problems using quantum computing technology. The researchers have demonstrated the potential of hybrid quantum-classical methods through a carefully designed case study, providing evidence of the practical benefits that quantum annealers can offer in logistics optimization.
However, it's important to note that the study was limited to a single case study with a specific logistics company. More research is needed to evaluate the generalizability of the approach and its performance on a wider range of delivery scenarios and problem instances.
Additionally, the paper does not provide a detailed analysis of the scalability of the proposed method as the problem size (i.e., the number of pickup and delivery locations) increases. This is an important consideration, as many real-world delivery problems involve hundreds or thousands of locations.
Furthermore, the paper does not address the potential challenges and limitations of implementing quantum annealing in a practical, large-scale setting. Issues such as hardware availability, reliability, and integration with existing logistics systems would need to be carefully considered before the technology can be widely adopted.
Conclusion
This paper demonstrates the potential of quantum computing, specifically quantum annealing, to solve a real-world package delivery routing problem. The researchers have developed a hybrid approach that combines quantum annealing with classical optimization techniques, showing improved performance over traditional methods.
The results of the case study suggest that quantum-based solutions could help logistics companies optimize their delivery operations, leading to cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and better service for customers. However, further research is needed to address the scalability and practical implementation challenges of this technology.
As quantum computing continues to advance, integrating it with classical algorithms may unlock new possibilities for solving complex optimization problems in various industries, including logistics, transportation, and supply chain management.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Hybrid Quantum Tabu Search for Solving the Vehicle Routing Problem
James Holliday, Braeden Morgan, Hugh Churchill, Khoa Luu

0
0
There has never been a more exciting time for the future of quantum computing than now. Near-term quantum computing usage is now the next XPRIZE. With that challenge in mind we have explored a new approach as a hybrid quantum-classical algorithm for solving NP-Hard optimization problems. We have focused on the classic problem of the Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP) because of its real-world industry applications. Heuristics are often employed to solve this problem because it is difficult. In addition, meta-heuristic algorithms have proven to be capable of finding reasonable solutions to optimization problems like the CVRP. Recent research has shown that quantum-only and hybrid quantum/classical approaches to solving the CVRP are possible. Where quantum approaches are usually limited to minimal optimization problems, hybrid approaches have been able to solve more significant problems. Still, the hybrid approaches often need help finding solutions as good as their classical counterparts. In our proposed approach, we created a hybrid quantum/classical metaheuristic algorithm capable of finding the best-known solution to a classic CVRP problem. Our experimental results show that our proposed algorithm often outperforms other hybrid approaches.
4/23/2024
❗
Hybrid quantum-classical computation for automatic guided vehicles scheduling
Tomasz 'Smierzchalski, {L}ukasz Pawela, Zbigniew Pucha{l}a, M'aty'as Koniorczyk, Bart{l}omiej Gardas, Sebastian Deffner, Krzysztof Domino

0
0
Motivated by global efforts to develop quantum computing for practical, industrial-scale challenges, we showcase the effectiveness of state-of-the-art hybrid quantum-classical solvers in addressing the business-centric optimization problem of scheduling Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs). These solvers leverage a noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) device, specifically a D-Wave quantum annealer. In our study, the hybrid solvers exhibit non-zero quantum processing times, indicating a significant contribution of the quantum component to solution efficiency. This hybrid methodology performs comparably to existing classical solvers, thus indicating `quantum readiness' for scheduling tasks. Our analysis focuses on a practical, business-oriented scenario: scheduling AGVs within a factory constrained by limited space, simulating a realistic production setting. Our new approach concerns mapping a realistic AGV problem onto a problem reminiscient of railway scheduling and demonstrating that the AGV problem more suits quantum computing than the railway counterpart and is more dense in terms of an average number of constraints per variable. We demonstrate that a scenario involving 15 AGVs, which holds practical significance due to common bottlenecks like shared main lanes leading to frequent deadlocks, can be efficiently addressed by a hybrid quantum-classical solver within seconds. Consequently, our research paves the way for the near-future business adoption of hybrid quantum-classical solutions for AGV scheduling, anticipating that forthcoming improvements in manufacturing efficiency will increase both the number of AGVs deployed and the premium on factory space.
5/9/2024
🛠️
Dynamic Optimization on Quantum Hardware: Feasibility for a Process Industry Use Case
Dennis Michael Nenno, Adrian Caspari

0
0
The quest for real-time dynamic optimization solutions in the process industry represents a formidable computational challenge, particularly within the realm of applications like model-predictive control, where rapid and reliable computations are critical. Conventional methods can struggle to surmount the complexities of such tasks. Quantum computing and quantum annealing emerge as textit{avant-garde} contenders to transcend conventional computational constraints. We convert a dynamic optimization problem, {characterized by an optimization problem with a system of differential-algebraic equations embedded}, into a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization problem, enabling quantum computational approaches. The empirical findings synthesized from classical methods, simulated annealing, quantum annealing via D-Wave's quantum annealer, and hybrid solver methodologies, illuminate the intricate landscape of computational prowess essential for tackling complex and high-dimensional dynamic optimization problems. Our findings suggest that while quantum annealing is a maturing technology that currently does not outperform state-of-the-art classical solvers, continuous improvements could eventually aid in increasing efficiency within the chemical process industry.
4/29/2024
🌀
Solving the Turbine Balancing Problem using Quantum Annealing
Arnold Unterauer, David Bucher, Matthias Knoll, Constantin Economides, Michael Lachner, Thomas Germain, Moritz Kessel, Smajo Hajdinovic, Jonas Stein

0
0
Quantum computing has the potential for disruptive change in many sectors of industry, especially in materials science and optimization. In this paper, we describe how the Turbine Balancing Problem can be solved with quantum computing, which is the NP-hard optimization problem of analytically balancing rotor blades in a single plane as found in turbine assembly. Small yet relevant instances occur in industry, which makes the problem interesting for early quantum computing benchmarks. We model it as a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization problem and compare the performance of a classical rule-based heuristic and D-Wave Systems' Quantum Annealer Advantage_system4.1. In this case study, we use real-world as well as synthetic datasets and observe that the quantum hardware significantly improves an actively used heuristic's solution for small-scale problem instances with bare disk imbalance in terms of solution quality. Motivated by this performance gain, we subsequently design a quantum-inspired classical heuristic based on simulated annealing that achieves extremely good results on all given problem instances, essentially solving the optimization problem sufficiently well for all considered datasets, according to industrial requirements.
5/13/2024