iHuman: Instant Animatable Digital Humans From Monocular Videos

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents "iHuman", a system that can create instant, animatable digital humans from monocular videos.
- The system uses a Gaussian splats-based surface representation to model human bodies and faces, allowing for efficient and high-fidelity animation.
- iHuman can generate digital humans that can be realistically animated and relit from a single input video, without the need for complex 3D scanning or reconstruction.
Plain English Explanation
The iHuman system aims to make it easy to create animated digital human characters from ordinary video footage. Rather than requiring specialized 3D scanning equipment or complex reconstruction processes, iHuman can take a simple video recorded on a smartphone or camera and use it to generate a realistic, animatable digital version of the person in the video.
At the core of iHuman is a novel representation called "Gaussian splats", which allows the system to model the human body and face in an efficient and high-quality way. Unlike traditional 3D models that use meshes or point clouds, Gaussian splats use a set of overlapping Gaussian functions to capture the shape and appearance of the person. This enables iHuman to generate digital humans that can be realistically animated and even relit, adjusting the lighting and shadows to match different scenes or contexts.
The key advantage of iHuman is that it makes the process of creating animated digital humans much more accessible. Instead of requiring specialized expertise or expensive equipment, iHuman can generate these digital avatars from common video footage. This could have a wide range of applications, from virtual reality and video games to communications and e-commerce.
Technical Explanation
The iHuman system builds on previous research in 3DGS-Avatar, Interactive Rendering, GomAvatar, Animatable Relightable Gaussians, and ASH, which have explored the use of Gaussian splats for efficient and high-fidelity human modeling and animation.
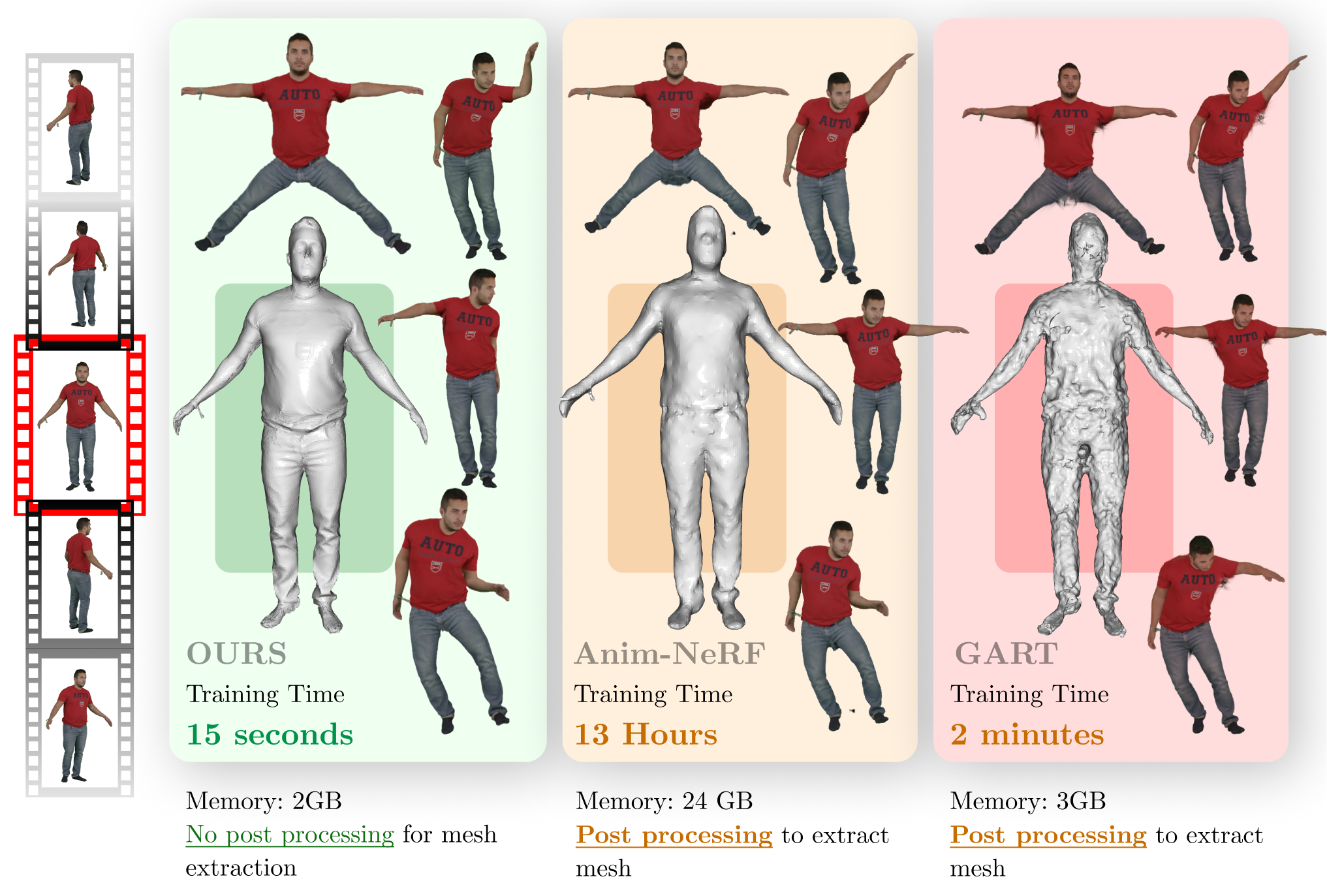
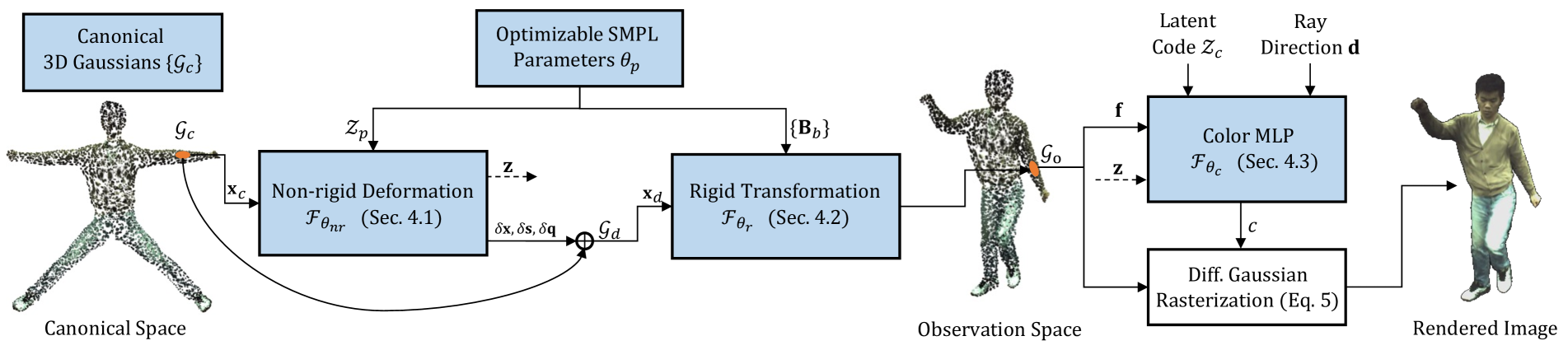
The key innovation in iHuman is its ability to generate these Gaussian splat-based digital humans directly from monocular video inputs, without the need for complex 3D reconstruction. The system first extracts 2D keypoints from the input video using a convolutional neural network, and then uses these keypoints to fit a parametric human body model. This body model is then represented as a set of Gaussian splats, which can be efficiently animated and relit.
The system also includes a neural network-based face modeling component that can capture the detailed facial geometry and appearance from the video input. By combining the body and face models, iHuman can create a complete, animatable digital human that preserves the details and nuances of the original person.
Critical Analysis
One potential limitation of the iHuman system is that it relies on the accuracy of the 2D keypoint extraction and parametric body model fitting, which could be affected by factors like video quality, occlusions, and clothing. The authors acknowledge this and suggest that incorporating additional cues, such as silhouettes or depth information, could potentially improve the robustness of the system.
Additionally, while the Gaussian splat representation enables efficient animation and relighting, it may not capture all the fine-grained details and subtleties of human appearance and movement. More complex representations, such as high-resolution mesh models or neural radiance fields, could potentially achieve even higher fidelity, but at the cost of computational efficiency.
Overall, the iHuman system represents a significant advancement in the field of digital human creation, making the process more accessible and practical for a wide range of applications. However, as with any research, there is room for further improvements and refinements to address the remaining challenges and limitations.
Conclusion
The iHuman system presented in this paper offers a novel approach to creating animatable digital humans from monocular video inputs. By leveraging a Gaussian splats-based representation, the system can generate high-fidelity, realistically animated digital humans without the need for complex 3D scanning or reconstruction.
This breakthrough has the potential to democratize the creation of digital avatars, making them more accessible for a wide range of applications, from virtual reality and video games to communications and e-commerce. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more advanced and realistic digital humans that can seamlessly integrate with our physical and digital worlds.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
iHuman: Instant Animatable Digital Humans From Monocular Videos
Pramish Paudel, Anubhav Khanal, Ajad Chhatkuli, Danda Pani Paudel, Jyoti Tandukar
Personalized 3D avatars require an animatable representation of digital humans. Doing so instantly from monocular videos offers scalability to broad class of users and wide-scale applications. In this paper, we present a fast, simple, yet effective method for creating animatable 3D digital humans from monocular videos. Our method utilizes the efficiency of Gaussian splatting to model both 3D geometry and appearance. However, we observed that naively optimizing Gaussian splats results in inaccurate geometry, thereby leading to poor animations. This work achieves and illustrates the need of accurate 3D mesh-type modelling of the human body for animatable digitization through Gaussian splats. This is achieved by developing a novel pipeline that benefits from three key aspects: (a) implicit modelling of surface's displacements and the color's spherical harmonics; (b) binding of 3D Gaussians to the respective triangular faces of the body template; (c) a novel technique to render normals followed by their auxiliary supervision. Our exhaustive experiments on three different benchmark datasets demonstrates the state-of-the-art results of our method, in limited time settings. In fact, our method is faster by an order of magnitude (in terms of training time) than its closest competitor. At the same time, we achieve superior rendering and 3D reconstruction performance under the change of poses.
Read more7/17/2024
⛏️

0
Animatable 3D Gaussian: Fast and High-Quality Reconstruction of Multiple Human Avatars
Yang Liu, Xiang Huang, Minghan Qin, Qinwei Lin, Haoqian Wang
Neural radiance fields are capable of reconstructing high-quality drivable human avatars but are expensive to train and render and not suitable for multi-human scenes with complex shadows. To reduce consumption, we propose Animatable 3D Gaussian, which learns human avatars from input images and poses. We extend 3D Gaussians to dynamic human scenes by modeling a set of skinned 3D Gaussians and a corresponding skeleton in canonical space and deforming 3D Gaussians to posed space according to the input poses. We introduce a multi-head hash encoder for pose-dependent shape and appearance and a time-dependent ambient occlusion module to achieve high-quality reconstructions in scenes containing complex motions and dynamic shadows. On both novel view synthesis and novel pose synthesis tasks, our method achieves higher reconstruction quality than InstantAvatar with less training time (1/60), less GPU memory (1/4), and faster rendering speed (7x). Our method can be easily extended to multi-human scenes and achieve comparable novel view synthesis results on a scene with ten people in only 25 seconds of training.
Read more7/30/2024

0
3DGS-Avatar: Animatable Avatars via Deformable 3D Gaussian Splatting
Zhiyin Qian, Shaofei Wang, Marko Mihajlovic, Andreas Geiger, Siyu Tang
We introduce an approach that creates animatable human avatars from monocular videos using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Existing methods based on neural radiance fields (NeRFs) achieve high-quality novel-view/novel-pose image synthesis but often require days of training, and are extremely slow at inference time. Recently, the community has explored fast grid structures for efficient training of clothed avatars. Albeit being extremely fast at training, these methods can barely achieve an interactive rendering frame rate with around 15 FPS. In this paper, we use 3D Gaussian Splatting and learn a non-rigid deformation network to reconstruct animatable clothed human avatars that can be trained within 30 minutes and rendered at real-time frame rates (50+ FPS). Given the explicit nature of our representation, we further introduce as-isometric-as-possible regularizations on both the Gaussian mean vectors and the covariance matrices, enhancing the generalization of our model on highly articulated unseen poses. Experimental results show that our method achieves comparable and even better performance compared to state-of-the-art approaches on animatable avatar creation from a monocular input, while being 400x and 250x faster in training and inference, respectively.
Read more4/5/2024


0
Interactive Rendering of Relightable and Animatable Gaussian Avatars
Youyi Zhan, Tianjia Shao, He Wang, Yin Yang, Kun Zhou
Creating relightable and animatable avatars from multi-view or monocular videos is a challenging task for digital human creation and virtual reality applications. Previous methods rely on neural radiance fields or ray tracing, resulting in slow training and rendering processes. By utilizing Gaussian Splatting, we propose a simple and efficient method to decouple body materials and lighting from sparse-view or monocular avatar videos, so that the avatar can be rendered simultaneously under novel viewpoints, poses, and lightings at interactive frame rates (6.9 fps). Specifically, we first obtain the canonical body mesh using a signed distance function and assign attributes to each mesh vertex. The Gaussians in the canonical space then interpolate from nearby body mesh vertices to obtain the attributes. We subsequently deform the Gaussians to the posed space using forward skinning, and combine the learnable environment light with the Gaussian attributes for shading computation. To achieve fast shadow modeling, we rasterize the posed body mesh from dense viewpoints to obtain the visibility. Our approach is not only simple but also fast enough to allow interactive rendering of avatar animation under environmental light changes. Experiments demonstrate that, compared to previous works, our method can render higher quality results at a faster speed on both synthetic and real datasets.
Read more7/16/2024