The Impact of Social Environment and Interaction Focus on User Experience and Social Acceptability of an Augmented Reality Game
2404.16479

0
0
📉
Abstract
One of the most promising technologies inside the Extended Reality (XR) spectrum is Augmented Reality. This technology is already in people's pockets regarding Mobile Augmented Reality with their smartphones. The scientific community still needs answers about how humans could and should interact in environments where perceived stimuli are different from fully physical or digital circumstances. Moreover, it is still being determined if people accept these new technologies in different social environments and interaction settings or if some obstacles could exist. This paper explores the impact of the Social Environment and the Focus of social interaction on users while playing a location-based augmented reality game, measuring it with user experience and social acceptance indicators. An empirical study in a within-subject fashion was performed in different social environments and under different settings of social interaction focus with N = 28 participants compiling self-reported questionnaires after playing a Scavenger Hunt in Augmented Reality. The measures from two different Social Environments (Crowded vs. Uncrowded) resulted in statistically relevant mean differences with indicators from the Social Acceptability dimension. Moreover, the analyses show statistically relevant differences between the variances from different degrees of Social Interaction Focus with Overall Social Presence, Perceived Psychological Engagement, Perceived Attentional Engagement, and Perceived Emotional Contagion. The results suggest that a location-based AR game played in different social environments and settings can influence the user experience's social dimension. Therefore, they should be carefully considered while designing immersive technological experiences in public spaces involving social interactions between players.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the impact of social environment and the focus of social interaction on the user experience and social acceptance of a location-based augmented reality (AR) game.
- The researchers conducted an empirical study with 28 participants, who played a Scavenger Hunt game in AR under different social conditions.
- The study measured various user experience and social acceptance indicators to understand how the social environment and the focus of social interaction affect the users' perceptions.
Plain English Explanation
The paper investigates how the social environment and the focus of social interaction can influence people's experience and acceptance of an augmented reality (AR) game. AR is a technology that overlays digital information, such as images or text, onto the real world, which can be viewed through a smartphone or other device.
The researchers wanted to understand how factors like being in a crowded or uncrowded space, and the degree of social interaction required during the game, might affect how people perceive and engage with the AR experience. To do this, they had 28 people play an AR Scavenger Hunt game in different social settings and conditions, and then asked them to report on their experiences.
The study found that the social environment (crowded vs. uncrowded) and the focus of social interaction (more or less) had a significant impact on the users' perceptions of social acceptability, overall social presence, psychological and attentional engagement, and emotional contagion.
These findings suggest that the social context is an important consideration when designing AR experiences that involve social interactions, such as location-based AR games or collaborative AR applications. Developers should carefully think about how the social environment and the level of social interaction might affect the user experience and acceptance of their AR technology.
Technical Explanation
The researchers conducted a within-subject empirical study with 28 participants to investigate the impact of social environment and social interaction focus on user experience and social acceptance of a location-based augmented reality (AR) game.
Participants played a Scavenger Hunt game in AR, which involved using their smartphones to find and interact with virtual objects overlaid on the real world. The study manipulated two independent variables:
- Social Environment: Participants played the game in either a crowded or uncrowded public space.
- Social Interaction Focus: Participants played the game under either a high or low degree of social interaction focus, where the game required more or less social engagement between players.
After each game session, participants completed self-report questionnaires to measure various user experience and social acceptance indicators, such as:
- Social Acceptability
- Overall Social Presence
- Perceived Psychological Engagement
- Perceived Attentional Engagement
- Perceived Emotional Contagion
The results showed statistically significant differences in the social acceptability scores between the crowded and uncrowded social environments. Additionally, the analyses revealed statistically significant differences in the variances of the overall social presence, perceived psychological engagement, perceived attentional engagement, and perceived emotional contagion measures between the high and low social interaction focus conditions.
These findings suggest that the social environment and the focus of social interaction during an AR game can influence the user experience and social acceptance of the technology. Designers of immersive AR experiences should carefully consider these factors when developing applications that involve social interactions, such as collaborative AR for remote work or education or AR-based mental health interventions.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides valuable insights into the importance of social context in the design of augmented reality (AR) experiences. The researchers have carefully designed and executed the study, considering relevant factors such as social environment and the focus of social interaction.
However, the study is limited to a relatively small sample size of 28 participants, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the study focused on a specific type of AR game (Scavenger Hunt), and the results may not fully apply to other types of AR applications, such as AR-based navigation or collaborative AR experiences.
It would be interesting to see further research exploring the impact of social context on user experience and acceptance in a wider range of AR applications, as well as studies with larger and more diverse participant samples. Additionally, incorporating objective measures of user behavior and performance, in addition to self-reported data, could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomena.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the importance of considering the social environment and the focus of social interaction when designing augmented reality (AR) experiences. The findings suggest that these factors can significantly influence user experience and social acceptance of AR technology, particularly in public spaces where social interactions are a key component of the experience.
The insights from this study can inform the development of AR applications that are better aligned with user needs and social contexts, leading to more engaging and socially acceptable immersive experiences. As AR technology continues to evolve and be adopted in various domains, such as remote work, education, and mental health interventions, understanding the role of social factors will be crucial for the successful deployment and acceptance of these technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Investigating the impact of virtual element misalignment in collaborative Augmented Reality experiences
Francesco Vona, Sina Hinzmann, Michael Stern, Tanja Koji'c, Navid Ashrafi, David Grieshammer, Jan-Niklas Voigt-Antons

0
0
The collaboration in co-located shared environments has sparked an increased interest in immersive technologies, including Augmented Reality (AR). Since research in this field has primarily focused on individual user experiences in AR, the collaborative aspects within shared AR spaces remain less explored, and fewer studies can provide guidelines for designing this type of experience. This article investigates how the user experience in a collaborative shared AR space is affected by divergent perceptions of virtual objects and the effects of positional synchrony and avatars. For this purpose, we developed an AR app and used two distinct experimental conditions to study the influencing factors. Forty-eight participants, organized into 24 pairs, participated in the experiment and jointly interacted with shared virtual objects. Results indicate that divergent perceptions of virtual objects did not directly influence communication and collaboration dynamics. Conversely, positional synchrony emerged as a critical factor, significantly enhancing the quality of the collaborative experience. On the contrary, while not negligible, avatars played a relatively less pronounced role in influencing these dynamics. The findings can potentially offer valuable practical insights, guiding the development of future collaborative AR/VR environments.
4/26/2024
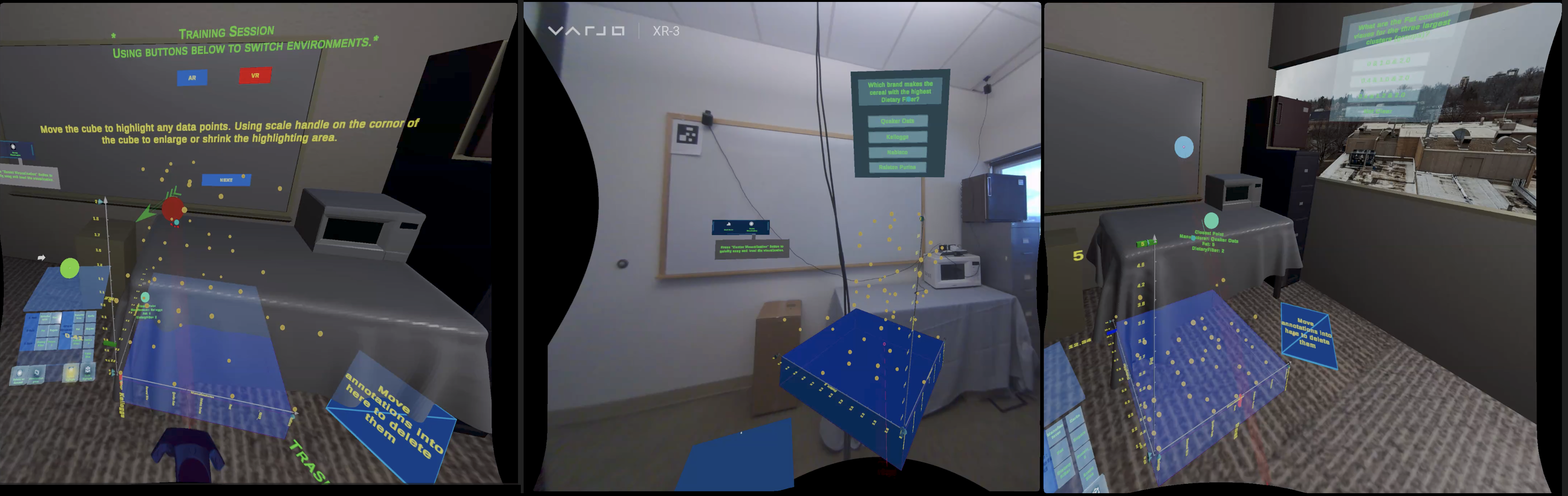
I Did Not Notice: A Comparison of Immersive Analytics with Augmented and Virtual Reality
Xiaoyan Zhou, Anil Ufuk Batmaz, Adam S. Williams, Dylan Schreiber, Francisco Ortega

0
0
Immersive environments enable users to engage in embodied interaction, enhancing the sensemaking processes involved in completing tasks such as immersive analytics. Previous comparative studies on immersive analytics using augmented and virtual realities have revealed that users employ different strategies for data interpretation and text-based analytics depending on the environment. Our study seeks to investigate how augmented and virtual reality influences sensemaking processes in quantitative immersive analytics. Our results, derived from a diverse group of participants, indicate that users demonstrate comparable performance in both environments. However, it was observed that users exhibit a higher tolerance for cognitive load in VR and travel further in AR. Based on our findings, we recommend providing users with the option to switch between AR and VR, thereby enabling them to select an environment that aligns with their preferences and task requirements.
4/8/2024
🔎
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Promote Awareness in Augmented Reality Systems
Wangfan Li, Rohit Mallick, Carlos Toxtli-Hernandez, Christopher Flathmann, Nathan J. McNeese

0
0
Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) have permeated through an array of different immersive environments, including virtual, augmented, and mixed realities. AI brings a wealth of potential that centers on its ability to critically analyze environments, identify relevant artifacts to a goal or action, and then autonomously execute decision-making strategies to optimize the reward-to-risk ratio. However, the inherent benefits of AI are not without disadvantages as the autonomy and communication methodology can interfere with the human's awareness of their environment. More specifically in the case of autonomy, the relevant human-computer interaction literature cites that high autonomy results in an out-of-the-loop experience for the human such that they are not aware of critical artifacts or situational changes that require their attention. At the same time, low autonomy of an AI system can limit the human's own autonomy with repeated requests to approve its decisions. In these circumstances, humans enter into supervisor roles, which tend to increase their workload and, therefore, decrease their awareness in a multitude of ways. In this position statement, we call for the development of human-centered AI in immersive environments to sustain and promote awareness. It is our position then that we believe with the inherent risk presented in both AI and AR/VR systems, we need to examine the interaction between them when we integrate the two to create a new system for any unforeseen risks, and that it is crucial to do so because of its practical application in many high-risk environments.
5/10/2024
🤿
From Virtual Gains to Real Pains: Potential Harms of Immersive Exergames
Sebastian Cmentowski, Sukran Karaosmanoglu, Frank Steinicke

0
0
Digitalization and virtualization are parts of our everyday lives in almost all aspects ranging from work, education, and communication to entertainment. A novel step in this direction is the widespread interest in extended reality (XR) [2]. The newest consumer-ready head-mounted displays (HMD) such as Meta Quest 3 or Apple Vision Pro, have reached unprecedented levels of visual fidelity, interaction capabilities, and computational power. The built-in pass-through features of these headsets enable both virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) with the same devices. However, the immersive nature of these experiences is not the only groundbreaking difference from established forms of media.
5/10/2024